The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) is the UN process for negotiating an agreement to limit dangerous climate change. It is an international treaty among countries to combat "dangerous human interference with the climate system". The main way to do this is limiting the increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. It was signed in 1992 by 154 states at the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED), informally known as the Earth Summit, held in Rio de Janeiro. The treaty entered into force on 21 March 1994. "UNFCCC" is also the name of the Secretariat charged with supporting the operation of the convention, with offices on the UN Campus in Bonn, Germany.

Power Shift is an annual youth summit which has been held in New Zealand, Australia, Canada, the United Kingdom and the United States. Other Power Shift Conferences are also being organised by members of the International Youth Climate Movement including Africa, Japan and India. The focus of the events is on climate change policy.

The politics of climate change results from different perspectives on how to respond to climate change. Global warming is driven largely by the emissions of greenhouse gases due to human economic activity, especially the burning of fossil fuels, certain industries like cement and steel production, and land use for agriculture and forestry. Since the Industrial Revolution, fossil fuels have provided the main source of energy for economic and technological development. The centrality of fossil fuels and other carbon-intensive industries has resulted in much resistance to climate friendly policy, despite widespread scientific consensus that such policy is necessary.
This timeline lists events in the external environment that have influenced events in human history. This timeline is for use with the article on environmental determinism. For the history of humanity's influence on the environment, and humanity's perspective on this influence, see timeline of history of environmentalism. See List of periods and events in climate history for a timeline list focused on climate.

350.org is an international environmental organization addressing the climate crisis. Its stated goal is to end the use of fossil fuels and transition to renewable energy by building a global, grassroots movement.

The Climate Vulnerable Forum (CVF) is a global partnership of countries that are disproportionately affected by the consequences of climate change. The forum addresses the negative effects of climate change as a result of heightened socioeconomic and environmental vulnerabilities. These countries actively seek a firm and urgent resolution to the current intensification of climate change, domestically and internationally. The CVF was formed to increase the accountability of industrialized nations for the consequences of global climate change. It also aims to exert additional pressure for action to tackle the challenge, which includes the local action by countries considered susceptible. Political leaders involved in this partnership are "using their status as those most vulnerable to climate change to punch far above their weight at the negotiating table". The governments which founded the CVF agree to national commitments to pursue low-carbon development and carbon neutrality.

Laurence Tubiana is a French economist, academic and diplomat. She served as France's Climate Change Ambassador and Special Representative for the 2015 COP21 Climate Change Conference in the Paris region, for which she became recognised as a key architect of the resulting Paris Agreement.

Enele Sosene Sopoaga PC is a Tuvaluan diplomat and politician who was Prime Minister of Tuvalu from 2013 to 2019.
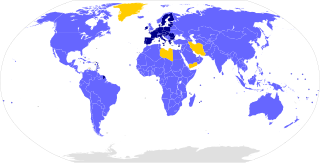
The Paris Agreement is an international treaty on climate change that was adopted in 2015. The treaty covers climate change mitigation, adaptation, and finance. The Paris Agreement was negotiated by 196 parties at the 2015 United Nations Climate Change Conference near Paris, France. As of February 2023, 195 members of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) are parties to the agreement. Of the three UNFCCC member states which have not ratified the agreement, the only major emitter is Iran. The United States withdrew from the agreement in 2020, but rejoined in 2021.

Human rights and climate change is a conceptual and legal framework under which international human rights and their relationship to global warming are studied, analyzed, and addressed. The framework has been employed by governments, United Nations organizations, intergovernmental and non-governmental organizations, human rights and environmental advocates, and academics to guide national and international policy on climate change under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and the core international human rights instruments. In 2022 Working Group II of the IPCC suggested that "climate justice comprises justice that links development and human rights to achieve a rights-based approach to addressing climate change".

The 2015 United Nations Climate Change Conference, COP 21 or CMP 11 was held in Paris, France, from 30 November to 12 December 2015. It was the 21st yearly session of the Conference of the Parties (COP) to the 1992 United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and the 11th session of the Meeting of the Parties (CMP) to the 1997 Kyoto Protocol.
The Climate Summit 2014 was a meeting on climate change in New York on September 23, 2014. UN Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon announced it in September 2013 and invited leaders of governments, the private sector, and civil society to unite in taking concrete action towards a low-carbon emission world.

The climate movement is a global social movement focused on pressuring governments and industry to take action addressing the causes and impacts of climate change. Environmental non-profit organizations have engaged in significant climate activism since the late 1980s and early 1990s, as they sought to influence the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). Climate activism has become increasingly prominent over time, gaining significant momentum during the 2009 Copenhagen Summit and particularly following the signing of the Paris Agreement in 2016.

The Climate Mobilization (TCM) is a grassroots environmental advocacy group working toward large-scale political action against global warming. It believes that the crisis of climate change requires a national economic effort on the scale of the American mobilization of the home front during World War II., in order to transform the USA economy speedily.
Doppelgangster is a UK/Australian experimental performance company that has been recognised internationally for its ecologically and socially engaged practice, which includes site-specific theatre, one-to-one encounters, and subversive political interventions. The company has been recognised by the International Network for Contemporary Performing Arts] (IETM) and the French Coalition for Art and Sustainable Development (COAL) for "creating cultural responses to climate change, forced migration and globalisation using technology to extend their reach to new audiences".

Hakima El Haite is a Moroccan climate scientist, entrepreneur and politician.

The 2019 United Nations Climate Change Conference, also known as COP25, was the 25th United Nations Climate Change conference. It was held in Madrid, Spain, from 2 to 13 December 2019 under the presidency of the Chilean government. The conference incorporated the 25th Conference of the Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), the 15th meeting of the parties to the Kyoto Protocol (CMP15), and the second meeting of the parties to the Paris Agreement (CMA2).
Climate change art is art inspired by climate change and global warming, generally intended to overcome humans' hardwired tendency to value personal experience over data and to disengage from data-based representations by making the data "vivid and accessible". One of the goal of climate change art is to "raise awareness of the crisis", as well as engage viewers politically and environmentally.
The history of climate change policy and politics refers to the continuing history of political actions, policies, trends, controversies and activist efforts as they pertain to the issue of climate change. Climate change emerged as a political issue in the 1970s, where activist and formal efforts were taken to ensure environmental crises were addressed on a global scale. International policy regarding climate change has focused on cooperation and the establishment of international guidelines to address global warming. The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) is a largely accepted international agreement that has continuously developed to meet new challenges. Domestic policy on climate change has focused on both establishing internal measures to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and incorporating international guidelines into domestic law.













