Related Research Articles

Dominica is an island in the Caribbean Sea, located about halfway between the French islands of Guadeloupe and Martinique. Its coordinates are 15 25 N, 61 20 W. It is known as "The Nature Island of the Caribbean" due to its spectacular, lush, and varied flora and fauna, which is protected by an extensive natural park system. It is the fourth largest island in the Eastern Caribbean with a population of people mainly of African descent.

The Lesser Antilles are a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea. Most of them are part of a long, partially volcanic island arc between the Greater Antilles to the north-west and the continent of South America. The islands of the Lesser Antilles form the eastern boundary of the Caribbean Sea where it meets the Atlantic Ocean. Together, the Lesser Antilles and the Greater Antilles make up the Antilles. The Lesser and Greater Antilles, together with the Lucayan Archipelago, are collectively known as the West Indies.

The Coast Mountains are a major mountain range in the Pacific Coast Ranges of western North America, extending from southwestern Yukon through the Alaska Panhandle and virtually all of the Coast of British Columbia south to the Fraser River. The mountain range's name derives from its proximity to the sea coast, and it is often referred to as the Coast Range. The range includes volcanic and non-volcanic mountains and the extensive ice fields of the Pacific and Boundary Ranges, and the northern end of the volcanic system known as the Cascade Volcanoes. The Coast Mountains are part of a larger mountain system called the Pacific Coast Ranges or the Pacific Mountain System, which includes the Cascade Range, the Insular Mountains, the Olympic Mountains, the Oregon Coast Range, the California Coast Ranges, the Saint Elias Mountains and the Chugach Mountains. The Coast Mountains are also part of the American Cordillera—a Spanish term for an extensive chain of mountain ranges—that consists of an almost continuous sequence of mountain ranges that form the western backbone of North America, Central America, South America and Antarctica.

The Ring of Fire is a region around much of the rim of the Pacific Ocean where many volcanic eruptions and earthquakes occur. The Ring of Fire is a horseshoe-shaped belt about 40,000 km (25,000 mi) long and up to about 500 km (310 mi) wide.

Island arcs are long chains of active volcanoes with intense seismic activity found along convergent tectonic plate boundaries. Most island arcs originate on oceanic crust and have resulted from the descent of the lithosphere into the mantle along the subduction zone. They are the principal way by which continental growth is achieved.

A volcanic arc is a chain of volcanoes formed above a subducting plate, positioned in an arc shape as seen from above. Offshore volcanoes form islands, resulting in a volcanic island arc. Generally, volcanic arcs result from the subduction of an oceanic tectonic plate under another tectonic plate, and often parallel an oceanic trench. The oceanic plate is saturated with water, and volatiles such as water drastically lower the melting point of the mantle. As the oceanic plate is subducted, it is subjected to greater and greater pressures with increasing depth. This pressure squeezes water out of the plate and introduces it to the mantle. Here the mantle melts and forms magma at depth under the overriding plate. The magma ascends to form an arc of volcanoes parallel to the subduction zone.

Mount Cleveland is a nearly symmetrical stratovolcano on the western end of Chuginadak Island, which is part of the Islands of Four Mountains just west of Umnak Island in the Fox Islands of the Aleutian Islands of Alaska. Mt. Cleveland is 5,675 ft (1,730 m) high, and one of the most active of the 75 or more volcanoes in the larger Aleutian Arc. Aleutian natives named the island after their fire goddess, Chuginadak, who they believed inhabited the volcano. In 1894 a team from the U.S. Coast and Geodetic Survey visited the island and gave Mount Cleveland its current name, after then-president Grover Cleveland.

Morne Diablotins is the highest mountain in Dominica, an island-nation in the Caribbean Lesser Antilles. It is the second highest mountain in the Lesser Antilles, after La Grande Soufrière in Guadeloupe. Morne Diablotins is located in the northern interior of the island, about 24 kilometres (15 mi) north of Dominica's capital Roseau and about 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) southeast of Portsmouth, the island's second-largest town. It is located within Morne Diablotin National Park.

The Borrowdale Volcanic Group is a group of igneous rock formations named after the Borrowdale area of the Lake District, in England. They are Caradocian in age. It is thought that they represent the remains of a volcanic island arc, approximately similar to the island arcs of the west Pacific today. This developed as oceanic crust to the (present) north-west and was forced by crustal movement under a continental land-mass to the present south-east. Such forcing under, as two plates meet, is termed subduction. This land-mass has been named Avalonia by geologists. It is now incorporated into England and Wales and a sliver of North America.

The Central American Volcanic Arc is a chain of volcanoes which extends parallel to the Pacific coastline of the Central American Isthmus, from Mexico to Panama. This volcanic arc, which has a length of 1,100 kilometers is formed by an active subduction zone, with the Cocos Plate subducting underneath the Caribbean Plate. The region has been volcanically and geologically active for at least the past several million years. Numerous volcanoes are spread throughout various Central American countries; many have been active in the geologic past, some more so than others.

Morne Trois Pitons National Park is a national park in Dominica established in July 1975, the first to be legally established in the country. It became a World Heritage Site in 1997. The park is named after its highest mountain, Morne Trois Pitons, meaning mountain of three peaks. The park is an area of significant volcanic activity. Features within the park include the Valley of Desolation, a region of boiling mud ponds and small geysers; the Boiling Lake; Titou Gorge; and Emerald Pool. The mountain is the second-highest peak in Dominica, being exceeded only by Morne Diablotins.

The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greater Antilles, the Lesser Antilles, and the Lucayan Archipelago.

A complex volcano, also called a compound volcano or a volcanic complex, is a mixed landform consisting of related volcanic centers and their associated lava flows and pyroclastic rock. They may form due to changes in eruptive habit or in the location of the principal vent area on a particular volcano. Stratovolcanoes can also form a large caldera that gets filled in by a lava dome, or else multiple small cinder cones, lava domes and craters may develop on the caldera's rim.

Volcanic activity is a major part of the geology of Canada and is characterized by many types of volcanic landform, including lava flows, volcanic plateaus, lava domes, cinder cones, stratovolcanoes, shield volcanoes, submarine volcanoes, calderas, diatremes, and maars, along with less common volcanic forms such as tuyas and subglacial mounds.

The geology of the Pacific Northwest includes the composition, structure, physical properties and the processes that shape the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The region is part of the Ring of Fire: the subduction of the Pacific and Farallon Plates under the North American Plate is responsible for many of the area's scenic features as well as some of its hazards, such as volcanoes, earthquakes, and landslides.
The Caribbean bioregion is a biogeographic region that includes the islands of the Caribbean Sea and nearby Atlantic islands, which share a fauna, flora and mycobiota distinct from surrounding bioregions.

The Coast Range Arc was a large volcanic arc system, extending from northern Washington through British Columbia and the Alaska Panhandle to southwestern Yukon. The Coast Range Arc lies along the western margin of the North American Plate in the Pacific Northwest of western North America. Although taking its name from the Coast Mountains, this term is a geologic grouping rather than a geographic one, and the Coast Range Arc extended south into the High Cascades of the Cascade Range, past the Fraser River which is the northward limit of the Cascade Range proper.
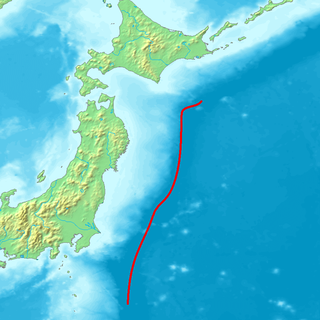
The Northeastern Japan Arc, also Northeastern Honshū Arc, is an island arc on the Pacific Ring of Fire. The arc runs north to south along the Tōhoku region of Honshū, Japan. It is the result of the subduction of the Pacific Plate underneath the Okhotsk Plate at the Japan Trench. The southern end of the arc converges with the Southwestern Japan Arc and the Izu–Bonin–Mariana Arc at the Fossa Magna at the east end of the Itoigawa-Shizuoka Tectonic Line (ITIL). This is the geologic border between eastern and western Honshū. Mount Fuji is at the point where these three arcs meet. To the north, the Northeastern Japan arc extends through the Oshima Peninsula of Hokkaidō. The arc converges in a collision zone with the Sakhalin Island Arc and the Kuril Island Arc in the volcanic Ishikari Mountains of central Hokkaidō. This collision formed the Teshio and Yūbari Mountains.

The Banda Arc is a set of island arcs in eastern Indonesia. It is the result of the collision of a continent and an intra-oceanic island arc. The presently active arc is located on what appears to be oceanic crust whereas the associated subduction trench is underlain by continental crust. The convergence of the Indo-Australian plates and Eurasia resulted in the formation of the Sunda and Banda island arcs. The transitional zone between the arcs is located south of Flores Island and is characterized by the change in the tectonic regime along the boundary.

The Lesser Sunda Islands are an archipelago in Maritime Southeast Asia, north of Australia. Together with the Greater Sunda Islands to the west they make up the Sunda Islands. The islands are part of a volcanic arc, the Sunda Arc, formed by subduction along the Sunda Trench in the Java Sea. A bit more than 20 million people live on the islands.
References
- ↑ Donovan, Steven K.; Jackson, Trevor A. (1994). Caribbean Geology: An Introduction. University of West Indies. p. 171-172.