
Dimetrodon is an extinct genus of non-mammalian synapsid belonging to the family Sphenacodontidae that lived during the Cisuralian age of the Early Permian period, around 295–272 million years ago. With most species measuring 1.7–4.6 m (5.6–15.1 ft) long and weighing 28–250 kg (62–551 lb), the most prominent feature of Dimetrodon is the large neural spine sail on its back formed by elongated spines extending from the vertebrae. It was an obligate quadruped and had a tall, curved skull with large teeth of different sizes set along the jaws. Most fossils have been found in the Southwestern United States, the majority of these coming from a geological deposit called the Red Beds of Texas and Oklahoma. More recently, its fossils have also been found in Germany and over a dozen species have been named since the genus was first erected in 1878.

Lepospondyli is a diverse taxon of early tetrapods. With the exception of one late-surviving lepospondyl from the Late Permian of Morocco, lepospondyls lived from the Early Carboniferous (Mississippian) to the Early Permian and were geographically restricted to what is now Europe and North America. Five major groups of lepospondyls are known: Adelospondyli; Aïstopoda; Lysorophia; Microsauria; and Nectridea. Lepospondyls have a diverse range of body forms and include species with newt-like, eel- or snake-like, and lizard-like forms. Various species were aquatic, semiaquatic, or terrestrial. None were large, and they are assumed to have lived in specialized ecological niches not taken by the more numerous temnospondyl amphibians that coexisted with them in the Paleozoic. Lepospondyli was named in 1888 by Karl Alfred von Zittel, who coined the name to include some tetrapods from the Paleozoic that shared some specific characteristics in the notochord and teeth. Lepospondyls have sometimes been considered to be either related or ancestral to modern amphibians or to Amniota. It has been suggested that the grouping is polyphyletic, with aïstopods being primitive stem-tetrapods, while recumbirostran microsaurs are primitive reptiles.

Diadectidae is an extinct family of early tetrapods that lived in what is now North America and Europe during the Late Carboniferous and Early Permian, and in Asia during the Late Permian. They were the first herbivorous tetrapods, and also the first fully terrestrial animals to attain large sizes. Footprints indicate that diadectids walked with an erect posture. They were the first to exploit plant material in terrestrial food chains, making their appearance an important stage in both vertebrate evolution and the development of terrestrial ecosystems.

Microsauria is an extinct, possibly polyphyletic order of amphibians from the late Carboniferous and early Permian periods. It is the most diverse and species-rich group of lepospondyls. Recently, Microsauria has been considered paraphyletic, as several other non-microsaur lepospondyl groups such as Lysorophia seem to be nested in it. Microsauria is now commonly used as a collective term for the grade of lepospondyls that were originally classified as members of Microsauria.
Wann Langston Jr. was an American paleontologist and professor at the University of Texas at Austin.

Carrolla is an extinct genus of brachystelechid 'microsaur' that lived in the Lower Permian in North America. It was named in 1986 by American paleontologists Wann Langston and Everett Olson. The type species, Carrolla craddocki, is the only known species.

Euryodus is an extinct genus of microsaur within the family Gymnarthridae. Euryodus is a Lepospondyl from the clade Microsauria that lived during the Lower Permian. The name comes from Greek, meaning ‘broad-tooth’. It has been found in the southern half of North America, from its original discovery in Texas up to Utah.
Elfridia is a poorly known extinct genus of microsaur within the family Gymnarthridae.

Leiocephalikon is an extinct genus of microsaur within the family Gymnarthridae. The type species is Amblyodon problematicum named by John William Dawson in 1882. Its fossil was found in the Joggins Formation which hailed from Carboniferous period. Although sometimes regarded as primitive gymnarthrids, Leiocephalikon classification is still debated as its fossil is scarce.
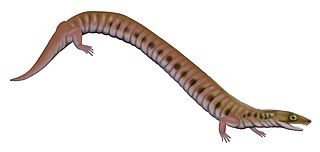
Rhynchonkos is an extinct genus of rhynchonkid microsaur. Originally known as Goniorhynchus, it was renamed in 1981 because the name had already been given to another genus; the family, likewise, was originally named Goniorhynchidae but renamed in 1988. The type and only known species is R. stovalli, found from the Early Permian Fairmont Shale in Cleveland County, Oklahoma. Rhynchonkos shares many similarities with Eocaecilia, an early caecilian from the Early Jurassic of Arizona. Similarities between Rhynchonkos and Eocaecilia have been taken as evidence that caecilians are descendants of microsaurs. However, such a relationship is no longer widely accepted.

Quasicaecilia is an extinct genus of microsaur. It is known from the Early Permian of Texas in the United States. A single specimen is known, collected from the Texas Permian redbeds by Charles Hazelius Sternberg in 1917. It was originally identified as a specimen of the gymnarthrid microsaur Cardiocephalus. The skull is small, less than 2 centimetres (0.79 in) in length, and the otic capsule is very large in comparison to the rest of the skull. The skull of Quasicaecilia superficially resembles those of extant but unrelated caecilians, hence the genus name. Quasicaecilia was assigned to the new family Brachystelechidae in 1991 along with the genera Batropetes and Carrolla.
Pariotichus is an extinct genus of gymnarthrid microsaurs from the early Permian of Texas.
Tersomius is an extinct genus of dissorophoid temnospondyl within the family Micropholidae. It is known from the early Permian of North America.

Tuditanomorpha is a suborder of microsaur lepospondyls. Tuditanomorphs lived from the Late Carboniferous to the Early Permian and are known from North America and Europe. Tuditanomorphs have a similar pattern of bones in the skull roof. Tuditanomorphs display considerable variability, especially in body size, proportions, dentition, and presacral vertebral count. Currently there are four families of tuditanomorphs, with two being monotypic. Tuditanids first appear in the Lower Pennsylvanian. Goniorhynchidae, Hapsidopareiidae, and Trihecatontidae appear in the Late Pennsylvanian and Early Permian.

Tuditanidae is an extinct family of microsaurian tetrapods. Fossils have been found from Nova Scotia, Ohio, and the Czech Republic and are Late Carboniferous in age.

Recumbirostra is a clade of tetrapods which lived during the Carboniferous and Permian periods. They are thought to have had a fossorial (burrowing) lifestyle and the group includes both short-bodied and long-bodied snake-like forms. At least one species, the long-bodied molgophid Nagini mazonense, lost its forelimbs entirely. Recumbirostra includes the families Pantylidae, Gymnarthridae, Ostodolepidae, Rhynchonkidae and Brachystelechidae, with additional families such as Microbrachidae and Molgophidae being included by some authors. Brachystelechidae and Molgophidae have also been grouped together in the suggested clade Chthonosauria.
Huskerpeton is an extinct genus of recumbirostran from the Early Permian period. They belong to the order Microsauria, which was established in 1863 by Dawson, and was quickly expanded to include many different small taxa. They lived in what is now Nebraska and Kansas. The holotype of Huskerpeton was uncovered at the Eskridge formation in Nebraska, which is part of how it got its name.
The Waggoner Ranch Formation is a geologic formation in northern Texas. It preserves fossils dating back to the Artinskian to Kungurian stages of the Permian period.
The Arroyo Formation, sometimes termed the Lower Clear Fork Formation, is a geologic formation in Texas. It preserves fossils dating back to the Kungurian stage of the Permian period. It is the lower-most portion of the Clear Fork Group, part of a series of fossiliferous Permian strata in the south-central United States known as the red beds.

Richards Spur is a Permian fossil locality located at the Dolese Brothers Limestone Quarry north of Lawton, Oklahoma. The locality preserves clay and mudstone fissure fills of a karst system eroded out of Ordovician limestone and dolomite, with the infilling dating to the Artinskian stage of the early Permian (Cisuralian), around 289 to 286 million years ago. Fossils of terrestrial animals are abundant and well-preserved, representing one of the most diverse Paleozoic tetrapod communities known. A common historical name for the site is Fort Sill, in reference to the nearby military base. Fossils were first reported at the quarry by workers in 1932, spurring a wave of collecting by local and international geologists. Early taxa of interest included the abundant reptile Captorhinus and microsaurs such as Cardiocephalus and Euryodus. Later notable discoveries include Doleserpeton, the most diverse assortment of parareptiles in the Early Permian, and the rare early diapsid Orovenator.














