| Hyaluronidase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
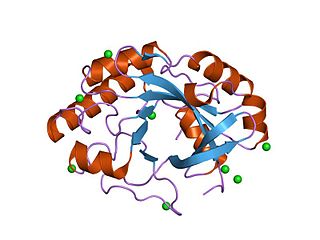
 crystal structure of bee venom hyaluronidase in complex with hyaluronic acid tetramer | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Glyco_hydro_56 | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF01630 | ||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0058 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR018155 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1fcv / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| OPM superfamily | 117 | ||||||||
| OPM protein | 1fcq | ||||||||
| CAZy | GH56 | ||||||||
| Membranome | 1078 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
In molecular biology, glycoside hydrolase family 56 is a family of glycoside hydrolases.
Glycoside hydrolases EC 3.2.1. are a widespread group of enzymes that hydrolyse the glycosidic bond between two or more carbohydrates, or between a carbohydrate and a non-carbohydrate moiety. A classification system for glycoside hydrolases, based on sequence similarity, has led to the definition of >100 different families. [1] [2] [3] This classification is available on the CAZy web site, [4] [5] and also discussed at CAZypedia, an online encyclopedia of carbohydrate active enzymes. [6] [7]
Glycoside hydrolase family 56 CAZY GH_56 includes enzymes with hyaluronidase EC 3.2.1.35 activity. The venom of Apis mellifera (Honeybee) contains several biologically-active peptides and two enzymes, one of which is a hyaluronidase. [8] The amino acid sequence of bee venom hyaluronidase contains 349 amino acids, and includes four cysteines and a number of potential glycosylation sites. [8] The sequence shows a high degree of similarity to PH-20, a membrane protein of mammalian sperm involved in sperm-egg adhesion, supporting the view that hyaluronidases play a role in fertilisation. [8]
PH-20 is required for sperm adhesion to the egg zona pellucida; it is located on both the sperm plasma membrane and acrosomal membrane. [9] The amino acid sequence of the mature protein contains 468 amino acids, and includes six potential N-linked glycosylation sites and twelve cysteines, eight of which are tightly clustered near the C-terminus. [9]