A quality management system (QMS) is a collection of business processes focused on consistently meeting customer requirements and enhancing their satisfaction. It is aligned with an organization's purpose and strategic direction. It is expressed as the organizational goals and aspirations, policies, processes, documented information, and resources needed to implement and maintain it. Early quality management systems emphasized predictable outcomes of an industrial product production line, using simple statistics and random sampling. By the 20th century, labor inputs were typically the most costly inputs in most industrialized societies, so focus shifted to team cooperation and dynamics, especially the early signaling of problems via a continual improvement cycle. In the 21st century, QMS has tended to converge with sustainability and transparency initiatives, as both investor and customer satisfaction and perceived quality are increasingly tied to these factors. Of QMS regimes, the ISO 9000 family of standards is probably the most widely implemented worldwide – the ISO 19011 audit regime applies to both and deals with quality and sustainability and their integration.
Good agricultural practice (GAP) is a certification system for agriculture, specifying procedures that must be implemented to create food for consumers or further processing that is safe and wholesome, using sustainable methods. While there are numerous competing definitions of what methods constitute good agricultural practice, there are several broadly accepted schemes that producers can adhere too.

Current good manufacturing practices (cGMP) are those conforming to the guidelines recommended by relevant agencies. Those agencies control the authorization and licensing of the manufacture and sale of food and beverages, cosmetics, pharmaceutical products, dietary supplements, and medical devices. These guidelines provide minimum requirements that a manufacturer must meet to assure that their products are consistently high in quality, from batch to batch, for their intended use. The rules that govern each industry may differ significantly; however, the main purpose of GMP is always to prevent harm from occurring to the end user. Additional tenets include ensuring the end product is free from contamination, that it is consistent in its manufacture, that its manufacture has been well documented, that personnel are well trained, and that the product has been checked for quality more than just at the end phase. GMP is typically ensured through the effective use of a quality management system (QMS).
Within quality management systems (QMS) and information technology (IT) systems, change control is a process—either formal or informal—used to ensure that changes to a product or system are introduced in a controlled and coordinated manner. It reduces the possibility that unnecessary changes will be introduced to a system without forethought, introducing faults into the system or undoing changes made by other users of software. The goals of a change control procedure usually include minimal disruption to services, reduction in back-out activities, and cost-effective utilization of resources involved in implementing change. According to the Project Management Institute, change control is a "process whereby modifications to documents, deliverables, or baselines associated with the project are identified, documented, approved, or rejected."
Good clinical practice (GCP) is an international quality standard, which governments can then transpose into regulations for clinical trials involving human subjects. GCP follows the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH), and enforces tight guidelines on ethical aspects of clinical research.
A source document is a document in which data collected for a clinical trial is first recorded. This data is usually later entered in the case report form. The International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH-GCP) guidelines define source documents as "original documents, data, and records." Source documents contain source data, which is defined as "all information in original records and certified copies of original records of clinical findings, observations, or other activities in a clinical trial necessary for the reconstruction and evaluation of the trial."
In the experimental (non-clinical) research arena, good laboratory practice or GLP is a quality system of management controls for research laboratories and organizations to ensure the uniformity, consistency, reliability, reproducibility, quality, and integrity of products in development for human or animal health through non-clinical safety tests; from physio-chemical properties through acute to chronic toxicity tests.
A standard operating procedure (SOP) is a set of step-by-step instructions compiled by an organization to help workers carry out routine operations. SOPs aim to achieve efficiency, quality output, and uniformity of performance, while reducing miscommunication and failure to comply with industry regulations.
The process of establishing documentary evidence demonstrating that a procedure, process, or activity carried out in testing and then production maintains the desired level of compliance at all stages. In the pharmaceutical industry, it is very important that in addition to final testing and compliance of products, it is also assured that the process will consistently produce the expected results. The desired results are established in terms of specifications for outcome of the process. Qualification of systems and equipment is therefore a part of the process of validation. Validation is a requirement of food, drug and pharmaceutical regulating agencies such as the US FDA and their good manufacturing practices guidelines. Since a wide variety of procedures, processes, and activities need to be validated, the field of validation is divided into a number of subsections including the following:
"Good engineering practice" or "GEP" is engineering and technical activities that ensure that a company manufactures products of the required quality as expected. Good engineering practices are to ensure that the development and/or manufacturing effort consistently generates deliverables that support the requirements for qualification or validation. Good engineering practices are applied to all industries that require engineering.
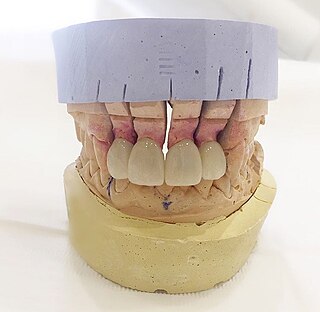
Dental laboratories manufacture or customize a variety of products to assist in the provision of oral health care by a licensed dentist. These products include crowns, bridges, dentures and other dental products. Dental lab technicians follow a prescription from a licensed dentist when manufacturing these items, which include prosthetic devices and therapeutic devices. The FDA regulates these products as medical devices and they are therefore subject to FDA's good manufacturing practice ("GMP") and quality system ("QS") requirements. In most cases, however, they are exempt from manufacturer registration requirements. Some of the most common restorations manufactured include crowns, bridges, dentures, and dental implants. Dental implants is one of the most advanced dental technologies in the field of dentistry.
Good automated manufacturing practice (GAMP) is both a technical subcommittee of the International Society for Pharmaceutical Engineering (ISPE) and a set of guidelines for manufacturers and users of automated systems in the pharmaceutical industry. More specifically, the ISPE's guide The Good Automated Manufacturing Practice (GAMP) Guide for Validation of Automated Systems in Pharmaceutical Manufacture describes a set of principles and procedures that help ensure that pharmaceutical products have the required quality. One of the core principles of GAMP is that quality cannot be tested into a batch of product but must be built into each stage of the manufacturing process. As a result, GAMP covers all aspects of production; from the raw materials, facility and equipment to the training and hygiene of staff. Standard operating procedures (SOPs) are essential for processes that can affect the quality of the finished product.
Verification and validation are independent procedures that are used together for checking that a product, service, or system meets requirements and specifications and that it fulfills its intended purpose. These are critical components of a quality management system such as ISO 9000. The words "verification" and "validation" are sometimes preceded with "independent", indicating that the verification and validation is to be performed by a disinterested third party. "Integration verification and validation" can be abbreviated as "IV&V".
Good clinical data management practice (GCDMP) is the current industry standards for clinical data management that consist of best business practice and acceptable regulatory standards. In all phases of clinical trials, clinical and laboratory information must be collected and converted to digital form for analysis and reporting purposes. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration and International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use have provided specific regulations and guidelines surrounding this component of the drug and device development process. The effective, efficient and regulatory-compliant management of clinical trial data is an essential component of drug and device development.
Good documentation practice is a term in the pharmaceutical and medical device industries to describe standards by which documents are created and maintained. While some GDP / GDocP standards are codified by various competent authorities, others are not but are considered cGMP. Some competent authorities release or adopt guidelines, and they may include non-codified GDP / GDocP expectations. While not law, authorities will inspect against these guidelines and cGMP expectations in addition to the legal requirements and make comments or observations if departures are seen. In the past years, the application of GDocP is also expanding to cosmetic industry, excipient and ingredient manufacturers.
Good clinical laboratory practice (GCLP) is a GxP guideline for laboratory samples from clinical studies.

The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PhMDA) is an Independent Administrative Institution responsible for ensuring the safety, efficacy and quality of pharmaceuticals and medical devices in Japan. It is similar in function to the Food and Drug Administration in the United States, the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency in the United Kingdom, the Spanish Agency of Medicines and Medical Devices in Spain or the Food and Drug Administration in the Philippines.
Guidances for statistics in regulatory affairs refers to specific documents or guidelines that provide instructions, recommendations, and standards pertaining to the application of statistical methodologies and practices within the regulatory framework of industries such as pharmaceuticals and medical devices. These guidances serve as a reference for statisticians, researchers, and professionals involved in designing, conducting, analyzing, and reporting studies and trials in compliance with regulatory requirements. These documents embody the prevailing perspectives of regulatory agencies on specific subjects. It is worth noting that in the United States, the term "Guidances" is used, while in Europe, the term "Guidelines" is employed.
The distribution of medications has special drug safety and security considerations. Some drugs require cold chain management in their distribution.
A certificate of analysis (COA) is a formal laboratory-prepared document that details the results of one or more laboratory analyses, signed—manually or electronically—by an authorized representative of the entity conducting the analyses. This document gives assurances to the recipient that the analyzed item is what it is designated to be, or has the features advertised by the producer. The design and content of a COA may be based upon a set of requirements identified by the lab, by regulatory-driven requirements, and/or by standards developed by standard developing organizations. The COA is used in a wide variety of industries, including but not limited to the agriculture, chemical, clinical research, food and beverage, and pharmaceutical industries.



