
Galls or cecidia are a kind of swelling growth on the external tissues of plants, fungi, or animals. Plant galls are abnormal outgrowths of plant tissues, similar to benign tumors or warts in animals. They can be caused by various parasites, from viruses, fungi and bacteria, to other plants, insects and mites. Plant galls are often highly organized structures so that the cause of the gall can often be determined without the actual agent being identified. This applies particularly to some insect and mite plant galls. The study of plant galls is known as cecidology.

Cecidomyiidae is a family of flies known as gall midges or gall gnats. As the name implies, the larvae of most gall midges feed within plant tissue, creating abnormal plant growths called galls. Cecidomyiidae are very fragile small insects usually only 2–3 mm (0.079–0.118 in) in length; many are less than 1 mm (0.039 in) long. They are characterised by hairy wings, unusual in the order Diptera, and have long antennae. Some Cecidomyiids are also known for the strange phenomenon of paedogenesis in which the larval stage reproduces without maturing first. In some species, the daughter larvae consume the mother, while in others, reproduction occurs later on in the egg or pupa.

Creosote gall midges are a species of gall-inducing flies in the Asphondylia auripila group. This group consists of 15 closely related species of flies which inhabit creosote bush sensu lato. They have partitioned the plant ecologically with different gall midge species inhabiting the leaves, stems, buds, and flowers of creosote bush. Each species induces a uniquely shaped gall but the insects are otherwise morphologically very similar and very difficult to tell apart.

Rabdophaga rosaria is a gall midge which forms Camellia galls or terminal rosette gall on willow species. It was first described by Hermann Loew in 1850.
Orseolia oryzae, also called the Asian rice gall midge, is a species of small fly in the family Cecidomyiidae. It is a major insect pest of rice. The damage to the crop is done by the larvae which form galls commonly known as "silver shoots" or "onion shoots". The rice plant is stunted and the seed heads fail to develop.

A gnat is any of many species of tiny flying insects in the dipterid suborder Nematocera, especially those in the families Mycetophilidae, Anisopodidae and Sciaridae. They can be both biting and non-biting. Most often they fly in large numbers, called clouds. "Gnat" is a loose descriptive category rather than a phylogenetic or other technical term, so there is no scientific consensus on what constitutes a gnat. Some entomologists consider only non-biting flies to be gnats. Certain universities and institutes also distinguish eye gnats: the Smithsonian Institution describes them as "non-biting flies, no bigger than a few grains of salt, ... attracted to fluids secreted by your eyes".

Ampelomyia viticola, the grape tube gallmaker, is a species of gall midge found in the eastern United States and Canada. It produces green or bright red galls on new world grape vines.
Rabdophaga strobilina is a gall midge and inquiline of Rabdophaga rosaria and Rabdophaga terminalis; also gall midges. It was first described by Johann Jacob Bremi-Wolf in 1847.

Rabdophaga rosariella is a species of gall midge which forms galls on sallows. It was first described by Jean-Jacques Kieffer in 1897.
Rabdophaga clausilia is a gall midge which, depending on the source, forms galls on the leaves of willows, or is an inquiline living in the galls of a Rabdophaga species, or a predator. It was first described by Johann Jacob Bremi-Wolf in 1847.

Iteomyia capreae is a gall midge which forms galls on willows. It was first described by Johannes Winnertz in 1853.

Rhopalomyia solidaginis, the goldenrod bunch gall, is a species of gall midges, insects in the family Cecidomyiidae The galls of this species have the following host species of goldenrods:Solidago altissima, Solidago canadensis, Solidago rugosa They have been found across eastern North American.

Asphondylia solidaginis is a species of gall midge (Cecidomyiidae) that induces galls on goldenrods in North America where it is widespread. It was first described by William Beutenmuller in 1907.
Dasineura fraxini is a gall midge which forms galls on the leaves of ash. It was first described by Johann Jacob Bremi-Wolf in 1847.

Mikiola fagi, the beech gall midge is a gall-causing fly in the family Cecidomyiidae. This species was first described by Theodor Hartig in 1839.
Acalitus stenaspis is an eriophyid mite which causes galls on beech. It is found in Europe and was first described by the Austrian zoologist Alfred Nalepa in 1891.
Massalongia rubra is a species of gall midge which forms galls in the leaves of birch. It was first described by the French naturalist and entomologist, Jean-Jacques Kieffer in 1890 and is found in Europe.
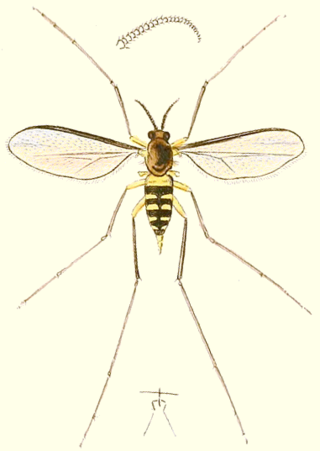
Lasioptera rubi is a species of gall midge in the family Cecidomyiidae and is found in Europe. It was first described in 1803 by the German priest, botanist and entomologist, Franz von Paula Schrank. The larvae feed within the tissue of brambles, creating abnormal plant growths known as galls.
Dasineura plicatrix is a species of gall midge, an insect in the family Cecidomyiidae, found in Europe. It was described by the German entomologist Friedrich Hermann Loew in 1850. The larvae feed within the tissue of bramble leaves, creating an abnormal growth known as a plant gall.
Placochela nigripes is a gall midge which forms galls on the flower buds of elder, honeysuckle and privet. It was described by F Löw in 1877.












