Related Research Articles

Anguilla is a British overseas territory in the Caribbean. It is one of the most northerly of the Leeward Islands in the Lesser Antilles, lying east of Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands and directly north of Saint Martin. The territory consists of the main island of Anguilla, approximately 16 miles long by 3 miles (5 km) wide at its widest point, together with a number of much smaller islands and cays with no permanent population. The territory's capital is The Valley. The total land area of the territory is 35 square miles (91 km2), with a population of approximately 14,731 (2018).

The Lesser Antilles are a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea. Most of them are part of a long, partially volcanic island arc between the Greater Antilles to the north-west and the continent of South America. The islands of the Lesser Antilles form the eastern boundary of the Caribbean Sea where it meets the Atlantic Ocean. Together, the Lesser Antilles and the Greater Antilles make up the Antilles. The Lesser and Greater Antilles, together with the Lucayan Archipelago, are collectively known as the West Indies.

The Antilles is an archipelago bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the south and west, the Gulf of Mexico to the northwest, and the Atlantic Ocean to the north and east.

The Lesser Antillean iguana is a large arboreal lizard endemic to the Lesser Antilles. It is one of three species of lizard of the genus Iguana and is in severe decline due to habitat destruction, introduced feral predators, hunting, and hybridization with its introduced sister species, the green iguana. Successful captive breeding of this species has been limited to only two instances, as most captive-laid eggs tend to be infertile.

The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greater Antilles, the Lesser Antilles, and the Lucayan Archipelago.

The Caribbean elaenia is a species of bird in the family Tyrannidae found in the West Indies and parts of Central America. Its natural habitats are tropical and subtropical dry broadleaf forest, subtropical or tropical moist lowland forest, and heavily degraded former forest.

The lesser Antillean bullfinch is a species of bird in the family Thraupidae. It is found in Saint Barth, Saint Martin, Anguilla, Antigua and Barbuda, Dominica, Grenada, Guadeloupe, Martinique, Montserrat, Netherlands Antilles, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, the British Virgin Islands, and the U.S. Virgin Islands.
The Caribbean bioregion is a biogeographic region that includes the islands of the Caribbean Sea and nearby Atlantic islands, which share a fauna, flora and mycobiota distinct from surrounding bioregions.

The Prickly Pear Cays, sometimes spelt as Prickley Pear Cays, are a small pair of uninhabited islands about six miles from Road Bay, Anguilla, in the Leeward Islands of the Caribbean. They are divided by a narrow boat channel between Prickly Pear East and Prickly Pear West. Prickly Pear Cays were classified as 'wildlands' by the "Eastern Caribbean Natural Area Management Programme" (ECNAMP). In addition, Prickly Pear Cays are one of six marine protected areas of Anguilla.

Île Fourchue, also known as Île Fourche is an island between Saint-Barthélemy and Saint Martin, belonging to the Collectivity of Saint Barthélemy. The island's inside is privately owned. It is located about 5 km north-west of the island of Saint Barthelemy. Previously, Fourchue Island was called Five Islands because of prominent five peaks visible from the distance. The highest point is 103 meter above sea level. It is situated within Réserve naturelle nationale de Saint-Barthélemy.

The Anguilla Formation is a geologic formation in Anguilla. It preserves fossils dating back to the Burdigalian to Serravallian period.

Île Frégate is a small, uninhabited island in the Caribbean Sea located off the north coast of Saint Barthélemy, an overseas collectivity of France. Île Frégate is situated within the Nature Reserve of Saint Bartholomew, which was established in 1996 with the objective of conserving coral reefs, sea grass beds and marine life.

Madeira began to form more than 100 million years ago in the Early Cretaceous, although most of the island has formed in the last 66 million years of the Cenozoic, particularly in the Miocene and Pliocene. The island is an example of hotspot volcanism, with mainly mafic volcanic and igneous rocks, together with smaller deposits of limestone, lignite and other sediments that record its long-running uplift.
The island of Aruba formed within the past 145 million years, beginning in the Cretaceous, as part of the Lesser Antilles island arc. The island is built on a thick sequence of volcanic rock, but also has carbonate sediment deposits because it was submerged for parts of its existence.
The geology of the island Barbados includes exposures of reef-related carbonate rocks spanning 85 percent of the island's surface. This Coral Rock Formation is 70 meters thick and dates to the Pleistocene. Unlike neighboring islands in the Lesser Antilles volcanic arc, Barbados is unusual because it is not a volcanic island. Instead, the island of Barbados is the exposed part of the Barbados Ridge Accretionary Prism, left as deep ocean sediments "scraped" to the surface as the Atlantic oceanic crust subducted beneath the Caribbean Plate.
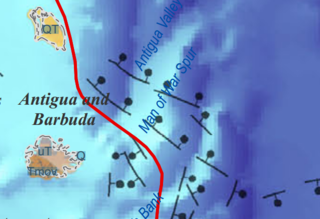
The geology of Antigua and Barbuda is part of the Lesser Antilles volcanic island arc. Both islands are the above water limestone "caps" of now inactive volcanoes. The two islands are the surface features of the undersea Barbuda Bank and have karst limestone landscapes. Barbuda is primarily flat and formed from coral reefs. The Middle Miocene Highlands Formation has limestones which are the oldest rocks on the island, rising 120 feet above sea level. The Beazer Formation and the Codrington Formation are both from the Pleistocene and include reef and lagoon related rocks.
The geology of the Collectivity of Saint Martin consists of andesite tuff and tuff breccia from the middle and late Eocene, intruded by hypabyssal basalt, quartz diorite and younger andesite. Volcanic activity led to metamorphism of many rocks and the tilting and folding of the tuff series. Limestone and marl was later unconformably deposited atop the eroded volcanic rocks as volcanic activity shifted elsewhere. Large boulder ridges and solitary boulders on high cliffs suggest tectonic-related tsunamis.
The geology of Sint Maarten consists of andesite tuff and tuff breccia from the middle and late Eocene, intruded by hypabyssal basalt, quartz diorite and younger andesite. Volcanic activity led to metamorphism of many rocks and the tilting and folding of the tuff series. Limestone and marl was later unconformably deposited atop the eroded volcanic rocks as volcanic activity shifted elsewhere.
The geology of Saint Barthélemy consists of andesite tuff and tuff breccia from the middle and late Eocene, intruded by hypabyssal basalt, quartz diorite and younger andesite. Volcanic activity on neighboring Saint Martin led to metamorphism of many rocks and the tilting and folding of the tuff series. Limestone and marl was later unconformably deposited atop the eroded volcanic rocks as volcanic activity shifted elsewhere.
References
- ↑ Budd, A. F.; Johnson, K. G.; Edwards, J. C. (1995). "Caribbean reef coral diversity during the early to middle Miocene: an example from the Anguilla Formation". Coral Reefs. 14 (2): 109–117. Bibcode:1995CorRe..14..109B. doi:10.1007/BF00303432. S2CID 22827668.
- ↑ Christman, Robert A. (1953). "Geology of St. Bartholomew, St. Martin, and Anguilla, Lesser Antilles | GSA Bulletin". Geological Society of America Bulletin. 64: 85. doi:10.1130/0016-7606(1953)64[85:GOSBSM]2.0.CO;2 . Retrieved 2018-11-09.