| Glycosyl hydrolases family 38 N-terminal domain | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
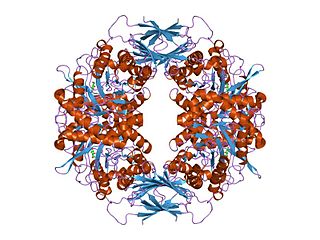
 golgi alpha-mannosidase ii | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Glyco_hydro_38 | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF01074 | ||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0158 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR000602 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1o7d / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| CAZy | GH38 | ||||||||
| Membranome | 311 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Alpha mannosidase, middle domain | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
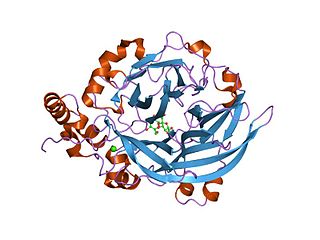
 golgi alpha-mannosidase ii | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Alpha-mann_mid | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF09261 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR015341 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1o7d / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Glycosyl hydrolases family 38 C-terminal domain | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
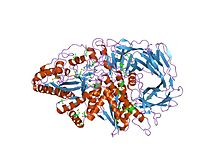
 golgi alpha-mannosidase ii | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Glyco_hydro_38C | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF07748 | ||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0103 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR011682 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1o7d / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| CAZy | GH38 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
In molecular biology, glycoside hydrolase family 38 is a family of glycoside hydrolases.
Glycoside hydrolases EC 3.2.1. are a widespread group of enzymes that hydrolyse the glycosidic bond between two or more carbohydrates, or between a carbohydrate and a non-carbohydrate moiety. A classification system for glycoside hydrolases, based on sequence similarity, has led to the definition of >100 different families. [1] [2] [3] This classification is available on the CAZy web site, [4] [5] and also discussed at CAZypedia, an online encyclopedia of carbohydrate active enzymes. [6] [7]
Glycoside hydrolase family 38 CAZY GH_38 comprises enzymes with only one known activity; alpha-mannosidase (EC 3.2.1.24) (EC 3.2.1.114).
Lysosomal alpha-mannosidase is necessary for the catabolism of N-linked carbohydrates released during glycoprotein turnover. The enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of terminal, non-reducing alpha-D-mannose residues in alpha-D-mannosides, and can cleave all known types of alpha-mannosidic linkages. Defects in the gene cause lysosomal alpha-mannosidosis (AM), a lysosomal storage disease characterised by the accumulation of unbranched oligo-saccharide chains.
A domain, which is found in the central region adopts a structure consisting of three alpha helices, in an immunoglobulin/albumin-binding domain-like fold. The domain is predominantly found in the enzyme alpha-mannosidase. [8]