Related Research Articles
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is a large locus on vertebrate DNA containing a set of closely linked polymorphic genes that code for cell surface proteins essential for the adaptive immune system. This locus got its name because it was discovered in the study of tissue compatibility upon transplantation. Later studies revealed that tissue rejection due to incompatibility is an experimental artifact masking the real function of MHC molecules - binding an antigen derived from self-proteins or from pathogen and the antigen presentation on the cell surface for recognition by the appropriate T-cells. MHC molecules mediate interactions of leukocytes, also called white blood cells (WBCs), which are immune cells, with other leukocytes or with body cells. The MHC determines compatibility of donors for organ transplant, as well as one's susceptibility to an autoimmune disease via cross-reacting immunization.

The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system or complex is a group of related proteins that are encoded by the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) gene complex in humans. These cell-surface proteins are responsible for the regulation of the immune system. The HLA gene complex resides on a 3 Mbp stretch within chromosome 6p21. HLA genes are highly polymorphic, which means that they have many different alleles, allowing them to fine-tune the adaptive immune system. The proteins encoded by certain genes are also known as antigens, as a result of their historic discovery as factors in organ transplants. Different classes have different functions:
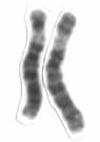
Chromosome 6 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 6 spans more than 170 million base pairs and represents between 5.5 and 6% of the total DNA in cells. It contains the Major Histocompatibility Complex, which contains over 100 genes related to the immune response, and plays a vital role in organ transplantation.
HLA-DR is an MHC class II cell surface receptor encoded by the human leukocyte antigen complex on chromosome 6 region 6p21.31. The complex of HLA-DR and peptide, generally between 9 and 30 amino acids in length, constitutes a ligand for the T-cell receptor (TCR). HLA were originally defined as cell surface antigens that mediate graft-versus-host disease. Identification of these antigens has led to greater success and longevity in organ transplant.

HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DRB1 beta chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-DRB1 gene. DRB1 encodes the most prevalent beta subunit of HLA-DR. Several alleles of DRB1 are associated with an increased incidence of rheumatoid arthritis.

HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DR alpha chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-DRA gene. HLA-DRA encodes the alpha subunit of HLA-DR. Unlike the alpha chains of other Human MHC class II molecules, the alpha subunit is practically invariable. However it can pair with, in any individual, the beta chain from 3 different DR beta loci, DRB1, and two of any DRB3, DRB4, or DRB5 alleles. Thus there is the potential that any given individual can form 4 different HLA-DR isoforms.

MHC class II molecules are a class of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules normally found only on professional antigen-presenting cells such as dendritic cells, mononuclear phagocytes, some endothelial cells, thymic epithelial cells, and B cells. These cells are important in initiating immune responses.
HLA-DQ (DQ) is a cell surface receptor protein found on antigen-presenting cells. It is an αβ heterodimer of type MHC class II. The α and β chains are encoded by two loci, HLA-DQA1 and HLA-DQB1, that are adjacent to each other on chromosome band 6p21.3. Both α-chain and β-chain vary greatly. A person often produces two α-chain and two β-chain variants and thus 4 isoforms of DQ. The DQ loci are in close genetic linkage to HLA-DR, and less closely linked to HLA-DP, HLA-A, HLA-B and HLA-C.
HLA-DQ5 (DQ5) is a human leukocyte antigen serotype subgroup within HLA-DQ(DQ) serotypes. The serotype is determined by the antibody recognition of β5.x subset of DQ β-chains. The β-chain of DQ is encoded by HLA-DQB1 locus and DQ5 are encoded by the HLA-DQB1*05 allele group. This group currently contains 4 common alleles, DQB1*0501, *0502, *0503, and *0504. HLA-DQ5 and HLA-DQB1*05 are almost synonymous in meaning. DQ5 β-chains combine with α-chains, encoded by genetically linked HLA-DQA1 alleles, to form the cis-haplotype isoforms. These isoforms, are all HLA-DQ1 encoded by the DQA1*01 allele group.
HLA-DQ7 (DQ7) is an HLA-DQ serotype that recognizes the common HLA DQB1*0301 and the less common HLA DQB1*0304 gene products. DQ7 is a form of 'split antigen' of the broad antigen group DQ3 which also contains DQ8 and DQ9.

Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DR beta 4, also known as HLA-DRB4, is a human gene.

HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DRB5 beta chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-DRB5 gene.
Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DQ beta 1, also known as HLA-DQB1, is a human gene and also denotes the genetic locus that contains this gene. The protein encoded by this gene is one of two proteins that are required to form the DQ heterodimer, a cell surface receptor essential to the function of the immune system.

Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DQ alpha 1, also known as HLA-DQA1, is a human gene present on short arm of chromosome 6 (6p21.3) and also denotes the genetic locus which contains this gene. The protein encoded by this gene is one of two proteins that are required to form the DQ heterodimer, a cell surface receptor essential to the function of the immune system.

HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DP(W2) beta chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-DPB1 gene.

HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DRB3-1 beta chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-DRB3 gene.

HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DO beta chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-DOB gene.

HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DQ(6) alpha chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-DQA2 gene. Also known as HLA-DXA or DAAP-381D23.2, it is part of the human leucocyte antigen system.

HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DX beta chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-DQB2 gene.
Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DP alpha 1, also known as HLA-DPA1, is a human gene.
References
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: HLA-DQB1 major histocompatibility complex, class II, DQ beta 1".
- ↑ Ando A, Kawai J, Maeda M, Tsuji K, Trowsdale J, Inoko H (1989). "Mapping and nucleotide sequence of a new HLA class II light chain gene, DQB3". Immunogenetics. 30 (4): 243–9. doi:10.1007/BF02421327. PMID 2571586. S2CID 24960351.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
| This protein-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |