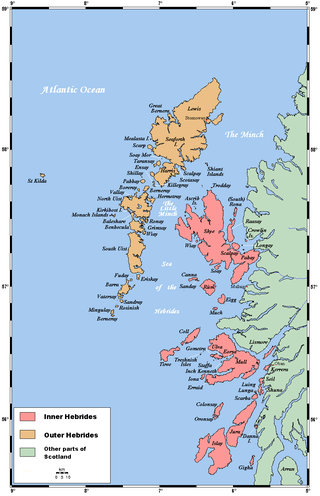
The Hebrides are an archipelago off the west coast of the Scottish mainland. The islands fall into two main groups, based on their proximity to the mainland: the Inner and Outer Hebrides.

The Mesolithic or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymously, especially for outside northern Europe, and for the corresponding period in the Levant and Caucasus. The Mesolithic has different time spans in different parts of Eurasia. It refers to the final period of hunter-gatherer cultures in Europe and the Middle East, between the end of the Last Glacial Maximum and the Neolithic Revolution. In Europe it spans roughly 15,000 to 5,000 BP; in the Middle East roughly 20,000 to 10,000 BP. The term is less used of areas farther east, and not at all beyond Eurasia and North Africa.

The Inner Hebrides is an archipelago off the west coast of mainland Scotland, to the south east of the Outer Hebrides. Together these two island chains form the Hebrides, which experience a mild oceanic climate. The Inner Hebrides comprise 35 inhabited islands as well as 44 uninhabited islands with an area greater than 30 hectares. Skye, Mull, and Islay are the three largest, and also have the highest populations. The main commercial activities are tourism, crofting, fishing and whisky distilling. In modern times the Inner Hebrides have formed part of two separate local government jurisdictions, one to the north and the other to the south. Together, the islands have an area of about 4,130 km2 (1,594 sq mi), and had a population of 18,948 in 2011. The population density is therefore about 4.6 inhabitants per square kilometre.

Oronsay, also sometimes spelt and pronounced Oransay by the local community, is a small tidal island south of Colonsay in the Scottish Inner Hebrides with an area of 543 hectares.

Trotternish is the northernmost peninsula of the Isle of Skye in Scotland, spanning in length from Portree to Rubha Hunish. The Trotternish escarpment runs almost the full length of the peninsula, some 30 kilometres, and contains landmarks such as the Old Man of Storr and the Quiraing. The summit of The Storr, overlooking the Old Man, is the highest point of the peninsula at 719 m above sea level. The north-eastern part of the peninsula around Quiraing is designated as a National Scenic Area and the entire escarpment is a Special Area of Conservation.

Franchthi Cave or Frankhthi Cave is an archaeological site overlooking Kiladha Bay, in the Argolic Gulf, opposite the village of Kiladha in southeastern Argolis, Greece.

The Rinns of Islay is an area on the west of the island of Islay in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland.

The Caldicot and Wentloog Levels are two areas of low-lying estuarine alluvial wetland and intertidal mudflats adjoining the north bank of the Severn Estuary, either side of the River Usk estuary near Newport in south east Wales. They are also known collectively as the Monmouthshire Levels or Gwent Levels, and the name Wentloog is sometimes spelled Wentlooge in official publications.

Doggerland was a large area of land in Northern Europe, now submerged beneath the southern North Sea. This region was repeatedly exposed at various times during the Pleistocene epoch due to the lowering of sea levels during glacial periods. However, the term "Doggerland" is generally specifically used for this region during the Late Pleistocene and Early Holocene. During the early Holocene following the glacial retreat at the end of the Last Glacial Period, the exposed land area of Doggerland stretched across the region between what is now the east coast of Great Britain, the Netherlands, north-west Germany, and the Danish peninsula of Jutland. Between 10,000 and 7,000 years ago, Doggerland was inundated by rising sea levels, disintegrating initially into a series of low-lying islands before submerging completely. The impact of the tsunami generated by the Storegga underwater landslide c. 8,200 years ago on Doggerland is controversial. The flooded land is known as the Dogger Littoral.
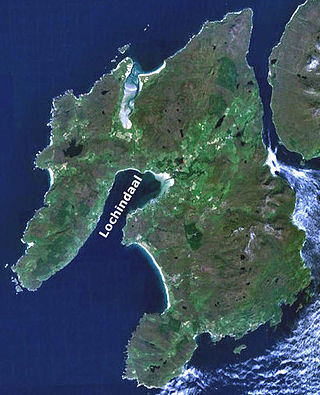
Loch Indaal is a sea loch on Islay, the southernmost island of the Hebrides, off the west coast of Scotland. Together with Loch Gruinart to the north, it was formed by the Loch Gruinart Fault, which branches off the Great Glen Fault.

Texa is a small island 700 metres directly south of Islay, in the Inner Hebrides, Scotland. It reaches a height of 48 metres at its highest point, Ceann Garbh. It is part of the parish of Kildalton on Islay. The distilleries of Laphroaig and Lagavulin are nearby on the Islay coast, as well as Port Ellen. It is currently uninhabited, but is home to wild goats, as well as otters.
Steven Mithen, is an archaeologist. He is noted for his work on the evolution of language, music and intelligence, prehistoric hunter-gatherers, and the origins of farming. He is professor of early prehistory at the University of Reading.

Nave Island lies to the north of Islay in the Inner Hebrides near the mouth of Loch Gruinart. It is uninhabited.

The Mount Sandel Mesolithic site is in Coleraine, County Londonderry, Northern Ireland, just to the east of the Iron Age Mount Sandel Fort. It is one of the oldest archaeological sites in Ireland with carbon dating indicating an age of 9,000 years old (7,000BC). Gwendoline Cave, County Clare is the only site in Ireland with evidence of human occupation that pre-dates this location. Mount Sandel Mesolithic site is a Scheduled Historic Monument in the townland of Mount Sandel, in Causeway Coast and Glens Council area, at Grid Ref: C8533 3076. It was excavated by Peter Woodman in the 1970s.

This timeline of prehistoric Scotland is a chronologically ordered list of important archaeological sites in Scotland and of major events affecting Scotland's human inhabitants and culture during the prehistoric period. The period of prehistory prior to occupation by the genus Homo is part of the geology of Scotland. Prehistory in Scotland ends with the arrival of the Romans in southern Scotland in the 1st century AD and the beginning of written records. The archaeological sites and events listed are the earliest examples or among the most notable of their type.

Islay is the southernmost island of the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. Known as "The Queen of the Hebrides", it lies in Argyll and Bute just south west of Jura and around 40 kilometres north of the Northern Irish coast. The island's capital is Bowmore where the distinctive round Kilarrow Parish Church and a distillery are located. Port Ellen is the main port.

Ardnave Point is a coastal promontory on the northwest of Islay, a Scottish island. This landform has a rocky northern shore and extensive dunes on the upland areas of the point.

The Neolithic period in the British Isles lasted from c. 4100 to c. 2,500 BC. Constituting the final stage of the Stone Age in the region, it was preceded by the Mesolithic and followed by the Bronze Age.
Trialetian is the name for an Upper Paleolithic-Epipaleolithic stone tool industry from the South Caucasus. It is tentatively dated to the period between 16,000 / 13,000 BP and 8,000 BP.