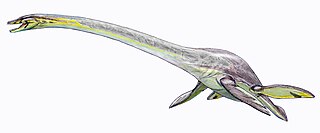
Plesiosauroidea is an extinct clade of carnivorous marine reptiles. They have the snake-like longest neck to body ratio of any reptile. Plesiosauroids are known from the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. After their discovery, some plesiosauroids were said to have resembled "a snake threaded through the shell of a turtle", although they had no shell.

The Trachypachidae are a family of beetles that generally resemble small ground beetles, but that are distinguished by the large coxae of their rearmost legs. There are only six known extant species in the family, with four species of Trachypachus found in northern Eurasia and northern North America, and two species of Systolosoma in Chile and Argentina. They were much more diverse in the past, with dozens of described species from the Mesozoic.

Ichthyornis is an extinct genus of toothy seabird-like ornithuran from the late Cretaceous period of North America. Its fossil remains are known from the chalks of Alberta, Alabama, Kansas, New Mexico, Saskatchewan, and Texas, in strata that were laid down in the Western Interior Seaway during the Turonian through Campanian ages, about 95–83.5 million years ago. Ichthyornis is a common component of the Niobrara Formation fauna, and numerous specimens have been found.

Enchodus is an extinct genus of aulopiform ray-finned fish related to lancetfish and lizardfish. Species of Enchodus flourished during the Late Cretaceous, and there is some evidence that they may have survived to the Paleocene or Eocene; however, this may just represent reworked Cretaceous material.
The Campanian is the fifth of six ages of the Late Cretaceous Epoch on the geologic timescale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). In chronostratigraphy, it is the fifth of six stages in the Upper Cretaceous Series. Campanian spans the time from 83.6 to 72.1 million years ago. It is preceded by the Santonian and it is followed by the Maastrichtian.
Niobrarasaurus is an extinct genus of nodosaurid ankylosaur which lived during the Cretaceous 87 to 82 million years ago. Its fossils were found in the Smoky Hill Chalk Member of the Niobrara Formation, in western Kansas, which would have been near the middle of Western Interior Sea during the Late Cretaceous. It was a nodosaurid, an ankylosaur without a clubbed tail. It was closely related to Nodosaurus.
Eonatator is an extinct genus of marine lizard belonging to the mosasaur family. It is a close relative of Halisaurus, and part of the same subfamily, the Halisaurinae. It is known from the Late Cretaceous of North America, Colombia and Sweden. Originally, this taxon was included within Halisaurus, but was placed in its own genus, which also led to the subfamily Halisaurinae being created for the two genera.

Protosphyraena is a fossil genus of swordfish-like marine fish, that thrived worldwide during the Cretaceous period (Albian-Maastrichtian). Fossil remains of this taxon are mainly discovered in North America and Europe, and potential specimens are also known from Asia, Africa and Australia. Its fossils are best known from the Smoky Hill Member of the Niobrara Chalk Formation of Kansas.

Baptornis is a genus of flightless, aquatic birds from the Late Cretaceous, some 87-80 million years ago. The fossils of Baptornis advenus, the type species, were discovered in Kansas, which at its time was mostly covered by the Western Interior Seaway, a shallow shelf sea. It is now known to have also occurred in today's Sweden, where the Turgai Strait joined the ancient North Sea; possibly, it occurred in the entire Holarctic.

Dolichorhynchops is an extinct genus of polycotylid plesiosaur from the Late Cretaceous of North America, containing the species D. osborni and D. herschelensis, with two previous species having been assigned to new genera. Definitive specimens of D. osborni have been found in the late Coniacian to early Campanian rocks, while those of D. herschelensis have been found in the late Campanian to early Maastrichtian rocks. Dolichorhynchops was a prehistoric marine reptile measuring around 3 metres (9.8 ft) long. Its Greek generic name means "long-nosed face".

Coilopoceratidae is a family of generally large, proper ammonites with strongly involute shells from the Cretaceous, Albian to Turonian. Coilopoceratids have variably compressed shells with flattish to broadly rounded sides and narrowly rounded to sharp keel-like venters. Whorl sections are generally lanceolate. The suture is ammonitic with an overall clumpy appearance.

Brachauchenius is an extinct genus of pliosaurs that lived during the Late Cretaceous in what are now North America and North Africa. Only one species is known, B. lucasi, initially described by Samuel Wendell Williston in 1903 from a partial fossil skeleton discovered in a quarry in Kansas, United States. Many other fossil specimens attributed to the species were subsequently discovered, including an individual from Morocco whose presence was made official in 2016. Many contemporary pliosaur specimens were formerly attributed to Brachauchenius, but have since been reidentified as belonging to other genera or are recognized as indeterminate.

The Craniidae are a family of brachiopods, the only surviving members of the subphylum Craniiformea. They are the only members of the order Craniida, the monotypic suborder Craniidina, and the superfamily Cranioidea; consequently, the latter two taxa are at present redundant and rarely used.There are three living genera within Craniidae: Neoancistrocrania, Novocrania, and Valdiviathyris. As adults, craniids either live freely on the ocean floor or, more commonly, cement themselves onto a hard object with all or part of the ventral valve.

Styxosaurus is a genus of plesiosaur of the family Elasmosauridae. Styxosaurus lived during the Campanian age of the Cretaceous period. Three species are known: S. snowii, S. browni, and S. rezaci.

Ptychodus is a genus of extinct large durophagous (shell-crushing) lamniform sharks from the Cretaceous period, spanning from the Albian to the Campanian. Fossils of Ptychodus teeth are found in many Late Cretaceous marine sediments worldwide.

The Pierre Shale is a geologic formation or series in the Upper Cretaceous which occurs east of the Rocky Mountains in the Great Plains, from Pembina Valley in Canada to New Mexico.
The Demopolis Chalk is a geological formation in North America, within the U.S. states of Alabama, Mississippi, and Tennessee. The chalk was formed by pelagic sediments deposited along the eastern edge of the Mississippi embayment during the middle Campanian age of the Late Cretaceous. It is a unit of the Selma Group and consists of the upper Bluffport Marl Member and a lower unnamed member. Dinosaur and mosasaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the Demopolis Chalk.

Perisphinctoidea, formerly Perisphinctaceae, is a superfamily of Middle Jurassic (Bajocian) to Lower Cretaceous (Barremian) ammonites, commonly with evolute shells with strong ribbing that typically divides about mid flank before crossing the venter.

The Benton Shale is a geologic formation name historically used in Montana, Wyoming, North Dakota, South Dakota, Colorado, Kansas, and Nebraska. In the "mile high" plains in the center of the continent, the named layers preserve marine fossils from the Late Cretaceous Period. The term Benton Limestone has also been used to refer to the chalky portions of the strata, especially the beds of the strata presently classified as Greenhorn Limestone, particularly the Fencepost limestone.

Inoceramus cuvieri is an extinct species of the extinct genus Inoceramus of Bivalve mollusks that serves as an index fossil of chalky rocks of Turonian age of the Cretaceous Period in Europe and North America.
















