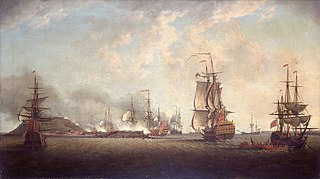HMS Monmouth was a 66-gun third-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, and was likely named for James, Duke of Monmouth. She served from 1667 to 1767, winning ten battle honours over a century of active service. She was rebuilt a total of three times during her career—each time effectively becoming a completely new ship.

HMS Royal Oak was a 74-gun third-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, built by Jonas Shish at Deptford and launched in 1674. She was one of only three Royal Navy ships to be equipped with the Rupertinoe naval gun. Life aboard her when cruising in the Mediterranean Sea in 1679 is described in the diary of Henry Teonge.

Association was a 90-gun second-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched at Portsmouth Dockyard in 1697. She served with distinction at the capture of Gibraltar, and was lost in 1707 by grounding on the Isles of Scilly in the greatest maritime disaster of the age. The wreck is a Protected Wreck managed by Historic England.
HMS Somerset was a three-decker 80-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched at Chatham Dockyard on 31 May 1698. She was the first ship to bear the name.

HMS Prince was a 100-gun first rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, built by Phineas Pett the Younger at Deptford Dockyard and launched in 1670.

HMS Royal Sovereign was a 100-gun first rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, built at Woolwich Dockyard and launched in July 1701. She had been built using some of the salvageable timbers from the previous Royal Sovereign, which had been destroyed by fire in 1697.

HMS Charles was a 96-gun first-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, built by Christopher Pett at Deptford Dockyard until his death in March 1668, then completed by Jonas Shish after being launched in the same month. Her name was formally Charles the Second, but she was known simply as Charles, particularly after 1673 when the contemporary Royal Charles was launched.

HMS St Andrew was a 96-gun first-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, built by Christopher Pett at Woolwich Dockyard under the supervision of Christopher Pett until his death in March 1668, completed by Jonas Shish, and launched in 1670. Commanded by George Churchill, she took part in the 1692 victory over the French navy at Barfleur & La Hogue.

HMS Edgar was a 72-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, built by Baylie of Bristol and launched in 1668. The diarist and naval administrator Samuel Pepys visited the town during its construction, noting that in his opinion, "it will be a fine ship". By 1685 she was carrying 74 guns.

HMS Swiftsure was a 70-gun third-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, built by Sir Anthony Deane at Harwich, and launched in 1673. By 1685 she had been reduced to a 66-gun ship.
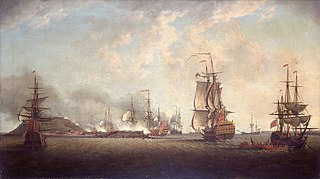
HMS Neptune was a 90-gun second-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy. She was built under the 1677 "Thirty Great Ships" Programme and launched in 1683 at Deptford Dockyard.

HMS Hampton Court was a 70-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched at Deptford Dockyard in 1678. Her initial commission was to move her to Chatham where she spent in the next ten years in Ordinary. She held an active commission for the War of the English Succession, participating in the Battles of Beachy Head and Barfleur. She was rebuilt at Blackwall in 1699/1701. During the War of Spanish Succession she served mainly in the Mediterranean. In 1707 she was taken by the French and incorporated into the French Navy for four years. She was sold to the Spanish in 1712. She was wrecked in Spanish service off the coast of Florida in a hurricane in 1715.

HMS Lenox was a 70-gun third rate built at Deptford Dockyard in 1677/78. She was in active commission for the War of English Succession fighting in the Battles of Beachy Head and Barfleur. She was rebuilt in 1699. Again in active commission for the War of Spanish Succession fighting in the Capture of Gibraltar and the Battle of Velez Malaga. She followed this with the Battle off Passero. She was rebuilt again in 1721. She was active in the War with Spain, capturing the Princesa then serving in Home Waters, the Mediterranean and finally the West Indies. She was in action off Havana in 1745. She returned home and was placed in Ordinary. She was finally sunk as a breakwater at Sheerness in 1756.

HMS Essex was a 70-gun third rate built by Sir Henry Johnson of Blackwall in 1678/79. During the War of the English Succession she fought in the last major action. She was rebuilt in 1699/1700. During the War of Spanish Succession she fought at Vigo Bay, the Capture of Gibraltar and Velez Malaga. She also fought at the Battle off Passero in 1718. She was rebuilt again in 1736-40. She was in action off Toulon in 1744. She was active in the Channel and against French ports during the Seven Years War. She fought at Quiberon Bay in 1759. She was wrecked in Quiberon Bay in November 1759.

HMS Expedition was a 70-gun third-rate ship of the line built at Portsmouth Dockyard in 1677/79. She was in active commission during the War of the English Succession participating in the battles of Beachy Head and Barfleur. She was rebuilt in 1699. Again, for the War of Spanish Succession she was in commission for the operation at Cadiz then returned to England where she sat for two years. She was in the Mediterranean for the Battle of Marbella in 1705. She then went to the West Indies and fought in Wager's action off Cartagena in 1708. She was rebuilt in 1709-14 to the 1706 Establishment. She spent her time split between the Baltic and as guard ship at Portsmouth before being broken at Portsmouth in 1736. She was rebuilt in 1736/40 at Deptford Dockyard.
HMS Ranelagh was a three-decker 80-gun third-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched at Deptford Dockyard on 25 June 1697. She took part in a number of actions during the War of the Spanish Succession, including the Battle of Vigo in 1702 and the Battle of Vélez-Málaga in 1704.

HMS Orford was a 70-gun third-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched at Deptford in 1698. She carried twenty-two 24-pounder guns and four (18-pounder) culverins on the lower deck; twenty-six 12-pounder guns on the upper deck; fourteen (5-pounder) sakers on the quarterdeck and forecastle; and four 3-pounder guns on the poop or roundhouse.
HMS Panther was a 50-gun fourth rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, built at Deptford Dockyard and launched on 15 March 1703.

HMS Burford was a 70-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, built at Deptford Dockyard to the 1719 Establishment, and launched on 19 July 1722. Burford was notably the early posting of both John Forbes and John Byng, both of whom rose to become admirals.
Captain Sir Andrew Leake was a Royal Navy officer of the late seventeenth and early eighteenth centuries, who distinguished himself at the Battle of Vigo Bay, during the War of the Spanish Succession. From Lowestoft, Leake joined the navy in 1688 under the patronage of John Ashby. Promoted to commander, Leake fought under Ashby as a supernumerary at the Action at La Hogue in 1692. His services at La Hogue brought him promotion to captain, and a series of commands that culminated in 1702 with Leake joining HMS Torbay. At Vigo Bay later that year Torbay broke the boom protecting a Franco-Spanish treasure fleet, resulting in the capture or destruction of the entire fleet. Leake was knighted for this, and went on to command HMS Grafton at the Capture of Gibraltar in 1704. He was mortally wounded at the Battle of Málaga later the same year.