
The Gruiformes are an order containing a considerable number of living and extinct bird families, with a widespread geographical diversity. Gruiform means "crane-like".

The Varanidae are a family of lizards in the superfamily Varanoidea and order Anguimorpha. The family, a group of carnivorous and frugivorous lizards, includes the living genus Varanus and a number of extinct genera more closely related to Varanus than to the earless monitor lizard (Lanthanotus). Varanus includes the Komodo dragon, crocodile monitor, savannah monitor, the goannas of Australia and Southeast Asia, and various other species with a similarly distinctive appearance. Their closest living relatives are the earless monitor lizard and Chinese crocodile lizard. The oldest members of the family are known from the Late Cretaceous of Mongolia.

Simplicidentata is a group of mammals that includes the rodents and their closest extinct relatives. The term has historically been used as an alternative to Rodentia, contrasting the rodents with their close relatives the lagomorphs. However, Simplicidentata is now defined as including all members of Glires that share a more recent common ancestor with living rodents than with living lagomorphs. Thus, Simplicidentata is a total group that is more inclusive than Rodentia, a crown group that includes all living rodents, their last common ancestor, and all its descendants. Under this definition, the loss of the second pair of upper incisors is a synapomorphic feature of Simplicidentata. The loss of the second upper premolar (P2) has also been considered as synapomorphic for Simplicidentata, but the primitive simplicidentate Sinomylus does have a P2.

The Laotian rock rat or kha-nyou, sometimes called the "rat-squirrel", is a species of rodent found in the Khammouan region of Laos. The species was first described in a 2005 article by Paulina Jenkins and coauthors, who considered the animal to be so distinct from all living rodents, they placed it in a new family, Laonastidae. It is in the monotypic genus Laonastes.

Gundis or comb rats are a group of small, stocky rodents found in Africa. They live in rocky deserts across the northern parts of the continent. The family comprises four living genera and five species, as well as numerous extinct genera and species. They are in the superfamily Ctenodactyloidea. Local people in northern Africa have always known about gundis, however they first came to the notice of western naturalists in Tripoli in 1774, and were given the name gundi mice. While they are not regarded as pests, some people hunt gundis for food.

Eosimias is a genus of early primates, first discovered and identified in 1999 from fossils collected in the Shanghuang fissure-fillings of Liyang, the southern city of Jiangsu Province, China. It is a part of the family Eosimiidae, and includes three known species: Eosimias sinensis, Eosimias centennicus, and Eosimias dawsonae. It provides us with a glimpse of a primate skeleton similar to that of the common ancestor of the Haplorhini. The name Eosimias is designed to mean "dawn monkey", from Greek eos "dawn" and Latin simius "monkey".

Hystricomorpha is a term referring to families and orders of rodents which has had many definitions throughout its history. In the broadest sense, it refers to any rodent with a hystricomorphous zygomasseteric system. This includes the Hystricognathi, Ctenodactylidae, Anomaluridae, and Pedetidae. Molecular and morphological results suggest the inclusion of the Anomaluridae and Pedetidae in Hystricomorpha may be suspect. Based on Carleton & Musser 2005, these two families are discussed here as representing a distinct suborder Anomaluromorpha.

Viverravidae is an extinct monophyletic family of mammals from extinct superfamily Viverravoidea within the clade Carnivoramorpha, that lived from the early Palaeocene to the late Eocene in North America, Europe and Asia. They were once thought to be the earliest carnivorans and ancestral to extant ones, but now are placed outside the order Carnivora based on cranial morphology as relatives to extant carnivorans.

Miacidae is a former paraphyletic family of extinct primitive placental mammals that lived in North America, Europe and Asia during the Paleocene and Eocene epochs, about 65–33.9 million years ago. These mammals were basal to order Carnivora, the crown-group within the Carnivoraformes.

Diatomyidae is a family of hystricomorph rodents. It is represented by a single living species, Laonastes aenigmamus, native to Laos in Southeast Asia. Fossil species are known from the Oligocene and Miocene of Asia and eastern Europe.

Mary R. Dawson was a vertebrate paleontologist and curator emeritus at the Carnegie Museum of Natural History in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania.

Carnivoramorpha is a clade of placental mammals of clade Pan-Carnivora from mirorder Ferae, that includes the modern order Carnivora and its extinct stem-relatives.
Alagomyidae is a family of rodents known from the late Paleocene and early Eocene of Asia and North America. Alagomyids have been identified as the most basal rodents, lying outside the common ancestry of living forms. Because of their phylogenetic position and their conservative dental morphology, alagomyids have played a key role in investigations of the origins and relationships of rodents.
The Irdin Manha Formation is a geological formation from the Eocene located in Inner Mongolia, China, a few kilometres south of the Mongolian border.

Ctenodactylomorphi is an infraorder of the rodent suborder Hystricomorpha that includes two living families, the Ctenodactylidae (gundis) and the Diatomyidae.
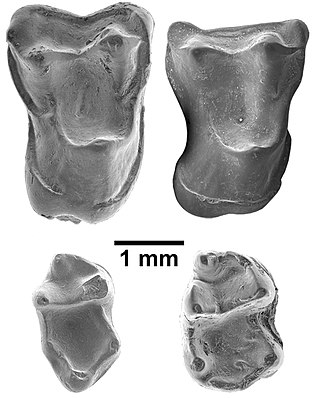
Afrasia djijidae is a fossil primate that lived in Myanmar approximately 37 million years ago, during the late middle Eocene. The only species in the genus Afrasia, it was a small primate, estimated to weigh around 100 grams (3.5 oz). Despite the significant geographic distance between them, Afrasia is thought to be closely related to Afrotarsius, an enigmatic fossil found in Libya and Egypt that dates to 38–39 million years ago. If this relationship is correct, it suggests that early simians dispersed from Asia to Africa during the middle Eocene and would add further support to the hypothesis that the first simians evolved in Asia, not Africa. Neither Afrasia nor Afrotarsius, which together form the family Afrotarsiidae, is considered ancestral to living simians, but they are part of a side branch or stem group known as eosimiiforms. Because they did not give rise to the stem simians that are known from the same deposits in Africa, early Asian simians are thought to have dispersed from Asia to Africa more than once prior to the late middle Eocene. Such dispersals from Asia to Africa also were seen around the same time in other mammalian groups, including hystricognathous rodents and anthracotheres.

Coryphodontidae is an extinct family of pantodont mammals known from the Late Paleocene to the Middle Eocene of Eurasia and North America.
The Margaret Formation is a geologic formation of the Eureka Sound Group in the Sverdrup Basin in Northwest Territories and Nunavut, Canada. The unit belonging to the Eureka Sound Group which crops out at Ellesmere Island preserves fossils dating back to the Early Eocene period, or Wasatchian in the NALMA classification.

Deperetellidae is an extinct family of herbivorous odd-toed ungulates containing the genera Bahinolophus, Deperetella, Irenolophus, and Teleolophus. Their closest living relatives are tapirs. Deperetellids are known from the Middle Eocene deposits of China, Mongolia, Kyrgyzstan and Myanmar.

Comptonia columbiana is an extinct species of sweet fern in the flowering plant family Myricaceae. The species is known from fossil leaves found in the early Eocene deposits of central to southern British Columbia, Canada, plus northern Washington state, United States, and, tentatively, the late Eocene of Southern Idaho and Earliest Oligocene of Oregon, United States.






























