Related Research Articles

Female genital mutilation (FGM) is the ritual cutting or removal of some or all of the vulva. The practice is found in some countries of Africa, Asia and the Middle East, and within their respective diasporas. As of 2023, UNICEF estimates that "at least 200 million girls... in 31 countries"—including Indonesia, Iraq, Yemen, and 27 African countries including Egypt—had been subjected to one or more types of FGM.

Hausa is a Chadic language that is spoken by the Hausa people in the northern parts of Nigeria, Ghana, Cameroon, Benin and Togo, and the southern parts of Niger, and Chad, with significant minorities in Ivory Coast. A small number of speakers also exist in Sudan.

In mammals and other animals, the vagina is the elastic, muscular reproductive organ of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vestibule to the cervix. The outer vaginal opening is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucosal tissue called the hymen. At the deep end, the cervix bulges into the vagina. The vagina allows for copulation and birth. It also channels menstrual flow, which occurs in humans and closely related primates as part of the menstrual cycle.
Infibulation is the ritual removal of the vulva and its suturing, a practice found mainly in northeastern Africa, particularly in Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Somalia, and Sudan. The World Health Organization refers to the procedure as Type III female genital mutilation.
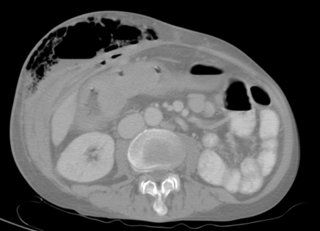
In anatomy, a fistula is an abnormal connection joining two hollow spaces, such as blood vessels, intestines, or other hollow organs to each other, often resulting in an abnormal flow of fluid from one space to the other. An anal fistula connects the anal canal to the perianal skin. An anovaginal or rectovaginal fistula is a hole joining the anus or rectum to the vagina. A colovaginal fistula joins the space in the colon to that in the vagina. A urinary tract fistula is an abnormal opening in the urinary tract or an abnormal connection between the urinary tract and another organ. An abnormal communication between the bladder and the uterus is called a vesicouterine fistula, while if it is between the bladder and the vagina it is known as a vesicovaginal fistula, and if between the urethra and the vagina: a urethrovaginal fistula. When occurring between two parts of the intestine, it is known as an enteroenteral fistula, between the small intestine and the skin as an enterocutaneous fistula, and between the colon and the skin as a colocutaneous fistula.
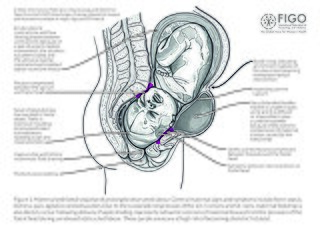
Obstetric fistula is a medical condition in which a hole develops in the birth canal as a result of childbirth. This can be between the vagina and rectum, ureter, or bladder. It can result in incontinence of urine or feces. Complications may include depression, infertility, and social isolation.
A pessary is a prosthetic device inserted into the vagina for structural and pharmaceutical purposes. It is most commonly used to treat stress urinary incontinence to stop urinary leakage and to treat pelvic organ prolapse to maintain the location of organs in the pelvic region. It can also be used to administer medications locally in the vagina or as a method of contraception.

The pelvic floor or pelvic diaphragm is an anatomical location in the human body, which has an important role in urinary and anal continence, sexual function and support of the pelvic organs. The pelvic floor includes muscles, both skeletal and smooth, ligaments and fascia. and separates between the pelvic cavity from above, and the perineum from below. It is formed by the levator ani muscle and coccygeus muscle, and associated connective tissue.
Vaginoplasty is any surgical procedure that results in the construction or reconstruction of the vagina. It is a type of genitoplasty. Pelvic organ prolapse is often treated with one or more surgeries to repair the vagina. Sometimes a vaginoplasty is needed following the treatment or removal of malignant growths or abscesses to restore a normal vaginal structure and function. Surgery to the vagina is done to correct congenital defects to the vagina, urethra and rectum. It may correct protrusion of the urinary bladder into the vagina (cystocele) and protrusion of the rectum (rectocele) into the vagina. Often, a vaginoplasty is performed to repair the vagina and its attached structures due to trauma or injury.

The cystocele, also known as a prolapsed bladder, is a medical condition in which a woman's bladder bulges into her vagina. Some may have no symptoms. Others may have trouble starting urination, urinary incontinence, or frequent urination. Complications may include recurrent urinary tract infections and urinary retention. Cystocele and a prolapsed urethra often occur together and is called a cystourethrocele. Cystocele can negatively affect quality of life.
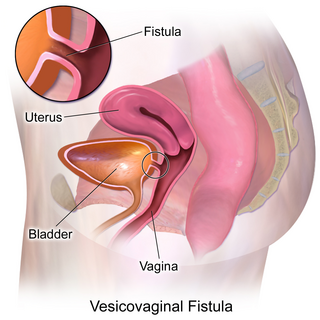
Vesicovaginal fistula (VVF) is a subtype of female urogenital fistula (UGF).

Stress incontinence, also known as stress urinary incontinence (SUI) or effort incontinence is a form of urinary incontinence. It is due to inadequate closure of the bladder outlet by the urethral sphincter.

The Hausa are a native ethnic group in West Africa. They speak the Hausa language, which is the second most spoken language after Arabic in the Afro-Asiatic language family. The Hausa are a culturally homogeneous people based primarily in the Sahelian and the sparse savanna areas of southern Niger and northern Nigeria respectively, numbering around 86 million people, with significant populations in Benin, Cameroon, Ivory Coast, Chad, Central African Republic, Togo, Ghana, as well as smaller populations in Sudan, Eritrea, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Senegal, Gambia. Predominantly Hausa-speaking communities are scattered throughout West Africa and on the traditional Hajj route north and east traversing the Sahara, with an especially large population in and around the town of Agadez. Other Hausa have also moved to large coastal cities in the region such as Lagos, Port Harcourt, Accra, Abidjan, Banjul and Cotonou as well as to parts of North Africa such as Libya over the course of the last 500 years. The Hausa traditionally live in small villages as well as in precolonial towns and cities where they grow crops, raise livestock including cattle as well as engage in trade, both local and long distance across Africa. They speak the Hausa language, an Afro-Asiatic language of the Chadic group. The Hausa aristocracy had historically developed an equestrian based culture. Still a status symbol of the traditional nobility in Hausa society, the horse still features in the Eid day celebrations, known as Ranar Sallah. Daura is the cultural center of the Hausa people. The town predates all the other major Hausa towns in tradition and culture.

A pelvic examination is the physical examination of the external and internal female pelvic organs. It is frequently used in gynecology for the evaluation of symptoms affecting the female reproductive and urinary tract, such as pain, bleeding, discharge, urinary incontinence, or trauma. It can also be used to assess a woman's anatomy in preparation for procedures. The exam can be done awake in the clinic and emergency department, or under anesthesia in the operating room. The most commonly performed components of the exam are 1) the external exam, to evaluate the vulva 2) the internal exam with palpation to examine the uterus, ovaries, and structures adjacent to the uterus (adnexae) and 3) the internal exam using a speculum to visualize the vaginal walls and cervix. During the pelvic exam, sample of cells and fluids may be collected to screen for sexually transmitted infections or cancer.
Urethroplasty is the surgical repair of an injury or defect within the walls of the urethra. Trauma, iatrogenic injury and infections are the most common causes of urethral injury/defect requiring repair. Urethroplasty is regarded as the gold standard treatment for urethral strictures and offers better outcomes in terms of recurrence rates than dilatations and urethrotomies. It is probably the only useful modality of treatment for long and complex strictures though recurrence rates are higher for this difficult treatment group.
Vaginal flatulence or vaginal wind is an emission or expulsion of air from the vagina. It may occur during or after sexual intercourse or during other sexual acts, stretching or exercise. The sound is often comparable to flatulence from the anus, but does not involve waste gases, and thus often does not have a specific odor associated. Slang terms for vaginal flatulence include queef, vart, and fanny fart. Tampons can treat or prevent vaginal wind.
Female genital mutilation in Sierra Leone is the common practice of removing all or part of the female's genitalia for cultural and religious initiation purposes, or as a custom to prepare them for marriage. Sierra Leone is one of 28 countries in Africa where female genital mutilation (FGM) is known to be practiced and one of few that has not banned it. It is widespread in part due to it being an initiation rite into the "Bondo," though initiation rite-related FGM was criminalised in 2019. The type most commonly practised in Sierra Leone is Type IIb, removal of part or all of the clitoris and the labia minora. As of 2013, it had a prevalence of 89.6%.
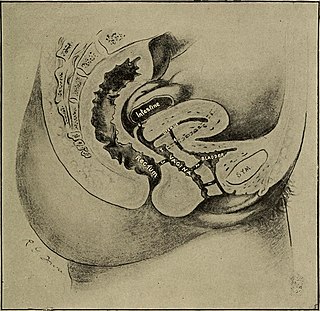
A ureterovaginal fistula is an abnormal passageway existing between the ureter and the vagina. It presents as urinary incontinence. Its impact on women is to reduce the "quality of life dramatically."
A urogenital fistula is an abnormal tract that exists between the urinary tract and bladder, ureters, or urethra. A urogenital fistula can occur between any of the organs and structures of the pelvic region. A fistula allows urine to continually exit through and out the urogenital tract. This can result in significant disability, interference with sexual activity, and other physical health issues, the effects of which may in turn have a negative impact on mental or emotional state, including an increase in social isolation. Urogenital fistulas vary in etiology. Fistulas are usually caused by injury or surgery, but they can also result from malignancy, infection, prolonged and obstructed labor and deliver in childbirth, hysterectomy, radiation therapy or inflammation. Of the fistulas that develop from difficult childbirth, 97 percent occur in developing countries. Congenital urogenital fistulas are rare; only ten cases have been documented. Abnormal passageways can also exist between the vagina and the organs of the gastrointestinal system, and these may also be termed fistulas.

Ancient Roman surgical practices developed from Greek techniques. Roman surgeons and doctors usually learned through apprenticeships or studying. Ancient Roman doctors such as Galen and Celsus described Roman surgical techniques in their medical literature, such as De Medicina. These methods encompassed modern oral surgery, cosmetic surgery, sutures, ligatures, amputations, tonsillectomies, mastectomies, cataract surgeries, lithotomies, hernia repair, gynecology, neurosurgery, and others. Surgery was a rare practice, as it was dangerous and often had fatal results. To perform these procedures, they used tools such as specula, catheters, enemas, bone levers, osteotomes, phlebotomes, probes, curettes, bone drills, bone forceps, cupping vessels, knives, scalpels, scissors, and spathas.
References
- 1 2 3 "Obstetric Fistula". Forward. Archived from the original on 2018-10-11. Retrieved 2014-04-01.
- 1 2 Romanzi, Lauri (December 2010). "'Yankan Gishiri' cutting, a home remedy, cause fistula in Niger and Nigeria". Archived from the original on April 26, 2017. Retrieved August 6, 2011.
- ↑ "Gishiri cutting". My Vagina. 2015-09-15. Retrieved 2024-02-03.