
Tilapia is the common name for nearly a hundred species of cichlid fish from the coelotilapine, coptodonine, heterotilapine, oreochromine, pelmatolapiine, and tilapiine tribes, with the economically most important species placed in the Coptodonini and Oreochromini. Tilapia are mainly freshwater fish inhabiting shallow streams, ponds, rivers, and lakes, and less commonly found living in brackish water. Historically, they have been of major importance in artisanal fishing in Africa, and they are of increasing importance in aquaculture and aquaponics. Tilapia can become a problematic invasive species in new warm-water habitats such as Australia, whether deliberately or accidentally introduced, but generally not in temperate climates due to their inability to survive in cold water.

The Savannah sparrow is a small New World sparrow that is the only member of the genus Passerculus. It is a widespread and abundant species that occupies open grassland habitats in North America.

Clinidae is a family of marine fish in the order Blenniiformes within the series Ovalentaria, part of the Percomorpha. Temperate blennies, the family ranges from the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans, in both the Southern and Northern Hemispheres. The family contains about 86 species in 20 genera, the 60-cm-long giant kelpfish being the largest; most are far smaller.

The Southern California Bight is a 692-kilometer-long stretch of curved coastline that runs along the west coast of the United States and Mexico, from Point Conception in California to Punta Colonet in Baja California, plus the area of the Pacific Ocean defined by that curve. This includes the Channel Islands of California and the Coronado Islands and Islas de Todo Santos of Baja California.
The flathead galaxias is a freshwater fish found in lowland rivers, streams and associated billabongs, backwaters, and wetlands of the southern Murray-Darling river system in southeastern Australia.

The school shark is a houndshark of the family Triakidae, and the only member of the genus Galeorhinus. Common names also include tope, tope shark, snapper shark, and soupfin shark. It is found worldwide in temperate seas at depths down to about 800 m (2,600 ft). It can grow to nearly 2 m long. It feeds both in midwater and near the seabed, and its reproduction is ovoviviparous. This shark is caught in fisheries for its flesh, its fins, and its liver, which has a very high vitamin A content. The IUCN has classified this species as critically endangered in its Red List of Threatened Species.

The least tern is a species of tern that breeds in North America and locally in northern South America. It is closely related to, and was formerly often considered conspecific with, the little tern of the Old World. Other close relatives include the yellow-billed tern and Peruvian tern, both from South America.

The longnose sucker is a species of cypriniform freshwater fish in the family Catostomidae. It is native to North America from the northern United States to the top of the continent. It is also found in Russia in rivers of eastern Siberia, and this one of only two species of sucker native to Asia.

The little sleeper shark is a small sleeper shark of the family Somniosidae found in the northeast Atlantic, western Mediterranean, and western Pacific around New Zealand, at depths between 200 and 1,000 m. Its length is up to 1.43 m.

Scinax rostratus is a species of frog in the family Hylidae. It is found in central Panama and eastward to Colombia, Venezuela, and coastal lowlands of Guyana, Suriname, and French Guiana. Common name Caracas snouted treefrog has been coined for this species.

Fossorochromis rostratus is a species of cichlid fish that is endemic to Lake Malawi in East Africa. The only species in its genus, it is a relatively large, sexually dimorphic cichlid.

The copperband butterflyfish, also known as the beaked coral fish, is found in reefs in both the Pacific and Indian Oceans. This butterflyfish is one of the three species that make up the genus Chelmon and all have long beaks.
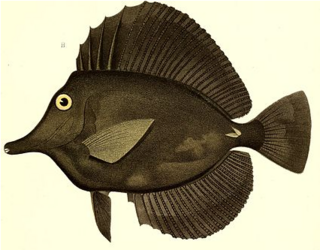
Zebrasoma rostratum, the longnose surgeonfish, longnose tang or black tang, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Acanthuridae, which includes the surgeonfishes, unicornfishes and tangs. This fish is found in the western central Pacific Ocean.

Gibbonsia elegans, the spotted kelpfish, is a species of clinid native to subtropical waters of the Pacific Ocean from central California, U.S. to southern Baja California, Mexico. It prefers subtidal rocky habitats with seaweed down to a depth of about 56 metres (184 ft). This species can reach a maximum length of 16 centimetres (6.3 in) TL. This species feeds on benthic crustaceans, gastropods, and polychaete worms. The genus Gibbonsia is named after William P. Gibbons who was a naturalist in the California Academy of Science. It is found in three different colors depending on their habitat. Males and females do not show sexual dimorphism.

The pointed-snout wrasse, also known as the long-snout wrasse, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a wrasse from the family Labridae which is native to coastal waters of the Mediterranean Sea and the Black Sea. This species can also be found in the aquarium trade and is occasionally taken in artisanal fisheries.

Fodiator is a genus of flying fishes. It is the only genus in the subfamily Fodiatorinae.
Himantolophus rostratus is a species of footballfish, a type of anglerfish. The fish is both mesopelagic and bathypelagic and can be found in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans.
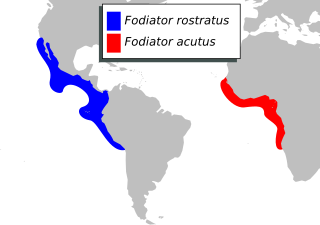
Fodiator rostratus is a species of flying fish in the genus Fodiator. It reaches a maximum length of 19 cm (7.4 in) and is endemic to the eastern Pacific Ocean from Baja California in the Gulf of California to Peru, including Clipperton Island and the Galapagos Islands.
Hypselognathus rostratus, also known as the knife-snouted pipefish is a species of marine fish belonging to the family Syngnathidae. This species can be found in very shallow coastal waters of southeastern Australia. Their habitat consists of sandy substrates, seagrass beds, and estuaries. Reproduction occurs through ovoviviparity in which the males brood eggs before giving live birth.

















