
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants that is formed from the ovary after flowering.

Rosaceae, the rose family, is a medium-sized family of flowering plants that includes 4,828 known species in 91 genera.

In botany, a drupe is an indehiscent type of fruit in which an outer fleshy part surrounds a single shell of hardened endocarp with a seed (kernel) inside. These fruits usually develop from a single carpel, and mostly from flowers with superior ovaries.

In botany a capsule is a type of simple, dry, though rarely fleshy dehiscent fruit produced by many species of angiosperms.
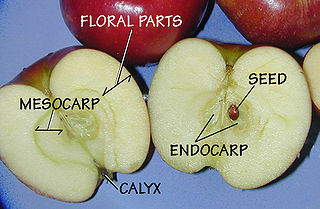
In botany, a pome is a type of fruit produced by flowering plants in the subtribe Malinae of the family Rosaceae. Pome fruits consist of a central "core" containing multiple small seeds, which is enveloped by a tough membrane and surrounded by an edible layer of flesh. Pome fruit trees are deciduous, and undergo a dormant winter period that requires cold temperatures to break dormancy in spring. Well-known pomes include the apple, pear, and quince.
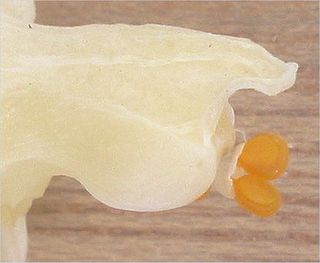
A pollinium is a coherent mass of pollen grains in a plant that are the product of only one anther, but are transferred, during pollination, as a single unit. This is regularly seen in plants such as orchids and many species of milkweeds (Asclepiadoideae). Usage of the term differs: in some orchids two masses of pollen are well attached to one another, but in other orchids there are two halves each of which is sometimes referred to as a pollinium.

An aril, also called an arillus, is a specialized outgrowth from a seed that partly or completely covers the seed. An arillode or false aril is sometimes distinguished: whereas an aril grows from the attachment point of the seed to the ovary, an arillode forms from a different point on the seed coat. The term "aril" is sometimes applied to any fleshy appendage of the seed in flowering plants, such as the mace of the nutmeg seed. Arils and arillodes are often edible enticements that encourage animals to transport the seed, thereby assisting in seed dispersal. Pseudarils are aril-like structures commonly found on the pyrenes of Burseraceae species that develop from the mesocarp of the ovary. The fleshy, edible pericarp splits neatly in two halves, then falling away or being eaten to reveal a brightly coloured pseudaril around the black seed.

Dehiscence is the splitting of a mature plant structure along a built-in line of weakness to release its contents. This is common among fruits, anthers and sporangia. Sometimes this involves the complete detachment of a part. Structures that open in this way are said to be dehiscent. Structures that do not open in this way are called indehiscent, and rely on other mechanisms such as decay or predation to release the contents.

An aggregate fruit or etaerio is a fruit that develops from the merger of several ovaries that were separated in a single flower. In contrast, a simple fruit develops from one ovary, and a multiple fruit develops from multiple flowers. In languages other than English, the meanings of "aggregate" and "multiple" fruit are reversed, so that "aggregate" fruits merge several flowers. The differences in meaning are due to a reversal in the terminology by John Lindley, which has been followed by most English-language authors.

Multi-fruits, also called collective fruits, are fruiting bodies formed from a cluster of flowers, the inflorescence. Each flower in the inflorescence produces a fruit, but these mature into a single mass. After flowering the mass is called an infructescence. Examples are the fig, pineapple, mulberry, osage-orange, and jackfruit.

In the flowering plants, an ovary is a part of the female reproductive organ of the flower or gynoecium. Specifically, it is the part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. The pistil may be made up of one carpel or of several fused carpels, and therefore the ovary can contain part of one carpel or parts of several fused carpels. Above the ovary is the style and the stigma, which is where the pollen lands and germinates to grow down through the style to the ovary, and, for each individual pollen grain, to fertilize one individual ovule. Some wind pollinated flowers have much reduced and modified ovaries.

In botany, a berry is a fleshy fruit without a stone (pit) produced from a single flower containing one ovary. Berries so defined include grapes, currants, and tomatoes, as well as cucumbers, eggplants (aubergines) and bananas, but exclude certain fruits that meet the culinary definition of berries, such as strawberries and raspberries. The berry is the most common type of fleshy fruit in which the entire outer layer of the ovary wall ripens into a potentially edible "pericarp". Berries may be formed from one or more carpels from the same flower. The seeds are usually embedded in the fleshy interior of the ovary, but there are some non-fleshy exceptions, such as Capsicum species, with air rather than pulp around their seeds.

A loment is a type of dehiscent legume fruit that breaks apart at constrictions occurring between segments, so that each segment contains one seed. It is a type of schizocarp.

Latania, commonly known as latan palm or latania palm, is a genus of flowering plant in the palm tree family, native to the Mascarene Islands in the western Indian Ocean.

Elaeocarpus angustifolius is a species of flowering plant in the family Elaeocarpaceae and occurs from India to New Caledonia and northern Australia. Common synonyms are E. ganitrus and E. sphaericus. It is a large evergreen tree, often with buttress roots, and has leaves with wavy serrations, creamy white flowers and more or less spherical bright blue drupe fruit. In English, the tree is known as utrasum bean tree in India. In Sri Lanka recorded names are woodenbegar and Indian bead tree. It is simply known as elaeocarpus in the Northern Territory of Australia. Other names used for this tree in Australia are Indian oil fruit and genitri. In Hawaii it is known as a blue marble tree.

Fruit anatomy is the plant anatomy of the internal structure of fruit. Fruits are the mature ovary or ovaries of one or more flowers. They are found in three main anatomical categories: aggregate fruits, multiple fruits, and simple fruits.

In botany, sessility is a characteristic of plant parts that have no stalk. Plant parts can also be described as subsessile, that is, not completely sessile.

Lepidobotryaceae is a family of plants in the order Celastrales. It contains only two species: Lepidobotrys staudtii and Ruptiliocarpon caracolito.
Amphicarpy is a reproductive strategy that occurs with 13 plant families, expressed mostly in species with an annual life cycle. It is characterized by production of two types of fruit, for different ecological roles. It is sometimes restricted to the situation where one fruit type is aerial and the other subterranean (hypogeous), and similar to, but distinguished from, heterocarpy, which latter means a plant that carries two distinct types of fruit or seeds. The word amphicarp is the contraction of the Greek words ἀμφί meaning "of both kinds" and καρπός meaning fruit.





















