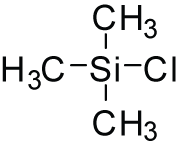Iron(III) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula FeCl3. Also called ferric chloride, it is a common compound of iron in the +3 oxidation state. The anhydrous compound is a crystalline solid with a melting point of 307.6 °C. The color depends on the viewing angle: by reflected light the crystals appear dark green, but by transmitted light they appear purple-red.
The Friedel–Crafts reactions are a set of reactions developed by Charles Friedel and James Crafts in 1877 to attach substituents to an aromatic ring. Friedel–Crafts reactions are of two main types: alkylation reactions and acylation reactions. Both proceed by electrophilic aromatic substitution.
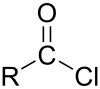
In organic chemistry, an acyl chloride is an organic compound with the functional group −C(=O)Cl. Their formula is usually written R−COCl, where R is a side chain. They are reactive derivatives of carboxylic acids. A specific example of an acyl chloride is acetyl chloride, CH3COCl. Acyl chlorides are the most important subset of acyl halides.

In organic chemistry, an acyl halide is a chemical compound derived from an oxoacid by replacing a hydroxyl group with a halide group.
An organochloride, organochlorine compound, chlorocarbon, or chlorinated hydrocarbon is an organic compound containing at least one covalently bonded atom of chlorine. The chloroalkane class provides common examples. The wide structural variety and divergent chemical properties of organochlorides lead to a broad range of names, applications, and properties. Organochlorine compounds have wide use in many applications, though some are of profound environmental concern, with TCDD being one of the most notorious.

Aluminium chloride, also known as aluminium trichloride, is an inorganic compound with the formula AlCl3. It forms hexahydrate with the formula [Al(H2O)6]Cl3, containing six water molecules of hydration. Both are colourless crystals, but samples are often contaminated with iron(III) chloride, giving a yellow color.
Manganese(II) chloride is the dichloride salt of manganese, MnCl2. This inorganic chemical exists in the anhydrous form, as well as the dihydrate (MnCl2·2H2O) and tetrahydrate (MnCl2·4H2O), with the tetrahydrate being the most common form. Like many Mn(II) species, these salts are pink, with the paleness of the color being characteristic of transition metal complexes with high spin d5 configurations.

Copper(I) chloride, commonly called cuprous chloride, is the lower chloride of copper, with the formula CuCl. The substance is a white solid sparingly soluble in water, but very soluble in concentrated hydrochloric acid. Impure samples appear green due to the presence of copper(II) chloride (CuCl2).
Copper(II) chloride is the chemical compound with the chemical formula CuCl2. The anhydrous form is yellowish brown but slowly absorbs moisture to form a blue-green dihydrate.

Chromium(III) chloride (also called chromic chloride) describes any of several chemical compounds with the formula CrCl3 · xH2O, where x can be 0, 5, and 6. The anhydrous compound with the formula CrCl3 is a violet solid. The most common form of the trichloride is the dark green hexahydrate, CrCl3 · 6 H2O. Chromium chlorides find use as catalysts and as precursors to dyes for wool.

Acetyl chloride (CH3COCl) is an acyl chloride derived from acetic acid. It belongs to the class of organic compounds called acid halides. It is a colorless, corrosive, volatile liquid. Its formula is commonly abbreviated to AcCl.

Oxalyl chloride is an organic chemical compound with the formula (COCl)2. This colorless, sharp-smelling liquid, the diacyl chloride of oxalic acid, is a useful reagent in organic synthesis.

Thionyl chloride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula SOCl2. It is a moderately volatile, colourless liquid with an unpleasant acrid odour. Thionyl chloride is primarily used as a chlorinating reagent, with approximately 45,000 tonnes per year being produced during the early 1990s, but is occasionally also used as a solvent. It is toxic, reacts with water, and is also listed under the Chemical Weapons Convention as it may be used for the production of chemical weapons.

Phosphorus pentachloride is the chemical compound with the formula PCl5. It is one of the most important phosphorus chlorides, others being PCl3 and POCl3. PCl5 finds use as a chlorinating reagent. It is a colourless, water-sensitive and moisture-sensitive solid, although commercial samples can be yellowish and contaminated with hydrogen chloride.

Palladium(II) chloride, also known as palladium dichloride and palladous chloride, are the chemical compounds with the formula PdCl2. PdCl2 is a common starting material in palladium chemistry – palladium-based catalysts are of particular value in organic synthesis. It is prepared by the reaction of chlorine with palladium metal at high temperatures.
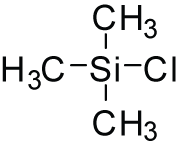
Trimethylsilyl chloride, also known as chlorotrimethylsilane is an organosilicon compound (silyl halide), with the formula (CH3)3SiCl, often abbreviated Me3SiCl or TMSCl. It is a colourless volatile liquid that is stable in the absence of water. It is widely used in organic chemistry.
Benzyl chloride, or α-chlorotoluene, is an organic compound with the formula C6H5CH2Cl. This colorless liquid is a reactive organochlorine compound that is a widely used chemical building block.
Stephen aldehyde synthesis, a named reaction in chemistry, was invented by Henry Stephen (OBE/MBE). This reaction involves the preparation of aldehydes (R-CHO) from nitriles (R-CN) using tin(II) chloride (SnCl2), hydrochloric acid (HCl) and quenching the resulting iminium salt ([R-CH=NH2]+Cl−) with water (H2O). During the synthesis, ammonium chloride is also produced.
The Schotten–Baumann reaction is a method to synthesize amides from amines and acid chlorides:
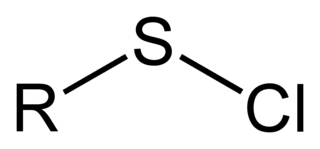
In organosulfur chemistry, a sulfenyl chloride is a functional group with the connectivity R−S−Cl, where R is alkyl or aryl. Sulfenyl chlorides are reactive compounds that behave as sources of RS+. They are used in the formation of RS−N and RS−O bonds. According to IUPAC nomenclature they are named as alkyl thiohypochlorites, i.e. esters of thiohypochlorous acid.