
Helsinki is the capital and most populous city in Finland. It is on the shore of the Gulf of Finland and is the seat of southern Finland's Uusimaa region. About 684,000 people live in the municipality, with 1.26 million in the capital region and 1.6 million in the metropolitan area. As the most populous urban area in Finland, it is the country's most significant centre for politics, education, finance, culture, and research. Helsinki is 80 kilometres (50 mi) north of Tallinn, Estonia, 400 kilometres (250 mi) east of Stockholm, Sweden, and 300 kilometres (190 mi) west of Saint Petersburg, Russia. Helsinki has significant historical connections with these three cities.
Colloquial or spoken Finnish is the unstandardized spoken variety of the Finnish language, in contrast with the standardized form of the language. It is used primarily in personal communication and varies somewhat between the different dialects.

Finland Swedish or Fenno-Swedish is a variety of the Swedish language and a closely related group of Swedish dialects spoken in Finland by the Swedish-speaking population, commonly also referred to as Finland Swedes, as their first language.

Inari Sámi is a Sámi language spoken by the Inari Sámi of Finland. It has approximately 400 speakers, the majority of whom are middle-aged or older and live in the municipality of Inari. According to the Sámi Parliament of Finland, 269 persons used Inari Sámi as their first language. It is the only Sámi language that is spoken exclusively in Finland. The language is classified as being seriously endangered, as few children learn it; however, more and more children are learning it in language nests. In 2018, Inari Sámi had about 400 speakers; due to revival efforts, the number had increased.

Meänkieli, or Tornedalian is a Finnic language or a group of distinct Finnish dialects spoken in the northernmost part of Sweden along the valley of the Torne River. Meänkieli is recognized in Sweden as country's five minority languages and is treated as a distinct language from Finnish, however its status as an independent Finnic language is sometimes disputed due to its mutual intelligibility with Finnish. According to the National Association of Swedish Tornedalians, 70,000 individuals are able to understand Meänkieli, at least to some level.
Finns or Finnish people are a Baltic Finnic ethnic group native to Finland. Finns are traditionally divided into smaller regional groups that span several countries adjacent to Finland, both those who are native to these countries as well as those who have resettled. Some of these may be classified as separate ethnic groups, rather than subgroups of Finns. These include the Kvens and Forest Finns in Norway, the Tornedalians in Sweden, and the Ingrian Finns in Russia.
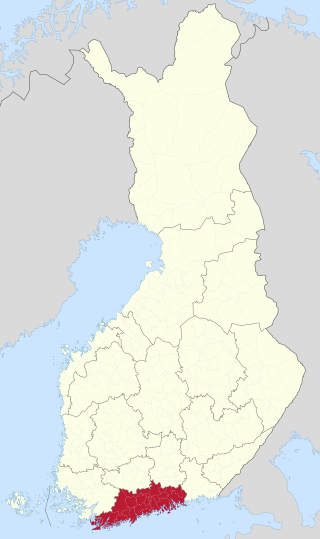
Uusimaa is a region of Finland. It borders the regions of Southwest Finland, Tavastia Proper (Kanta-Häme), Päijänne Tavastia (Päijät-Häme), and Kymenlaakso. Finland's capital and largest city, Helsinki, along with the surrounding metropolitan area, are both contained in the region, and Uusimaa is Finland's most populous region. The population of Uusimaa is 1,734,000.
In sociolinguistics, a sociolect is a form of language or a set of lexical items used by a socioeconomic class, profession, age group, or other social group.

SpåraKoff is a HM V type tram converted into a mobile bar in Helsinki, Finland. Known as the pub tram, the vehicle does circular tours of downtown Helsinki picking up passengers for a fee during summer months. It is operated jointly by Sinebrychoff, HOK-Elanto, and Helsinki City Transport.

Pite Sámi or Arjeplog Sámi is a Sámi language traditionally spoken in Sweden and Norway. It is a critically endangered language that has only about 25–50 native speakers left and is now almost only spoken on the Swedish side of the border along the Pite River in the north of Arjeplog and Arvidsjaur and in the mountainous areas of the Arjeplog municipality.

Sörnäinen is a neighbourhood in the city of Helsinki, Finland.

The two main official languages of Finland are Finnish and Swedish. There are also several official minority languages: three variants of Sami, as well as Romani, Finnish Sign Language, Finland-Swedish Sign Language and Karelian.

Swedish is the official language of Sweden and is spoken by the vast majority of the 10.23 million inhabitants of the country. It is a North Germanic language and quite similar to its sister Scandinavian languages, Danish and Norwegian, with which it maintains partial mutual intelligibility and forms a dialect continuum. A number of regional Swedish dialects are spoken across the country. In total, more than 200 languages are estimated to be spoken across the country, including regional languages, indigenous Sámi languages, and immigrant languages.

The official translation used by the state church, the Evangelical Lutheran Church of Finland, is approved by its Synod. There have been three official translations: Biblia, se on Coco Pyhä Ramattu Suomexi (1642), Pyhä Raamattu (1933/1938), and the current one Uusi kirkkoraamattu (1992/2007). The term kirkkoraamattu means that the edition has to be suited for service of worship and other needs of the church.

Finnish is a Finnic language of the Uralic language family, spoken by the majority of the population in Finland and by ethnic Finns outside of Finland. Finnish is one of the two official languages of Finland, alongside Swedish. In Sweden, both Finnish and Meänkieli are official minority languages. Kven, which like Meänkieli is mutually intelligible with Finnish, is spoken in the Norwegian counties of Troms and Finnmark by a minority of Finnish descent.

The Stadin derby, also known as the Helsinki derby, is the name for a Helsinki association football fixture played between HIFK Fotboll and HJK Helsinki. The name of the derby derives from the common slang word nickname for Helsinki (Stadi), widely used by the locals. Both the teams play at the highest level of football in Finland, in Veikkausliiga. Before 2015, the clubs had not faced each other at the highest level since 1972 when HIFK got relegated from the top league, which was then known as Mestaruussarja.

Anna Taina Aleksandra Kortelainen is a Finnish scholar, art historian and non-fiction writer.
Marja-Leena Leinonen was a Finnish linguist.
Karelians, also known as Finnish Karelians or Karelian Finns, are a subgroup of the Finnish people, traditionally living in Finnish Karelia. Karelians speak eastern dialects of the Finnish language: the South Karelian dialects are spoken in South Karelia, while the eastern Savonian dialects are spoken in North Karelia. The South Karelian dialects were spoken in the Karelian Isthmus prior to the Winter War. Karelians are traditionally Lutheran Christians, with an Orthodox Christian minority, belonging to either the Evangelical Lutheran Church of Finland or the Orthodox Church of Finland respectively.
















