Anbar was an ancient and medieval town in central Iraq. It played a role in the Roman–Persian Wars of the 3rd–4th centuries, and briefly became the capital of the Abbasid Caliphate before the founding of Baghdad in 762. It remained a moderately prosperous town through the 10th century, but quickly declined thereafter. As a local administrative centre, it survived until the 14th century, but was later abandoned.

Hersonissos, also transliterated as Chersonissos and Hersónisos, is a town and a local government unit in the north of Crete, bordering the Mediterranean / Aegean Sea. The town is about 25 kilometers east of Heraklion and west of Agios Nikolaos. What is usually called Hersonissos is in fact its peninsula and harbour. It is part of the Heraklion regional unit. It is situated 25 km from the Heraklion airport and 27 km from the Heraklion port. The seat of the local government unit is the village of Gournes.

Lambaesis (Lambæsis), Lambaisis or Lambaesa, is a Roman archaeological site in Algeria, 11 km (7 mi) southeast of Batna and 27 km (17 mi) west of Timgad, located next to the modern village of Tazoult. The former bishopric is also a Latin Catholic titular bishopric.

Zaraï was a Berber, Carthaginian, and Roman town at the site of present-day Aïn Oulmene, Algeria. Under the Romans, it formed part of the province of Numidia.

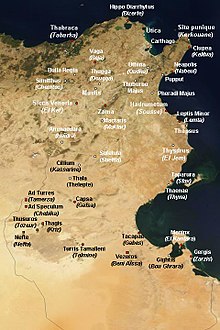
Musti or Mustis was an ancient city and bishopric in the Roman province of Proconsular Africa, now in northern Tunisia. Its ruins, called Mest Henshir, are about eight miles from Dougga, near Sidi-Abd-Er-Rebbou. It is also a Catholic titular see.

Boughrara is a coastal town in central-eastern Tunisia. It is located at around 33°32′16″N10°40′34″E. During the Roman occupation of North Africa, Boughrara was known as Gigthis.
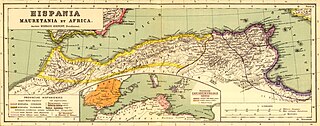
Zuccabar was an ancient town in the Roman province of Mauretania Caesariensis. It is located in present-day Miliana, Algeria.

Olba or Olbe was an ancient city and bishopric in the Roman province of Isauria, in present-day southern Turkey. It is included in the Catholic Church's list of Latin titular sees.

Hypaepa or Hypaipa was an Ancient city and (arch)bishopric in ancient Lydia, near the north bank of the Cayster River, and 42 miles from Ephesus, Ephesus and remains a Latin Catholic titular see.
Ruspe or Ruspae was a town in the Roman province of Byzacena, in Africa propria. It served as the episcopal see of Saint Fulgentius of Ruspe. It is now a Roman Catholic titular bishopric.
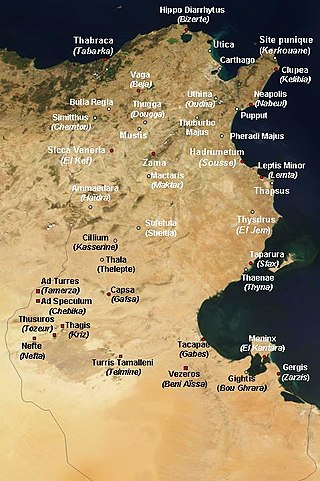
Turris Tamalleni was a town in North Africa, dating from the Carthageinian, Roman, Byzantine and Vandal era.

Setae or Setai, or Settae or Settai (Σέτται), or Saettae or Saittai or Saittae (Σαίτται) was a town of ancient Lydia, located at Sidas Kaleh in Modern Turkey. The ruins of that town consist of a stadium, tombs and ruins of several temples. The town is not mentioned by any of the earlier writers, but appears in Ptolemy and Hierocles.
Tymandus or Tymandos also known as Mandos, Mandas Kiri, or Yassi Veran, was a Roman and Byzantine-era city in northern Pisidia. A number of monuments from Roman times remain in the area.

Djebba, also known as Thigibba Bure, is a town and an ancient archaeological site is located in Bājah, Tunisia. Djebba is an archaeological/prehistoric site in Tunisia located at latitude: 36°28'32.45" longitude: 9°4'53.54" in the Béja Governorate of northwestern Tunisia. The estimated terrain elevation above sea level is 355 metres located below the slopes of Djebel Gorra, 700 meters above sea level. Djebba also has a national park, which is the subject of a development project
Limnae (in Pisidia) was a city and bishopric in the Roman province of Pisidia (Asia Minor), which is now a Latin Catholic titular see.

Zian, also known as Zitha, is a locality and archaeological site near Bou Gharain south Tunisia.
The diocese of Siccesi is a suppressed and titular see of the Roman Catholic Church.

Præsidium also known as Praesidium Diolele was a town of the Roman Province of Byzacena in North Africa during the Roman Empire.

Libertina was a town of the Roman province of Byzacena in North Africa during the Roman Empire. The town is tentatively identified with ruins near Souc-El-Arba, Tunisia.
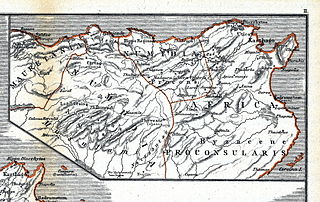
Numidia was a Roman province on the North African coast, comprising roughly the territory of north-east Algeria.