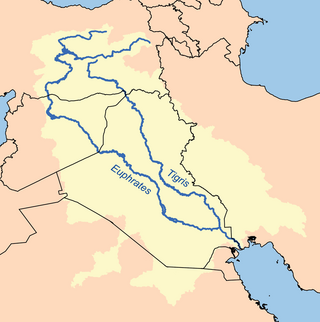
The Tigris–Euphrates river system is a large river system in Western Asia that discharges into the Persian Gulf. Its principal rivers are the Tigris and Euphrates, along with smaller tributaries.

The red garra, also known as the doctor fish or nibble fish, is a species of cyprinid that is native to a wide range of freshwater habitats in subtropical parts of Western Asia. This small fish typically is up to about 14 centimeters in total length, but locally individuals can reach as much as 24 cm (9.5 in).

Glyptothorax is a genus of catfishes order Siluriformes of the family Sisoridae. It is the most species-rich and widely distributed genus in the family with new species being discovered on a regular basis. These species are distributed in the Black Sea basin, northern Turkey, south and east to the Yangtze River drainage in China and south throughout Indo-China to Java, Indonesia. They are found in Asia Minor and southwards to Southeast Asia. The genus is very diverse in the Indian subcontinent. Southeast Asian species tend to have restricted distributions.

Garra is a genus of fish in the family Cyprinidae. These fish are one example of the "log suckers", sucker-mouthed barbs and other cyprinids commonly kept in aquaria to keep down algae. The doctor fish of Anatolia and the Middle East belongs in this genus. The majority of the more than 140 species of garras are native to Asia, but about one-fifth of the species are from Africa.

Mesogobius is one of the genera of benthophiline gobiid fishes native to the basins of the Black and Caspian Seas.
Aphanius vladykovi is a species of old world pupfish endemic to a restricted area of the central Zagros Mountains of Iran. It can also be found in the aquarium trade. Its specific name honours the zoologist Vadim D. Vladykov (1898-1986) who studied the fishes of the Caspian basin and the person who accepted the species author, Brian W. Coad, as a graduate student.
Alma Gol Lake, also called Lake Ulmagol, is a freshwater lake in Golestān Province, Iran near the Turkmenistan border.

The Asian stinging catfish or fossil cat is a species of airsac catfish found in India, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Nepal, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Myanmar, and Bhutan. It has also been introduced to the Tigris River Basin in Iran.
Schizothorax zarudnyi is a species of cyprinid freshwater fish from Iran and Afghanistan, where restricted to lakes in the Sistan Basin.
Capoeta aculeata is a cyprinid fish endemic to Iran. It is close to Capoeta capoeta and has sometimes been considered either synonymous with it or a subspecies Capoeta capoeta aculeata. However, Coad & Krupp concluded, on morphological grounds, that it deserves to be a valid species. This species has been reported from several water bodies in Iran, including Armand River, Kaaj River, Chaghakhor Laggon, Gandoman Lagoon, Gizehrud River, Na’in, Kor River, Namak Lake, and Zayandeh Rud River.

Proterorhinus semipellucidus is a species of gobiid fish, a tubenose goby originally described from the Gharasu River near Gorgan Bay of the Caspian Sea in Iran. Following the systematic decomposition of the tubenose gobies it was suggested to be a more widespread and invasive taxon distributed in the fresh waters of the Caspian Sea basin. It may be the same species as that known as Proterorhinus nasalis.

Proterorhinus is a genus of fishes, known as the tubenose gobies. These gobiid fish are native to Eurasia where they occur in the region of the Caspian and Black seas, inhabiting marine, brackish and fresh waters. The species Proterorhinus semilunaris was introduced to the St. Clair River in Michigan during the late 1990s. Until recently, the genus was considered monotypic, comprising only the tubenose goby. Following molecular and further morphological investigations it has been split into several taxa, with distinct distributions in marine vs. fresh waters and in the Black Sea vs. Caspian Sea basins.

Ponticola cyrius, the Kura goby, is a species of gobiid fish endemic to the Kura River in the southern Caucasus countries of Georgia, Turkey, Iran and Azerbaijan. It reaches a length of 13 centimetres (5.1 in) SL. It lives in the upper parts of the Kura River, Massuleh River and the Pasikhan River and in the Anzali Mordab (Iran). Downstream in Kura it is replaced by Ponticola gorlap.

Mesogobius nonultimus, or the Caspian toad goby, is one of the species of gobiid fish endemic to the brackish-waters Caspian Sea (lake). It will grow up to a length of 17.4 cm.

The duckbill pugolovka is a species of gobiid fish endemic to the southern part of the Caspian Sea. It is characterized by its special flattened and elongated head that resembles a duck's bill. It is the only known species in its genus.
Benthophiloides turcomanus is a tiny species of gobiid fish native to the Caspian Sea. It is only known from two specimens collected from the waters of Turkmenistan at a depth of 27 metres (89 ft). The specimens, no longer than 3 centimetres (1.2 in) TL, have since been lost.

Alburnoides qanati is a fish species of family Cyprinidae. It is widespread in the Pulvar River system and Kor River in Iran. Benthopelagic subtropical freshwater fish, up to 7.2 cm in length.
Glyptothorax kurdistanicus is a species of sisorid catfish. It is known by several common names, including Mesopotamian sucker catfish, Kordestan catfish and Iran cat. This grey or brown fish with black spots is best known from the Little Zab in Iran and Iraq. It is poorly studied; the full extent of its range is not known and the taxonomic relationships between members of its genus are uncertain.
Glyptothorax armeniacus, the Armenian mountain catfish, is a species of catfish that was first described by Berg, 1918. Glyptothorax armeniacus is a species in genus Glyptothorax, family Sisoridae and order Siluriformes. No subspecies are listed in Catalogue of Life. It is endemic to southern and eastern Turkey.

Glyptothorax conirostris is a species of catfish that was first described by Steindachner, 1867. Glyptothorax conirostris is a species in genus Glyptothorax, family Sisoridae and order Siluriformes. IUCN categorise the species as insufficiently studied globally. No subspecies are listed in Catalogue of Life.











