
Marine angelfish are perciform fish of the family Pomacanthidae. They are found on shallow reefs in the tropical Atlantic, Indian, and mostly western Pacific Oceans. The family contains seven genera and about 86 species. They should not be confused with the freshwater angelfish, tropical cichlids of the Amazon Basin.
The wolf herrings are a family (Chirocentridae) of two marine species of ray-finned fish related to the herrings.

Acanthuridae are a family of ray-finned fish which includes surgeonfishes, tangs, and unicornfishes. The family includes about 86 extant species of marine fish living in tropical seas, usually around coral reefs. Many of the species are brightly colored and popular in aquaria.

The Moorish idol is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Zanclidae. It is the only member of the monospecific genus Zanclus and the only extant species within the Zanclidae. This species is found on reefs in the Indo-Pacific region.
The Mastacembelidae are a family of fishes, known as the spiny eels. The Mastacembelids are part of the Order Synbranchiformes, the swamp eels, which are part of the Actinopterygii.

Sweepers are small, tropical marine ray-finned fish of the family Pempheridae. Found in the western Atlantic Ocean and Indo-Pacific region, the family contains about 26 species in two genera. One species is the target of subsistence fisheries in Japan, where the fish is much enjoyed for its taste. Sweepers are occasionally kept in marine aquaria.
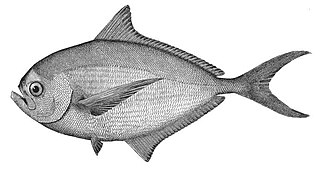
Pomfrets are scombriform fish belonging to the family Bramidae. The family currently includes 20 species across seven genera. Several species are important food sources for humans, especially Brama brama in South Asia. The earlier form of the pomfret's name was "pamflet", a word which probably ultimately comes from Portuguese pampo, referring to various fish such as the blue butterfish. The fish meat is white in color.

Trichogaster is a genus of gouramis native to South Asia from Pakistan to Myanmar. It is the only genus in the monotypic subfamily Trichogastrinae as set out in the 5th Edition of Fishes of the World, although that book states that there are two genera, the other being Colisa which is treated as a synonym of Trichogaster by Fishbase and the Catalog of Fishes. Fishbase also places the genus in the Luciocephalinae. Species of this genus are very popular in the aquarium trade.

Drepane is a genus of marine and brackish water ray-finned fishes, known commonly as the sicklefishes. It is the only genus in the monotypic percomorph family Drepaneidae. These fish occur in the Indian and western Pacific Oceans, and in the eastern Atlantic near Africa.

The Anabantoidei are a suborder of anabantiform ray-finned freshwater fish distinguished by their possession of a lung-like labyrinth organ, which enables them to breathe air. The fish in the Anabantoidei suborder are known as anabantoids or labyrinth fish, or colloquially as gouramies. Some labyrinth fish are important food fish, and many others, such as the Siamese fighting fish and paradise fish, are popular as aquarium fish.
Algae eater or algivore is a common name for any bottom-dwelling or filter-feeding aquatic animal species that specialize in feeding on algae and phytoplanktons. Algae eaters are important for the fishkeeping hobby and many are commonly kept by aquarium hobbyists to improve water quality. They are also important primary consumers that relay the biomass and energy from photosynthetic autotrophes up into the food web, as well as protecting the aquatic ecosystem against algae blooms.

Beaufortia kweichowensis is a species of gastromyzontid loach. It is endemic to China where it is known from the Xi River. The common names for this popular aquarium species are Chinese hillstream loach, Hong Kong pleco, butterfly hillstream loach, and Chinese sucker fish.

The Microcanthinae, commonly known as footballers, mados, stripeys, and moonlighters, are a subfamily of the sea chubs, a family of marine ray-finned fish in the order Perciformes.

Nothobranchiidae are a family of bony fishes containing roughly 300 species, also known as African rivulines. They are small killifish, usually measuring about 5 centimetres (2.0 in). They are limited to Africa, living in fresh water but being also somewhat salt-tolerant. They are also found in muddy or brackish water. Some species are kept as aquarium pets. They have frilly fins and many are brightly colored. They were formerly included in the family Aplocheilidae ; a return to that broader family has recently been suggested.

Lutjanidae or snappers are a family of perciform fish, mainly marine, but with some members inhabiting estuaries, feeding in fresh water. The family includes about 113 species. Some are important food fish. One of the best known is the red snapper.

The bluespine unicornfish, also known as the short-nose unicornfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Acanthuridae, the surgeonfishes, unicornfishes and tangs. This species is found in the Indo-Pacific. It is occasionally found in the aquarium trade. It grows to a size of 70 cm in length. It is called kala ('thorn') in Hawaii, dawa in New Caledonia, and ta or tā in Fiji. However the name kala refers to all three species of horned unicornfish found around Hawaii.

Gyrinocheilus aymonieri is a freshwater fish native to large parts of Southeast Asia. It is of interest as a local food source and for the aquarium trade. Its common names include honey sucker, sucking loach and Chinese algae eater.

Indostomus is a genus of small fishes native to slow moving or stagnant freshwater habitats in Indochina. It is the sole genus of the monogeneric family Indostomidae, Long considered to be sticklebacks, within the order Gasterosteiformes, modern analyses place the Indostomids within the order Synbranchiformes, related to the spiny eels and swamp eels.

Loaches are ray-finned fish of the suborder Cobitoidei. They are freshwater, benthic (bottom-dwelling) fish found in rivers and creeks throughout Eurasia and northern Africa. Loaches are among the most diverse groups of fish; the 1249 known species of Cobitoidei comprise about 107 genera divided among 9 families.
Gyrinocheilus pennocki, also known as the spotted algae eater, is a species of freshwater fish endemic to the Mekong basin in Cambodia, Vietnam, Laos, and Thailand. It grows to 28 cm (11 in) SL. It is an important species caught both in commercial and artisanal fisheries.















