
Anemonoides quinquefolia, a flowering plant in the buttercup family Ranunculaceae, is native to North America. It is commonly called wood anemone or windflower, not to be confused with Anemonoides nemorosa, a closely related European species also known by these common names. The specific epithet quinquefolia means "five-leaved", which is a misnomer since each leaf has just three leaflets. A plant typically has a single, small white flower with 5 sepals.

Echinodorus, commonly known as burhead or Amazon sword, is a genus of plants in the family Alismataceae, native to the Western Hemisphere from the central United States to Argentina. Its scientific name is derived from Ancient Greek echius – "rough husk" - and doros – "leathern bottle" - alluding to ovaries, which in some species are armed with persistent styles, forming prickly head of fruit. Some of the species are commonly cultivated in artificial aquatic habitats.

Echinodorus cordifolius, the spade-leaf sword or creeping burhead, is a species of aquatic plants in the Alismatales. It is native to Mexico, the West Indies, Central America, South America and the southeastern United States.

Echinodorus horizontalis is a species of plant in the Alismataceae family. It is native to northern South America.

Echinodorus tunicatus is a species of aquatic plants in the family Alismataceae.

Echinodorus longiscapus is a perennial, aquatic plant of the Alismataceae, native to South America. It is cultivated as a pond or aquarium plant.

Echinodorus macrophyllus is a species of aquatic plants in the Alismataceae. It is native to Brazil and Bolivia.

In Rataj's taxonomy Echinodorus ovalis is in Section Cordifolii, Subgenus Echinodorus. It is related to Echinodorus cordifolius and listed by some authorities and importers as a synonym of that species, e.g. E. cordifolius 'ovalis'.

Echinodorus subalatus is a species of aquatic plants in the Alismataceae. It is native to Cuba, Mexico, Central America, Guyana, Venezuela, Bolivia, Brazil and Paraguay. It is found naturally growing in mud by the side of streams.
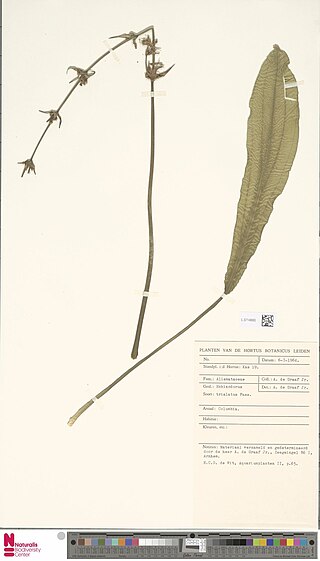
Echinodorus trialatus is a type of plant. In Rataj's taxonomy, E. trialatus is in Section Paniculati, Subgenus Echinodorus.

Echinodorus uruguayensis is a plant species in the Alismataceae. It is native to South America.

Echinodorus berteroi is an aquatic plant species in the Alismataceae It is native to the southern and central parts of the United States, as well as Central America, the West Indies, and South America as far south as Argentina.

Echinodorus bracteatus is a species of plants in the Alismataceae. It is native to Costa Rica, Nicaragua, Panama, Colombia and Ecuador.

Thalictrum thalictroides, the rue-anemone or windflower, is a herbaceous perennial plant native to woodland in eastern North America. It has white or pink flowers surrounded by a whorl of leaflets, and it blooms in spring.

Echinodorus grandiflorus is a plant species in the Alismataceae. It is native to Brazil, Paraguay, Uruguay, Argentina, Venezuela and Florida.

Trillium petiolatum, the Idaho trillium, also known as the long-petioled trillium or round-leaved trillium, is a species of flowering plant in the family Melanthiaceae. It is native to the northwestern United States, in Idaho, Oregon, and Washington. Its type specimen was gathered by Meriwether Lewis during the return trip of the Lewis and Clark Expedition in 1806.

Ribes velutinum is a species of currant known by the common name desert gooseberry.

Astrantia minor, the lesser masterwort, is a species of herbaceous plant belonging to the family of Apiaceae. It is native within Europe, to the countries of France, Italy, Spain and Switzerland. It is clump-forming herbaceous perennial.

Albidella is a genus of plants in Alismataceae. Currently, three species are known. It is native to Cuba and the Yucatán Peninsula.

Gonocarpus tetragynus is an Australian herb in the watermilfoil family Haloragaceae native to eastern Australia. Common names include common raspwort. A widespread species particularly found in dry eucalyptus forests, scrubland, and heathland.




















