Related Research Articles

Microsauria is an extinct, possibly polyphyletic order of tetrapods from the late Carboniferous and early Permian periods. It is the most diverse and species-rich group of lepospondyls. Recently, Microsauria has been considered paraphyletic, as several other non-microsaur lepospondyl groups such as Lysorophia seem to be nested in it. Microsauria is now commonly used as a collective term for the grade of lepospondyls that were originally classified as members of Microsauria.

Eocaecilia is an extinct genus of gymnophionan amphibian from the early Jurassic Kayenta Formation of Arizona, United States. One species is described, Eocaecilia micropodia.

Labidosaurikos is a genus of extinct captorhinid anapsid reptile that lived around 279 to 272 million years ago during Kungurian age of the lower Permian. The American Paleontologist John Willis Stovall first described Labidosaurikos in 1950, naming it "Labidosaurus like" for the striking similarity of the holotype skull of his specimen to the cranial anatomy of another captorhinid Labidosaurus hamatus. Labidosaurus or generally called “lipped lizard” is another genus of the family Captorhinidae whose name is derived from the Greek “forceps lizard” based on τσιμπίδα and σαυρος ("lizard")

Colobomycter is an extinct genus of lanthanosuchoid parareptile known from the Early Permian of Oklahoma.
Carrolla is an extinct genus of brachystelechid 'microsaur' that lived in the Lower Permian in North America. It was named in 1986 by American paleontologists Wann Langston and Everett Olson. The type species, Carrolla craddocki, is the only known species.
Doleserpeton is an extinct, monospecific genus of dissorophoidean temnospondyl within the family Amphibamidae that lived during the Upper Permian, 285 million years ago. Doleserpeton is represented by a single species, Doleserpeton annectens, which was first described by John R. Bolt in 1969. Fossil evidence of Doleserpeton was recovered from the Dolese Brothers Limestone Quarry in Fort Sill, Oklahoma. The genus name Doleserpeton is derived from the initial discovery site in Dolese quarry of Oklahoma and the Greek root "serp-", meaning "low or close to the ground". This transitional fossil displays primitive traits of amphibians that allowed for successful adaptation from aquatic to terrestrial environments. In many phylogenies, lissamphibians appear as the sister group of Doleserpeton.
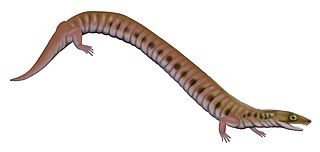
Rhynchonkos is an extinct genus of microsaur. It is the only known member of the family Rhynchonkidae. Originally known as Goniorhynchus, it was renamed in 1981 because the name had already been given to another genus; the family, likewise, was originally named Goniorhynchidae but renamed in 1988. The type and only known species is R. stovalli, found from the Early Permian Fairmont Shale in Cleveland County, Oklahoma. Rhynchonkos shares many similarities with Eocaecilia, an early caecilian from the Early Jurassic of Arizona. Similarities between Rhynchonkos and Eocaecilia have been taken as evidence that caecilians are descendants of microsaurs. However, such a relationship is no longer widely accepted.
Pariotichus is an extinct genus of gymnarthrid microsaurs from the early Permian of Texas.
Stegotretus is an extinct genus of lepospondyl microsaur referred to the Pantylidae. It is known from the Carboniferous–Permian boundary Cutler Formation exposures of New Mexico.

Delorhynchus is an extinct genus of lanthanosuchoid parareptile known from the late Early Permian Garber Formation of Comanche County, Oklahoma, south-central United States. It contains the type species D. priscus as well as a better preserved second species D. cifellii.
Pasawioops is an extinct genus of early Permian dissorophoid temnospondyl within the clade Amphibamiformes.

Ostodolepidae, also spelled Ostodolepididae, is an extinct family of Early Permian microsaurs. They are unique among microsaurs in that they were large, reaching lengths of up to 2 feet (61 cm), terrestrial, and presumably fossorial. Ostodolepid remains have been found from Early Permian beds in Texas, Oklahoma, and Germany.

Rubeostratilia is an extinct genus of amphibamiform temnospondyl from the early Permian of Texas. It is known from a single skull. This genus was named by Hélène Bourget and Jason S. Anderson in 2011, and the type species is Rubeostratilia texensis. The genus name comes from the Latin translation of 'redbeds' in reference to the Texas redbeds that produced both the holotype and many other early Permian fossils. The species name is for the state of Texas. The holotype and only known specimen was collected in 1941 from the Nocona Formation exposures in Clay County by a Works Projects Administration project that was transferred to the Field Museum of Natural History through an interinstitutional exchange with the Texas Memorial Museum.
Plemmyradytes is an extinct genus of dissorophoid temnospondyl from the early Permian. It is an amphibamiform from the Eskridge Formation exposures of Nebraska. The type species is Plemmyradytes shintoni. The genus name derives from the Greek plemmyris and dytes ('diver'), while the species name honors John Shinton, a fossil preparator at the Denver Museum of Natural History where all known specimens of this taxon are reposited following collection in the late 20th century.
Tambaroter is an extinct genus of ostodolepid microsaur from the Early Permian of Germany. The type species T. carrolli was named in 2011. Tambaroter is known from a single skull found in the Tambach Formation, which is the lowermost unit of the Upper Rotliegend. It is the only vertebrate that has been found outside the Bromacker Quarry, the most productive locality of the formation. It is also the first ostodolepid known from outside North America.

Recumbirostra is a clade of lepospondyl amphibians from the Carboniferous and Permian that includes the families Pantylidae, Gymnarthridae, Ostodolepidae, Goniorhynchidae, Brachystelechidae, and Microbrachidae. Recumbirostra was erected as a clade in 2007. It includes many lepospondyls traditionally grouped in "Microsauria", which has since been shown to be a paraphyletic grouping. Not all phylogenetic analyses recognize Recumbirostra as a valid grouping. An alternative clade called Tuditanomorpha is occasionally supported and includes many of the same taxa. Below is a cladogram showing the phylogenetic relationships of recumbirostrans from Glienke (2012):
Huskerpeton is an extinct genus of recumbirostran microsaur amphibian from the Early Permian Eskridge Formation of Nebraska, United States. It contains a single species, Huskerpeton englehorni. The genus was named for the University of Nebraska Cornhuskers.
Proxilodon is an extinct genus of recumbirostran microsaur from the Early Permian Speiser Formation of Kansas, United States. It contains a single species, Proxilodon bonneri,.

Abyssomedon is an extinct genus of a nyctiphruretid parareptile known from Early Permian fissure fills at Richards Spur in Comanche County, Oklahoma, south-central United States. It contains a single species, Abyssomedon williamsi, which represents oldest known nyctiphrureptid species and the first to be discovered in North America.

Richards Spur is a Permian fossil locality located at the Dolese Brothers Limestone Quarry north of Lawton, Oklahoma. The locality preserves clay and mudstone fissure fills of a karst system eroded out of Ordovician limestone and dolostone. Fossils of terrestrial animals are abundant and well-preserved, representing one of the most diverse Paleozoic tetrapod communities known. A common historical name for the site is Fort Sill, in reference to the nearby military base. Fossils were first reported at the quarry by workers in 1932, spurring a wave of collecting by local and international geologists. Early taxa of interest included the abundant reptile Captorhinus and microsaurs such as Cardiocephalus and Euryodus. Later notable discoveries include Doleserpeton, the most diverse assortment of parareptiles in the Early Permian, and the rare early diapsid Orovenator.
References
- 1 2 Anderson, J.S.; Scott, D.; Reisz, R.R. (2009). "Nannaroter mckinziei, a new ostodolepid 'microsaur' (Tetrapoda, Lepospondyli, Recumbirostra) from the Early Permian of Richards Spur (Ft. Sill), Oklahoma". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 29 (2): 379–388. doi:10.1671/039.029.0222.
- ↑ Huttenlocker, Adam K.; Pardo, Jason D.; Small, Bryan J.; Anderson, Jason S. (2013). "Cranial morphology of recumbirostrans (Lepospondyli) from the Permian of Kansas and Nebraska, and early morphological evolution inferred by micro-computed tomography". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 33 (3): 540–552. doi:10.1080/02724634.2013.728998. ISSN 0272-4634.



