HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DX beta chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-DQB2 gene. [3] [4]
HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DX beta chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-DQB2 gene. [3] [4]

Envelope glycoprotein GP120 is a glycoprotein exposed on the surface of the HIV envelope. It was discovered by Professors Tun-Hou Lee and Myron "Max" Essex of the Harvard School of Public Health in 1988. The 120 in its name comes from its molecular weight of 120 kDa. Gp120 is essential for virus entry into cells as it plays a vital role in attachment to specific cell surface receptors. These receptors are DC-SIGN, Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycan and a specific interaction with the CD4 receptor, particularly on helper T-cells. Binding to CD4 induces the start of a cascade of conformational changes in gp120 and gp41 that lead to the fusion of the viral membrane with the host cell membrane. Binding to CD4 is mainly electrostatic although there are van der Waals interactions and hydrogen bonds.
HLA-DR is an MHC class II cell surface receptor encoded by the human leukocyte antigen complex on chromosome 6 region 6p21.31. The complex of HLA-DR and peptide, generally between 9 and 30 amino acids in length, constitutes a ligand for the T-cell receptor (TCR). HLA were originally defined as cell surface antigens that mediate graft-versus-host disease. Identification of these antigens has led to greater success and longevity in organ transplant.

HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DR alpha chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-DRA gene. HLA-DRA encodes the alpha subunit of HLA-DR. Unlike the alpha chains of other Human MHC class II molecules, the alpha subunit is practically invariable. However it can pair with, in any individual, the beta chain from 3 different DR beta loci, DRB1, and two of any DRB3, DRB4, or DRB5 alleles. Thus there is the potential that any given individual can form 4 different HLA-DR isoforms.
Env is a viral gene that encodes the protein forming the viral envelope. The expression of the env gene enables retroviruses to target and attach to specific cell types, and to infiltrate the target cell membrane.

Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DR beta 4, also known as HLA-DRB4, is a human gene.

HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DRB5 beta chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-DRB5 gene.

T-cell surface glycoprotein CD3 gamma chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD3G gene.
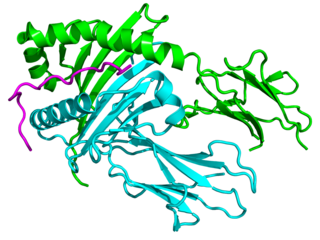
Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DQ alpha 1, also known as HLA-DQA1, is a human gene present on short arm of chromosome 6 (6p21.3) and also denotes the genetic locus which contains this gene. The protein encoded by this gene is one of two proteins that are required to form the DQ heterodimer, a cell surface receptor essential to the function of the immune system.

HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DP(W2) beta chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-DPB1 gene.

HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DRB3-1 beta chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-DRB3 gene.

HLA class I histocompatibility antigen, alpha chain F is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-F gene. It is an empty intracellular molecule that encodes a non-classical heavy chain anchored to the membrane and forming a heterodimer with a β-2 microglobulin light chain. It belongs to the HLA class I heavy chain paralogues that separate from most of the HLA heavy chains. HLA-F is localized in the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus, and is also unique in the sense that it exhibits few polymorphisms in the human population relative to the other HLA genes; however, there have been found different isoforms from numerous transcript variants found for the HLA-F gene. Its pathways include IFN-gamma signaling and CDK-mediated phosphorylation and removal of the Saccharomycescerevisiae Cdc6 protein, which is crucial for functional DNA replication.
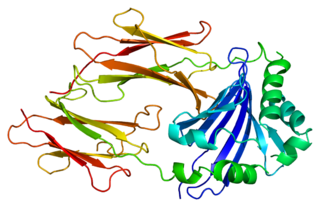
HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DM beta chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-DMB gene.

HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DM alpha chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-DMA gene.

HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DO alpha chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-DOA gene.

HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DO beta chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-DOB gene.

HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DQ(6) alpha chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-DQA2 gene. Also known as HLA-DXA or DAAP-381D23.2, it is part of the human leucocyte antigen system.

Phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 3-kinase C2 domain-containing gamma polypeptide is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIK3C2G gene.

Interferon alpha-7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IFNA7 gene.

CD8a, is a human gene.

Interferon alpha-16, also known as IFN-alpha-16, is a protein that in humans is encoded by theIFNA16 gene.