Related Research Articles

The Handley Page Victor is a British jet-powered strategic bomber developed and produced by Handley Page during the Cold War. It was the third and final V bomber to be operated by the Royal Air Force (RAF), the other two being the Vickers Valiant and the Avro Vulcan. Entering service in 1958, the Victor was initially developed as part of the United Kingdom's airborne nuclear deterrent, but it was retired from the nuclear mission in 1968, following the discovery of fatigue cracks which had been exacerbated by the RAF's adoption of a low-altitude flight profile to avoid interception, and due to the pending introduction of the Royal Navy's submarine-launched Polaris missiles in 1969.

The Handley Page Type O was a biplane bomber used by Britain during the First World War. When built, the Type O was one of the largest aircraft in the world. There were two main variants, the Handley Page O/100 (H.P.11) and the Handley Page O/400 (H.P.12).
The Society of British Aerospace Companies was the UK's national trade association representing companies supplying civil air transport, aerospace defence, homeland security and space. As of October 2009 SBAC merged with the Defence Manufacturers Association and the Association of Police and Public Security Suppliers to form the ADS Group.
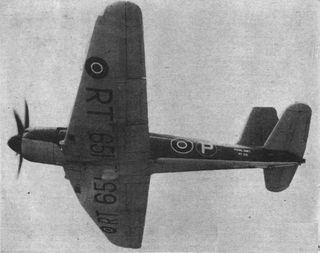
The Blackburn B.48 Firecrest, given the SBAC designation YA.1, was a single-engine naval strike fighter built by Blackburn Aircraft for service with the British Fleet Air Arm during the Second World War. It was a development of the troubled Firebrand, designed to Air Ministry Specification S.28/43, for an improved aircraft more suited to carrier operations. Three prototypes were ordered with the company designation of B-48 and the informal name of "Firecrest", but only two of them actually flew. The development of the aircraft was prolonged by significant design changes and slow deliveries of components, but the determination by the Ministry of Supply in 1946 that the airframe did not meet the requirements for a strike fighter doomed the aircraft. Construction of two of the prototypes was continued to gain flight-test data and the third was allocated to strength testing. The two flying aircraft were sold back to Blackburn in 1950 for disposal and the other aircraft survived until 1952.

The Supermarine Type 224 was a British gull-wing monoplane fighter aircraft designed by R.J. Mitchell at Supermarine in response to Air Ministry Specification F.7/30, which sought to introduce a new fighter to succeed the Gloster Gauntlet. The Type 224 was powered by a Rolls-Royce Goshawk engine, which used an experimental evaporative cooling system.

The Vickers Vanox was a British biplane bomber design intended as a successor to the Virginia for the Royal Air Force. Although it underwent extensive development, it was not successful, only a single aircraft being built.

The Blackburn B.T.1 Beagle was a British single-engine, two-seat biplane bomber/torpedo aircraft from 1928. Designed to Air Ministry specifications which led to no contracts for any manufacturer, only one Beagle was built.

The Vickers Type 207 was a single-engined two-seat biplane designed as a shipborne torpedo bomber to an early 1930s specification. Structurally innovative, only one was built.
The Miles Merchantman was a scaled-up and four-engined development of the Miles Aerovan light freighter. It flew in 1947 but the design was abandoned when Miles Aircraft was taken over by Handley Page in 1948.
The Handley Page H.P.51 was a monoplane conversion of the earlier, unsuccessful biplane bomber-transport aircraft, the Handley Page H.P.43. The Air Ministry ordered the production variant off the drawing board as the Handley Page H.P.54 Harrow bomber.
The Handley Page H.P.46 was a two-seat, single-engined biplane built to an Air Ministry specification for a carrier-based torpedo bomber. With an advanced combination of high lift, slow flying controls it was beset by handling problems and made few flights.

The Handley Page H.P.47 was a British single-engined low-wing monoplane built to an Air Ministry specification for a general-purpose bomber and torpedo bomber aircraft. Only one was built.

The Handley Page H.P.31 was a two-seat single-engined biplane built to a British specification for a carrier-based torpedo bomber and reconnaissance aircraft. After trials, the Blackburn Ripon was preferred, though the Harrow played a significant role in the development of automatic slots.
The Westland PV.7 was a private venture submission to a 1930s British specification for a general-purpose military aircraft with two crew. It was a single-engined, high-wing monoplane of promise, but was destroyed early in official tests.

The Timm T-840 was a twin engine, high wing passenger aircraft designed and flown in the United States in 1938. Equipped with a tricycle undercarriage and low speed aerodynamic devices, it could be configured to carry between six and ten passengers. Only one was built.
The Stephens Akro is a single engine monoplane designed in the United States for aerobatic competitions. It first flew in 1967 and proved very successful, leading to several developments of which one won seven US Championships and one World Championship between 1975 and 1982. The Extra EA-230 and Extra EA-300 were also Akro developments with over two hundred built.
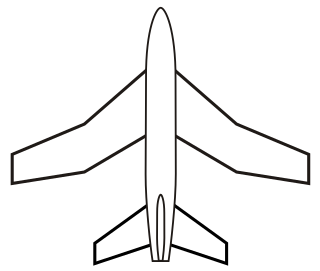
The crescent wing is a fixed-wing aircraft configuration in which a swept wing has a greater sweep angle on the inboard section than the outboard, giving the wing a crescent shape.
The Chasle LMC-1 Sprintair is an all-metal, single-seat sports light aircraft designed in France in the early 1970s and intended to be built by aero clubs from plans.

The Villiers XXIV or Villiers 24 CAN2 was a French army night fighter most notable as the first French military aircraft to be fitted with leading edge slats.
The Villiers 26 was a French naval seaplane which used Handley Page slats to provide the wide speed range required for escort and patrol duties. It was tested, behaved satisfactorily but received no production order.
References
Notes
- ↑ Jones 1994, p. 32.
- ↑ Bombers of the West, Bill Gunston 1997, Ian Allan Ltd., SBN 684-13623-6, p.84
- ↑ Taylor, 1976. p. 103.
- ↑ Lednicer, David. "The Incomplete Guide to Airfoil Usage". m-selig.ae.illinois.edu. Retrieved 16 April 2019.
Bibliography
- Barnes, C. H. Handley Page Aircraft Since 1907. London: Putnam & Company, Ltd., 1987. ISBN 0-85177-803-8.
- Buttler, Tony and Jean-Louis Delezenne. X-Planes of Europe: Secret Research Aircraft from the Golden Age 1946-1974. Manchester, UK: Hikoki Publications, 2012. ISBN 978-1-902-10921-3
- Clayton, Donald C. Handley Page, an Aircraft Album. Shepperton, Surrey, UK: Ian Allan, 1969. ISBN 0-7110-0094-8.
- Hygate, B.; British experimental jet aircraft, Argus, 1990, Pages 106-112.
- Jones, Barry (January 1994). "Crescent-Wing Crusader". Aeroplane Monthly . Vol. 22, no. 1. pp. 28–33. ISSN 0143-7240.
- Taylor, John W.R. Jane's Pocket Book of Research and Experimental Aircraft, London, Macdonald and Jane's Publishers Ltd, 1976. ISBN 0-356-08409-4.