Related Research Articles

Tuff is a type of rock made of volcanic ash ejected from a vent during a volcanic eruption. Following ejection and deposition, the ash is lithified into a solid rock. Rock that contains greater than 75% ash is considered tuff, while rock containing 25% to 75% ash is described as tuffaceous. A pyroclastic rock containing 25–75% volcanic bombs and/or volcanic blocks is called tuff breccia. Tuff composed of sandy volcanic material can be referred to as volcanic sandstone.

Lapilli is a size classification of tephra, which is material that falls out of the air during a volcanic eruption or during some meteorite impacts. Lapilli is Latin for "little stones".

Goat Rocks is an extinct stratovolcano in the Cascade Range, located between Mount Rainier and Mount Adams in southern Washington, in the United States. Part of the Cascade Volcanoes, it was formed by the subduction of the Juan de Fuca Plate under the western edge of the North American Plate. The volcano was active from 3.2 million years ago until eruptions ceased between 1 and 0.5 million years ago. Throughout its complex eruptive history, volcanism shifted from silicic explosive eruptions to voluminous, mafic activity.

The Boulder Creek Wilderness is a wilderness area located in the Umpqua National Forest in the southern Cascade Range of Oregon, United States. It was designated by the United States Congress in 1984 and comprises 19,100 acres (7,729 ha).
The Mount Pleasant Caldera is a large eroded Late Devonian volcanic caldera complex, located in the northern Appalachian Mountains of southwestern New Brunswick, Canada. It is one of few noticeable pre-Cenozoic calderas, and its formation is associated to a period of crustal thinning that followed the Acadian orogeny in the northern Appalachian Mountains. It sits relatively near to the coastline.
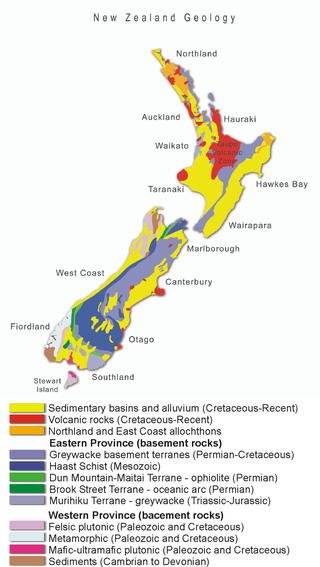
The Auckland Region of New Zealand is built on a basement of greywacke rocks that form many of the islands in the Hauraki Gulf, the Hunua Ranges, and land south of Port Waikato. The Waitākere Ranges in the west are the remains of a large andesitic volcano, and Great Barrier Island was formed by the northern end of the Coromandel Volcanic Zone. The Auckland isthmus and North Shore are composed of Waitemata sandstone and mudstone, and portions of the Northland Allochthon extend as far south as Albany. Little Barrier Island was formed by a relatively isolated andesitic volcano, active around 1 to 3 million years ago.

The Canadian Cascade Arc, also called the Canadian Cascades, is the Canadian segment of the North American Cascade Volcanic Arc. Located entirely within the Canadian province of British Columbia, it extends from the Cascade Mountains in the south to the Coast Mountains in the north. Specifically, the southern end of the Canadian Cascades begin at the Canada–United States border. However, the specific boundaries of the northern end are not precisely known and the geology in this part of the volcanic arc is poorly understood. It is widely accepted by geologists that the Canadian Cascade Arc extends through the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains. However, others have expressed concern that the volcanic arc possibly extends further north into the Kitimat Ranges, another subdivision of the Coast Mountains, and even as far north as Haida Gwaii.
The San Juan volcanic field is part of the San Juan Mountains in southwestern Colorado. It consists mainly of volcanic rocks that form the largest remnant of a major composite volcanic field that covered most of the southern Rocky Mountains in the Middle Tertiary geologic time. There are approximately fifteen calderas known in the San Juan Volcanic Fields; however, it is possible that there are two or even three more in the region.

The Mogollon-Datil volcanic field is a large silicic volcanic field in western New Mexico. It is a part of an extensive Eocene to Oligocene volcanic event which includes the San Juan volcanic field in southwestern Colorado, the Trans-Pecos volcanic field in west Texas and north central Mexico, the Boot Heel volcanic field in the bootheel of southwestern New Mexico and adjacent areas of Arizona and Mexico; and the vast volcanic field of the Sierra Madre Occidental of western Mexico. The Mogollon-Datil volcanic field was formed in "four discrete pulses representing synchronized activity of two separate cauldron complexes".
The Carmacks Group is a Late Cretaceous volcanic group in southwest-central Yukon, Canada, located between the communities of Dawson City and Whitehorse. It consists of flood basalts, coarse volcaniclastic rocks and sandy tuffs interbedded with subordinate andesite and basaltic lava flows. It has been interpreted to be a displaced portion of the Yellowstone hotspot track that was formed 70 million years ago.
Calabozos is a Holocene caldera in central Chile's Maule Region. Part of the Chilean Andes' volcanic segment, it is considered a member of the Southern Volcanic Zone (SVZ), one of the three distinct volcanic belts of South America. This most active section of the Andes runs along central Chile's western edge, and includes more than 70 of Chile's stratovolcanoes and volcanic fields. Calabozos lies in an extremely remote area of poorly glaciated mountains.
The Palm Park Formation is a geologic formation in southern New Mexico. It preserves fossils dating back to the Eocene epoch.
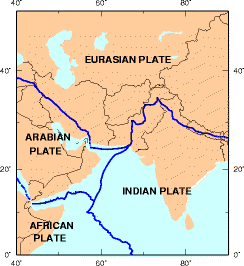
Koh-i-Sultan is a volcano in Balochistan, Pakistan. It is part of the tectonic belt formed by the collision of the Eurasian Plate and Indian Plate: specifically, a segment influenced by the subduction of the Arabian plate beneath the Asian plate and forming a volcanic arc which includes the Bazman and Taftan volcanoes in Iran. The volcano consists of three main cones, with heavily eroded craters running west-northwest and surrounded by a number of subsidiary volcanic centres. Its summit is 2,334 metres (7,657 ft) high, and the crater associated with the Miri cone has a smaller crater inside.

La Reforma is a Plio-Pleistocene caldera on the Baja California Peninsula in Mexico. It is part of eleven volcanoes in Baja California, which formed with the Gulf of California during the Miocene, about ten million years ago. Previously, a volcanic arc had existed on the peninsula. The caldera's basement consists of granites and monzonites, formed between the Cretaceous and the Middle Miocene.
The geology of the U.S. Virgin Islands includes mafic volcanic rocks, with complex mineralogy that first began to erupt in the Mesozoic overlain and interspersed with carbonate and conglomerate units.
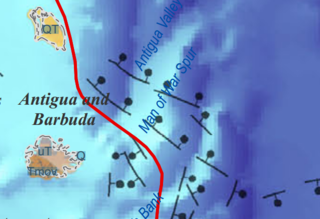
The geology of Antigua and Barbuda is part of the Lesser Antilles volcanic island arc. Both islands are the above water limestone "caps" of now inactive volcanoes. The two islands are the surface features of the undersea Barbuda Bank and have karst limestone landscapes. Barbuda is primarily flat and formed from coral reefs. The Middle Miocene Highlands Formation has limestones which are the oldest rocks on the island, rising 120 feet above sea level. The Beazer Formation and the Codrington Formation are both from the Pleistocene and include reef and lagoon related rocks.
The geology of Anguilla consists of Lesser Antilles island arc volcanic rocks overlain by Oligocene, Miocene and Pliocene reef limestone. Older tuff and basalt outcrops in only two places on the island, which are tilted. During the Pliocene and Pleistocene, the underlying Anguilla Bank likely connected Saint Bartholomew and Saint Martin as one island.
The geology of Sint Maarten consists of andesite tuff and tuff breccia from the middle and late Eocene, intruded by hypabyssal basalt, quartz diorite and younger andesite. Volcanic activity led to metamorphism of many rocks and the tilting and folding of the tuff series. Limestone and marl was later unconformably deposited atop the eroded volcanic rocks as volcanic activity shifted elsewhere.
The geology of Saint Barthélemy consists of andesite tuff and tuff breccia from the middle and late Eocene, intruded by hypabyssal basalt, quartz diorite and younger andesite. Volcanic activity on neighboring Saint Martin led to metamorphism of many rocks and the tilting and folding of the tuff series. Limestone and marl was later unconformably deposited atop the eroded volcanic rocks as volcanic activity shifted elsewhere.
The geology of Guatemala encompasses rocks divided into two tectonic blocks. The Maya Block in the north has igneous and metamorphic North American Craton basement rocks, overlain by late Paleozoic metasedimentary rocks, which experienced deformation during the Devonian. Red beds, evaporites and marine limestone from the Mesozoic overlie these rocks. A karst landscape formed in the thick limestone units across the north of the country. During a collisional orogeny, these Paleozoic and Mesozoic rocks were uplifted, thrust and folded as the Central Guatemalan Cordillera. Paleogene rocks from the early Cenozoic include volcanic and marine clastic rocks, associated with high rates of erosion.
References
- ↑ Christman, Robert A. (January 1953). "Geology of St. Bartholomew, St. Martin, and Anguilla, Lesser Antilles". GSA Bulletin. 64 (1): 65–96. Bibcode:1953GSAB...64...85C. doi:10.1130/0016-7606(1953)64[85:GOSBSM]2.0.CO;2 . Retrieved 2018-11-09.
- ↑ Scheffers, Anja; Kelletat, Dieter (2006). "New Evidence and Datings of Holocene Paleo-Tsunami Events in the Caribbean (Barbados, St. Martin and Anguilla)". Caribbean Tsunami Hazard. pp. 178–202. doi:10.1142/9789812774613_0008. ISBN 978-981-256-535-8.