| Glycosyl hydrolases family 2, sugar binding domain | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
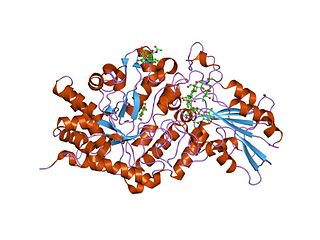
 e. coli (lacz) beta-galactosidase-trapped 2-deoxy-galactosyl enzyme intermediate | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Glyco_hydro_2_N | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF02837 | ||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0202 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR006104 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00531 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1bgl / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| CAZy | GH2 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Glycosyl hydrolases family 2 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 e. coli (lacz) beta-galactosidase-trapped 2-deoxy-galactosyl enzyme intermediate | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Glyco_hydro_2 | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00703 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR006102 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00531 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1bgl / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| CAZy | GH2 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Glycosyl hydrolases family 2, TIM barrel domain | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 human beta-glucuronidase at 2.6 a resolution | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Glyco_hydro_2_C | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF02836 | ||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0058 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR006103 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00531 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1bgl / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| CAZy | GH2 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
In molecular biology, Glycoside hydrolase family 2 is a family of glycoside hydrolases EC 3.2.1., which are a widespread group of enzymes that hydrolyse the glycosidic bond between two or more carbohydrates, or between a carbohydrate and a non-carbohydrate moiety. A classification system for glycoside hydrolases, based on sequence similarity, has led to the definition of >100 different families. [1] [2] [3] This classification is available on the CAZy web site, [4] [5] and also discussed at CAZypedia, an online encyclopedia of carbohydrate active enzymes. [6] [7]
Glycoside hydrolase family 2 [8] comprises enzymes with several known activities: beta-galactosidase (EC 3.2.1.23); beta-mannosidase (EC 3.2.1.25); beta-glucuronidase (EC 3.2.1.31). These enzymes contain a conserved glutamic acid residue which has been shown, [9] in Escherichia coli lacZ ( P00722 ), to be the general acid/base catalyst in the active site of the enzyme.
The catalytic domain of Beta-galactosidases have a TIM barrel core surrounded several other largely beta domains. [10] The sugar binding domain of these proteins has a jelly-roll fold. [10] These enzymes also include an immunoglobulin-like beta-sandwich domain. [10]