
Onobrychis viciifolia, also known as O. sativa or common sainfoin was an important forage legume in temperate regions until the 1950s. During the Green Revolution it was replaced by high yielding alfalfa and clover species. Due to its anthelmintic properties, common sainfoin is a natural alternative to drugs to control nematode parasitism in the guts of small ruminants. This is the main reason why O. viciifolia returned to the scientific agenda in recent years.

Basil ), also called great basil, is a culinary herb of the family Lamiaceae (mints). It is a tender plant, and is used in cuisines worldwide. In Western cuisine, the generic term "basil" refers to the variety also known as Genovese basil or sweet basil. Basil is native to tropical regions from Central Africa to Southeast Asia. In temperate climates basil is treated as an annual plant, but it can be grown as a short-lived perennial or biennial in warmer horticultural zones with tropical or Mediterranean climates.

Haemonchus contortus, also known as the barber's pole worm, is a very common parasite and one of the most pathogenic nematodes of ruminants. Adult worms attach to abomasal mucosa and feed on the blood. This parasite is responsible for anemia, oedema, and death of infected sheep and goats, mainly during summer in warm, humid climates.
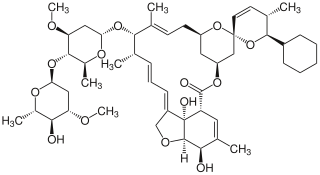
Doramectin, sold under the brand name Dectomax among others, is a veterinary medication approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of parasites such as gastrointestinal roundworms, lungworms, eyeworms, grubs, sucking lice, and mange mites in cattle. It is available as a generic medication. It is available as a combination with levamisole under the brand name Valcor.

Moxidectin is an anthelmintic drug used in animals to prevent or control parasitic worms (helminths), such as heartworm and intestinal worms, in dogs, cats, horses, cattle, sheep and wombats. Moxidectin kills some of the most common internal and external parasites by selectively binding to a parasite's glutamate-gated chloride ion channels. These channels are vital to the function of invertebrate nerve and muscle cells; when moxidectin binds to the channels, it disrupts neurotransmission, resulting in paralysis and death of the parasite.

Morada Nova is a Brazilian breed of domestic sheep. It originates in the state of Ceará, in Nordeste, the north-eastern region of Brazil, on the Atlantic coast.

Oxfendazole is a broad spectrum benzimidazole anthelmintic. Its main use is for protecting livestock against roundworm, strongyles and pinworms. Oxfendazole is the sulfoxide metabolite of fenbendazole.

The Gulf Coast Native is a breed of sheep found in the U.S. states bordering the Gulf Coast. Also occasionally known as the Louisiana Scrub, Pineywoods Native or simply Gulf Coast sheep, the breed is a mix of many of the sheep varieties brought to the Southern United States during the European colonization of the region. It is now an exceedingly rare breed, but one valuable for its ability to adapt to the hot humid climate of the Gulf Coast.

The Red Maasai is a breed of sheep indigenous to East Africa. True to its name, the breed is kept by the Maasai, though both pastoralists and smallholder farmers in Kenya, Tanzania, and Uganda keep Red Maasai flocks.

Omphalocarpum elatum Miers is a tall, tropical African tree belonging to the family Sapotaceae, remarkable for the large fruits growing directly from the trunk, and in many ways resembling the Lecythidaceae genus Napoleonaea. It is found in Equatorial Guinea, Sierra Leone, Ghana, the Central African Republic, Gabon, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Nigeria, Liberia, Cameroon, Côte d’Ivoire and Angola in the south. The fruits are favoured by elephants, the only animals able to break through the hard shell. They do this by skewering the fruit with a tusk while using their trunk to brace it against the ground. Having passed through the elephant's digestive tract, seeds germinate more readily. Although not yet endangered, the tree's life cycle is tied to that of forest elephants, and may become threatened in regions where elephant populations are under pressure.

FAMACHA is a selective treatment method for controlling the level of parasitic barber's pole worm among domesticated small ruminant populations. In contrast with earlier, more aggressive approaches, under FAMACHA only certain sheep or goats in a flock are selected for treatment. Selection for treatment is based on the degree of anaemia the animals are displaying in their mucous membranes, which is assessed through a colour guided chart.

Trichstrongyloidea is a superfamily of nematodes under the order Strongylida.

Harposporium anguillulae is a member of the genus Harposporium. It is an endoparasitic nematophagous fungus that attacks nematodes and eelworms and is isolated commonly from field and agricultural soils as well as used as an experimental organism in the laboratory.

Nitroxinil is an anthelmintic, a veterinary medicine against parasitic worms in sheep and cattle. The substance is active against the liver fluke the Fasciola hepatica and to a lesser extent against thread worms in the gastrointestinal tract. Brand names include Fluconix, Dovenix and Trodax. Nitroxynil is also used against strains of the red gum worm that have become resistant to benzimidazoles.

Cooperia is a genus of nematode from the Cooperiidae family that is one of the most common intestinal parasitic nematodes in cattle in temperate regions. Infections with Cooperia may result in mild clinical symptoms, but can lead to weight loss and damage of the small intestine, especially when co-infections with other nematodes such as Ostertagia ostertagi occur. Infections are usually treated with broad-spectrum anthelmintics such as benzimidazole, but resistance to these drugs has developed in the last decades and is now very common. Cooperia has a direct life cycle. Infective larvae are ingested by the host. The larvae grow to adults, which reproduce in the small intestines. Eggs are shed onto the pasture with the faeces, which leads to new infections. Co-infections with other gastro-intestinal nematodes such as O. ostertagi and Haemonchus contortus are common.
"Chryseobacterium nematophagum" is a Gram-negative, aerobic and rod-shaped bacteria in the genus Chryseobacterium, which was first isolated from Caenorhabditis briggsae nematodes in rotting apples in France. It exhibits gliding motility. After ingestion by a nematode, they attack it from within, breaking down its extracellular matrices and killing it. In laboratory tests C. nematophagum infected and killed a wide variety of nematodes, including the model organism Caenorhabditis elegans, and the vertebrate parasites Ancylostoma caninum, Cooperia curtecei, Cooperia oncophera, Haemonchus contortus, Nippostrongylus brasiliensis, Ostertagia ostertagi, Parastrongyloides trichosura and Trichostrongylus vitrinus.
The DAF-8 nematode gene encoding a R-SMAD protein of TGF-beta signaling pathway, which was originally found in model organism Caenorhabditis elegans. When the TGF-β ligand daf-7 binds to the TGF-β receptors daf-1/daf-4 on the surface of nematode cell, daf-8 will be phosphorylated and forms a heterodimer with daf-14, then enter to the nucleus to inhibit transcription regulated by daf-3/daf-5.
Cytochrome P450, family 23, also known as CYP23, is a nematoda cytochrome P450 monooxygenase family. The first gene identified in this family is the CYP23A1 from the Caenorhabditis elegans, is a homolog of the human gene CYP7B1.

Monepantel is an anthelmintic approved for use in sheep and cattle to control gastrointestinal nematodes. It belongs to a new class of anthelmintics called aminoacetonitrile derivatives (AAD). It is marketed by Elanco as Zolvix as a single active, or Zolvix Plus in combination with the macrocyclic lactone abamectin.
Heather Vivian Simpson is a New Zealand animal physiologist, and is professor emerita at Massey University, specialising in the biology of gastrointestinal parasites of sheep.














