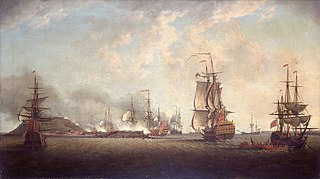HMS Cornwall was an 80-gun, third rate, ship of the line built for the Royal Navy in the 1690s. She served in the War of the Grand Alliance, and in her first year took part in the Battle of Barfleur and the action at La Hougue.

HMS Superb was a 74-gun Bellona-class third-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, designed by Sir Thomas Slade and built by Adam Hayes at Deptford Dockyard, launched on 27 October 1760 as a sister ship to HMS Dragon.

HMS Warspite was a 74-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 8 April 1758 at Deptford.

HMS Duke was a 90-gun second-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 13 June 1682 at Woolwich Dockyard.

HMS Charles was a 96-gun first-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, built by Christopher Pett at Deptford Dockyard until his death in March 1668, then completed by Jonas Shish after being launched in the same month. Her name was formally Charles the Second, but she was known simply as Charles, particularly after 1673 when the contemporary Royal Charles was launched.
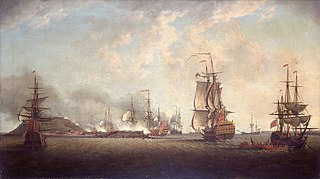
HMS Neptune was a 90-gun second-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy. She was built under the 1677 "Thirty Great Ships" Programme and launched in 1683 at Deptford Dockyard.

HMS Captain was a 70-gun third rate built at Woolwich Dockyard in 1677/78. After sitting in Ordinary for ten years she was in active commission for the War of the English Succession fighting at Beachy Head and Barfleur. She was in Ordinary until 1706 when she was rebuilt. She was in active commission for the last half of the War of Spanish Succession but fought in no major engagements. She was at the Battle of Passero I 1718. She was rebuilt in 1720/22. She made two forays in to the Baltic though the bulk of her late career was spent as guardship at Portsmouth. She was hulked in 1740 and finally broken in 1762.

HMS Lenox was a 70-gun third rate built at Deptford Dockyard in 1677/78. She was in active commission for the War of English Succession fighting in the Battles of Beachy Head and Barfleur. She was rebuilt in 1699. Again in active commission for the War of Spanish Succession fighting in the Capture of Gibraltar and the Battle of Velez Malaga. She followed this with the Battle off Passero. She was rebuilt again in 1721. She was active in the War with Spain, capturing the Princesa then serving in Home Waters, the Mediterranean and finally the West Indies. She was in action off Havana in 1745. She returned home and was placed in Ordinary. She was finally sunk as a breakwater at Sheerness in 1756.
HMS Burford was a 70-gun third rate ship of the line built at Woolwich Dockyard in 1677/79 as part of the Thirty Ships Programme of 1677. She fought in the War of the English Succession, including the Battle of Barfleur, before being rebuilt at Deptford in 1699, remaining as a 70-gun third rate. During the War of Spanish Succession she was mostly in the Mediterranean fleet and fought at the capture of Gibraltar and the Battle of Málaga in 1704 before being extensively repaired between 1710 and 1712 at Portsmouth Dockyard. Burford served in the Baltic in 1715 and 1717 before returning to the Mediterranean to fight the Spanish at the Battle of Cape Passaro in 1718. She was wrecked on the Italian coast in a storm on 14 February 1719.

HMS Kent was a 70-gun third rate ship of the line built by Sir Henry Johnson of Blackwall in 1677/79. She served during the War of English Succession 1699 to 1697, participating in the Battle of Barfleur. She was rebuilt in 1697/99. She served during the War of Spanish Succession 1702 to 1712 and partook in the Battles of Vigo and Velez-Malaga. She partook in the Battle of Passaro then served during the short war with Spain, December 1718 to February 1720. She was rebuilt in 1722/26. She spent the next thirteen years as a guard ship at Portsmouth. In the 1740s, she was off Cape Finisterre then in the West Indies. She returned home and was finally broken in 1744.
HMS Deptford was a 50-gun fourth-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched at Woolwich Dockyard in 1687. This was the second of three 50-gun ships ordered in 1682/3.
HMS St Albans was a 50-gun fourth rate ship of the line of the English Royal Navy, launched at Deptford Dockyard in 1687. One of only three 50-gun ships to be built during James II's brief reign, she was first commissioned on 22 October 1688 under Captain William Constable, and joined Lord Dartmouth's fleet in that month. The ship fought in the Battle of Bantry Bay on 1 May 1689, at the capture of a French 36-gun ship on 18 July 1690 off Rame Head and in the Battle of Barfleur on 24 May 1692 and in the Battle of Placentia, Newfoundland on 16–21 September 1693.

HMS Canterbury was a 60-gun fourth-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched at Deptford on 18 December 1693.
HMS Worcester was a 50-gun fourth rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, one of eight such ships authorised by the Navy Board on 24 December 1695 to be newly built ; the others were the Hampshire, Dartmouth, Salisbury, Winchester, Jersey, Carlisle and Tilbury. The contract for the Worcester was signed with shipbuilder Robert Winter on 26 February 1696, for the ship to be built in his yard at Northam in Southampton, and she was launched there on 31 May 1698.
HMS Centurion was a 50-gun fourth rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched in 1691. She was ordered on 20 March 1690 to be built at Deptford Dockyard by Master Shipwright Fisher Harding - on thye same day as her stable-mate Chester, and six days after the first ship of this batch - to a similar design to the prototype of this "123-ft" type - the Sedgemoor of 1687. The specified dimensions in the ordxer were for a length of 125 ft by 32ft 6in by 13ft 4in, but on completion she measured about 8 inches longer and in breadth. She was launched on 6 March 1691.

HMS Guernsey was a 50-gun fourth rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, one of four ordered in September 1694 to be built by commercial contracts; eight further ships of this type were ordered on 24 December. The Guernsey was built by Sir Henry Johnson's Blackwall Yard and launched on 6 July 1696.
HMS Nonsuch was a 50-gun fourth rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, one of four ordered in September 1694 to be built by commercial contracts; eight further ships of this type were ordered on 24 December. The Nonsuch was built by Robert and John Castle at their Deptford shipyard and launched on 20 August 1696.
HMS Warwick was a 50-gun fourth rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, one of four ordered in September 1694 to be built by commercial contracts; eight further ships of this type were ordered on 24 December. The Warwick was built by Robert and John Castle at their Deptford shipyard and launched on 20 August 1696.
HMS Yarmouth was a 70-gun third rate ship of the line of the English Royal Navy, built for the navy by a private contractor at Harwich under the 1690 Programme, and launched in 1695.

HMS Gloucester was a 50-gun fourth-rate ship of the line built at Deptford by Joseph Allin the elder for the Royal Navy in 1710/11. She participated in the War of the Spanish Succession. The ship was burned to prevent capture after she was damaged in a storm during Commodore George Anson's voyage around the world in 1742.