
The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e., it has both an endocrine and a digestive exocrine function. 99% of the pancreas is exocrine and 1% is endocrine. As an endocrine gland, it functions mostly to regulate blood sugar levels, secreting the hormones insulin, glucagon, somatostatin and pancreatic polypeptide. As a part of the digestive system, it functions as an exocrine gland secreting pancreatic juice into the duodenum through the pancreatic duct. This juice contains bicarbonate, which neutralizes acid entering the duodenum from the stomach; and digestive enzymes, which break down carbohydrates, proteins and fats in food entering the duodenum from the stomach.

Upper gastrointestinal bleeding is gastrointestinal bleeding (hemorrhage) in the upper gastrointestinal tract, commonly defined as bleeding arising from the esophagus, stomach, or duodenum. Blood may be observed in vomit or in altered form as black stool. Depending on the amount of the blood loss, symptoms may include shock.

In medicine (gastroenterology), angiodysplasia is a small vascular malformation of the gut. It is a common cause of otherwise unexplained gastrointestinal bleeding and anemia. Lesions are often multiple, and frequently involve the cecum or ascending colon, although they can occur at other places. Treatment may be with colonoscopic interventions, angiography and embolization, medication, or occasionally surgery.

Dieulafoy's lesion is a medical condition characterized by a large tortuous artery most commonly in the stomach wall (submucosal) that erodes and bleeds. It can present in any part of the gastrointestinal tract. It can cause gastric hemorrhage but is relatively uncommon. It is thought to cause less than 5% of all gastrointestinal bleeds in adults. It was named after French surgeon Paul Georges Dieulafoy, who described this condition in his paper "Exulceratio simplex: Leçons 1-3" in 1898. It is also called "caliber-persistent artery" or "aneurysm" of gastric vessels. However, unlike most other aneurysms, these are thought to be developmental malformations rather than degenerative changes.

Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is a technique that combines the use of endoscopy and fluoroscopy to diagnose and treat certain problems of the biliary or pancreatic ductal systems. It is primarily performed by highly skilled and specialty trained gastroenterologists. Through the endoscope, the physician can see the inside of the stomach and duodenum, and inject a contrast medium into the ducts in the biliary tree and pancreas so they can be seen on radiographs.

Gastric varices are dilated submucosal veins in the lining of the stomach, which can be a life-threatening cause of bleeding in the upper gastrointestinal tract. They are most commonly found in patients with portal hypertension, or elevated pressure in the portal vein system, which may be a complication of cirrhosis. Gastric varices may also be found in patients with thrombosis of the splenic vein, into which the short gastric veins that drain the fundus of the stomach flow. The latter may be a complication of acute pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer, or other abdominal tumours, as well as hepatitis C. Gastric varices and associated bleeding are a potential complication of schistosomiasis resulting from portal hypertension.

Acute pancreatitis (AP) is a sudden inflammation of the pancreas. Causes, in order of frequency, include: a gallstone impacted in the common bile duct beyond the point where the pancreatic duct joins it; heavy alcohol use; systemic disease; trauma; and, in children, mumps. Acute pancreatitis may be a single event; it may be recurrent; or it may progress to chronic pancreatitis and/or pancreatic failure.
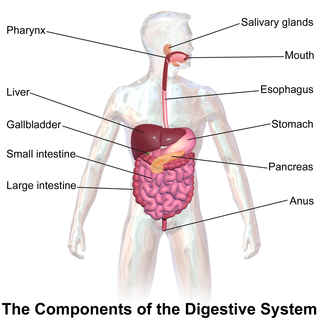
Gastrointestinal diseases refer to diseases involving the gastrointestinal tract, namely the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine and rectum; and the accessory organs of digestion, the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas.

A pancreaticoduodenectomy, also known as a Whipple procedure, is a major surgical operation most often performed to remove cancerous tumours from the head of the pancreas. It is also used for the treatment of pancreatic or duodenal trauma, or chronic pancreatitis. Due to the shared blood supply of organs in the proximal gastrointestinal system, surgical removal of the head of the pancreas also necessitates removal of the duodenum, proximal jejunum, gallbladder, and, occasionally, part of the stomach.

Pseudocysts are like cysts, but lack epithelial or endothelial cells. Initial management consists of general supportive care. Symptoms and complications caused by pseudocysts require surgery. Computed tomography (CT) scans are used for initial imaging of cysts, and endoscopic ultrasounds are used in differentiating between cysts and pseudocysts. Endoscopic drainage is a popular and effective method of treating pseudocysts.

A pancreatic fistula is an abnormal communication between the pancreas and other organs due to leakage of pancreatic secretions from damaged pancreatic ducts. An external pancreatic fistula is one that communicates with the skin, and is also known as a pancreaticocutaneous fistula, whereas an internal pancreatic fistula communicates with other internal organs or spaces. Pancreatic fistulas can be caused by pancreatic disease, trauma, or surgery.

Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) or echo-endoscopy is a medical procedure in which endoscopy is combined with ultrasound to obtain images of the internal organs in the chest, abdomen and colon. It can be used to visualize the walls of these organs, or to look at adjacent structures. Combined with Doppler imaging, nearby blood vessels can also be evaluated.

In human anatomy, the greater pancreatic artery, is the largest artery that supplies the pancreas. It arises from the splenic artery.

The inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery is a branch of the superior mesenteric artery. It supplies the head of the pancreas, and the ascending and inferior parts of the duodenum. Rarely, it may have an aneurysm.
Pancreatic diseases are diseases that affect the pancreas, an organ in most vertebrates and in humans and other mammals located in the abdomen. The pancreas plays a role in the digestive and endocrine system, producing enzymes which aid the digestion process and the hormone insulin, which regulates blood sugar levels. The most common pancreatic disease is pancreatitis, an inflammation of the pancreas which could come in acute or chronic form. Other pancreatic diseases include diabetes mellitus, exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, cystic fibrosis, pseudocysts, cysts, congenital malformations, tumors including pancreatic cancer, and hemosuccus pancreaticus.

Ascending cholangitis, also known as acute cholangitis or simply cholangitis, is inflammation of the bile duct, usually caused by bacteria ascending from its junction with the duodenum. It tends to occur if the bile duct is already partially obstructed by gallstones.

A self-expandable metallic stent is a metallic tube, or stent that holds open a structure in the gastrointestinal tract to allow the passage of food, chyme, stool, or other secretions related to digestion. Surgeons insert SEMS by endoscopy, inserting a fibre optic camera—either through the mouth or colon—to reach an area of narrowing. As such, it is termed an endoprosthesis. SEMS can also be inserted using fluoroscopy where the surgeon uses an X-ray image to guide insertion, or as an adjunct to endoscopy.

An endoclip is a metallic mechanical device used in endoscopy in order to close two mucosal surfaces without the need for surgery and suturing. Its function is similar to a suture in gross surgical applications, as it is used to join together two disjointed surfaces, but, can be applied through the channel of an endoscope under direct visualization. Endoclips have found use in treating gastrointestinal bleeding, in preventing bleeding after therapeutic procedures such as polypectomy, and in closing gastrointestinal perforations. Many forms of endoclips exist of different shapes and sizes, including two and three prong devices, which can be administered using single use and reloadable systems, and may or may not open and close to facilitate placement.
Cystogastrostomy is a surgery to create an opening between a pancreatic pseudocyst and the stomach when the cyst is in a suitable position to be drained into the stomach. This conserves pancreatic juices that would otherwise be lost. This surgery is performed by a pancreatic surgeon to avoid a life-threatening rupture of the pancreatic pseudocyst.

Kenneth Frank Binmoeller is a medical doctor and author of multiple scientific contributions and over 300 publications, as well as the inventor of the lumen-apposing metal stent (LAMS) and AXIOS System. These are medical devices used to relieve blockages while creating a direct connection between two bodily structures. He practices in the field of Gastroenterology with a specialty of Advanced Endoscopic Intervention. Binmoeller has been published for his innovations in medical devices and training in the field of Endoscopy.
















