Mercury(II) chloride (or mercury bichloride, mercury dichloride), historically also known as sulema or corrosive sublimate, is the inorganic chemical compound of mercury and chlorine with the formula HgCl2. It is white crystalline solid and is a laboratory reagent and a molecular compound that is very toxic to humans. Once used as a treatment for syphilis, it is no longer used for medicinal purposes because of mercury toxicity and the availability of superior treatments.

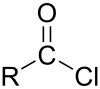
An acyl halide is a chemical compound derived from an oxoacid by replacing a hydroxyl group with a halide group.

Thionyl chloride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula SOCl
2. It is a moderately volatile colourless liquid with an unpleasant acrid odour. Thionyl chloride is primarily used as a chlorinating reagent, with approximately 45,000 tonnes per year being produced during the early 1990s, but is occasionally also used as a solvent. It is toxic, reacts with water, and is also listed under the Chemical Weapons Convention as it may be used for the production of chemical weapons.
The chemical compound 1,2-dichloroethane, commonly known as ethylene dichloride (EDC), is a chlorinated hydrocarbon. It is a colourless liquid with a chloroform-like odour. The most common use of 1,2-dichloroethane is in the production of vinyl chloride, which is used to make polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes, furniture and automobile upholstery, wall coverings, housewares, and automobile parts. 1,2-Dichloroethane is also used generally as an intermediate for other organic chemical compounds, and as a solvent. It forms azeotropes with many other solvents, including water and other chlorocarbons.

Palladium(II) chloride, also known as palladium dichloride and palladous chloride, are the chemical compounds with the formula PdCl2. PdCl2 is a common starting material in palladium chemistry – palladium-based catalysts are of particular value in organic synthesis. It is prepared by the reaction of chlorine with palladium metal at high temperatures.

Dimethyl methylphosphonate is an organophosphorus compound with the chemical formula CH3PO(OCH3)2. It is a colourless liquid, which is primarily used as a flame retardant.

Sulfur dichloride is the chemical compound with the formula SCl2. This cherry-red liquid is the simplest sulfur chloride and one of the most common, and it is used as a precursor to organosulfur compounds. It is a highly corrosive and toxic substance, and it reacts on contact with water to form chlorine-containing acids.

Disulfur dichloride is the inorganic compound of sulfur and chlorine with the formula S2Cl2.

Vanadium(II) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula VCl2, and is the most reduced vanadium chloride. Vanadium(II) chloride is an apple-green solid that dissolves in water to give purple solutions.

Tritellurium dichloride is the inorganic compound with the formula Te3Cl2. It is one of the more stable lower chlorides of tellurium.
Zirconocene dichloride is an organozirconium compound composed of a zirconium central atom, with two cyclopentadienyl and two chloro ligands. It is a colourless diamagnetic solid that is somewhat stable in air.

Xenon dichloride (XeCl2) is a xenon compound and the only known stable chloride of xenon. The compound can be prepared by using microwave discharges towards the mixture of xenon and chlorine, and it can be isolated from a condensate trap. One experiment tried to use xenon, chlorine and boron trichloride to produce XeCl2·BCl3, but only generated xenon dichloride.

Methylphosphonyl dichloride (DC) or dichloro is an organophosphorus compound. It has a number of commercial uses but is most notable as being a precursor to several chemical weapons agents. It is a white crystalline solid that melts slightly above room temperature.

Westlake Chemical is an international manufacturer and supplier of petrochemicals, polymers and fabricated building products, which are fundamental to various consumer and industrial markets. The company was founded by Ting Tsung Chao in 1986. it is the largest producer of low-density polyethylene (LDPE) in the US and ranks among the Forbes Global 2000. Westlake Chemical operates in two segments: Olefins and Vinyls, and is also an integrated producer of vinyls, with substantial downstream integration into polyvinyl chloride (PVC) building products.

Pentamminechlororhodium dichloride is the dichloride salt of the coordination complex [RhCl(NH3)5]2+. It is a yellow, water-soluble solid. The salt is an intermediate in the purification of rhodium from its ores.
In organophosphorus chemistry, the Kinnear–Perren reaction (sometimes the Clay-Kinnear-Perren reaction) is used to prepare alkylphosphonyl dichlorides (RP(O)Cl2) and alkylphosphonate esters (RP(O)(OR')2). The reactants are alkyl chloride, phosphorus trichloride, and aluminium trichloride as catalyst. The reaction proceeds via the alkyltrichlorophosphonium salt:
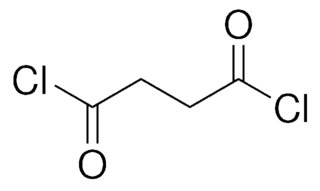
Succinyl chloride is the organic compound with the formula (CH2)2(COCl)2. It is the acyl chloride derivative of succinic acid and a simple diacid chloride. It is a colorless liquid. It used as a reagent in organic synthesis.

Europium dichloride is an inorganic compound with a chemical formula EuCl2. When it is irradiated by ultraviolet light, it has bright blue fluorescence.
Americium(II) chloride, also known as dichloroamericium, is the chemical compound composed of americium and chloride with the formula AmCl2.
Dysprosium(II) chloride (DyCl2), also known as dysprosium dichloride, is an ionic chemical compound of dysprosium and chlorine. This salt is a reduced compound, as the normal oxidation state of dysprosium in dysprosium compounds is +3.