| Groove-Toothed Bat | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Chiroptera |
| Family: | Vespertilionidae |
| Genus: | Phoniscus |
| Species: | P. atrox |
| Binomial name | |
| Phoniscus atrox Miller, 1905 | |
 | |
| Synonyms | |
Kerivoula atrox (Miller, 1905) | |
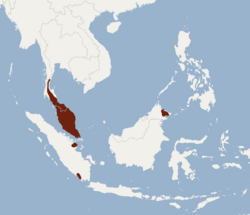
The groove-toothed bat (Phoniscus atrox) is a species of bat in the family Vespertilionidae, the vesper bats. It is native to Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand. It is an uncommon species that depends on forests for survival, and it is threatened by deforestation. [1]
