
A chordate is a deuterostomal bilaterian animal belonging to the phylum Chordata. All chordates possess, at some point during their larval or adult stages, five distinctive physical characteristics (synapomorphies) that distinguish them from other taxa. These five synapomorphies are a notochord, a hollow dorsal nerve cord, an endostyle or thyroid, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anal tail.

A flatfish is a member of the ray-finned demersal fish order Pleuronectiformes, also called the Heterosomata, sometimes classified as a suborder of Perciformes. In many species, both eyes lie on one side of the head, one or the other migrating through or around the head during development. Some species face their left sides upward, some face their right sides upward, and others face either side upward.

Gnathostomata are the jawed vertebrates. Gnathostome diversity comprises roughly 60,000 species, which accounts for 99% of all living vertebrates, including humans. Most gnathostomes have retained ancestral traits like true teeth, a stomach, and paired appendages. Other traits are elastin, a horizontal semicircular canal of the inner ear, myelin sheaths of neurons, and an adaptive immune system which has discrete lymphoid organs, and uses V(D)J recombination to create antigen recognition sites, rather than using genetic recombination in the variable lymphocyte receptor gene.

Vertebrate paleontology is the subfield of paleontology that seeks to discover, through the study of fossilized remains, the behavior, reproduction and appearance of extinct vertebrates. It also tries to connect, by using the evolutionary timeline, the animals of the past and their modern-day relatives.

A transitional fossil is any fossilized remains of a life form that exhibits traits common to both an ancestral group and its derived descendant group. This is especially important where the descendant group is sharply differentiated by gross anatomy and mode of living from the ancestral group. These fossils serve as a reminder that taxonomic divisions are human constructs that have been imposed in hindsight on a continuum of variation. Because of the incompleteness of the fossil record, there is usually no way to know exactly how close a transitional fossil is to the point of divergence. Therefore, it cannot be assumed that transitional fossils are direct ancestors of more recent groups, though they are frequently used as models for such ancestors.

Placoderms are vertebrate animals of the class Placodermi, an extinct group of prehistoric fish known from Paleozoic fossils during the Silurian and the Devonian periods. While their endoskeletons are mainly cartilaginous, their head and thorax were covered by articulated armoured plates, and the rest of the body was scaled or naked depending on the species.

"Labyrinthodontia" is an informal grouping of extinct predatory amphibians which were major components of ecosystems in the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. Traditionally considered a subclass of the class Amphibia, modern classification systems recognize that labyrinthodonts are not a formal natural group (clade) exclusive of other tetrapods. Instead, they consistute an evolutionary grade, ancestral to living tetrapods such as lissamphibians and amniotes. "Labyrinthodont"-grade vertebrates evolved from lobe-finned fishes in the Devonian, though a formal boundary between fish and amphibian is difficult to define at this point in time.

Mesonychia is an extinct taxon of small- to large-sized carnivorous ungulates related to artiodactyls. Mesonychians first appeared in the early Paleocene, went into a sharp decline at the end of the Eocene, and died out entirely when the last genus, Mongolestes, became extinct in the early Oligocene. In Asia, the record of their history suggests they grew gradually larger and more predatory over time, then shifted to scavenging and bone-crushing lifestyles before the group became extinct.

Pakicetus is an extinct genus of amphibious cetacean of the family Pakicetidae, which was endemic to Indian Subcontinent during the Ypresian period, about 50 million years ago. It was a wolf-like mammal, about 1–2 m long, and lived in and around water where it ate fish and other animals. The name Pakicetus comes from the fact that the first fossils of this extinct amphibious whale were discovered in Pakistan. The vast majority of paleontologists regard it as the most basal whale, representing a transitional stage between land mammals and whales. It belongs to the even-toed ungulates with the closest living non-cetacean relative being the hippopotamus.

Tiktaalik is a monospecific genus of extinct sarcopterygian from the Late Devonian Period, about 375 Mya, having many features akin to those of tetrapods. Tiktaalik is estimated to have had a total length of 1.25–2.75 metres (4.1–9.0 ft) on the basis of various specimens.

Eobothus is an extinct genus of flatfish known from China, India and Europe. Its geological range extend through part of the Eocene: some studies date it to the Ypresian stage, while others date it to the Lutetian.
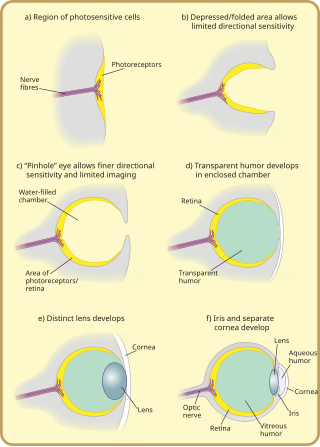
Many scientists have found the evolution of the eye attractive to study because the eye distinctively exemplifies an analogous organ found in many animal forms. Simple light detection is found in bacteria, single-celled organisms, plants and animals. Complex, image-forming eyes have evolved independently several times.

Ichthyolestes is an extinct genus of archaic cetacean that was endemic to Indo-Pakistan during the Lutetian stage. To date, this monotypic genus is only represented by Ichthyolestes pinfoldi.

Pezosiren portelli, also known as the "walking manatee", is a basal sirenian from the early Eocene of Jamaica, 50 million years ago. The type specimen is represented by a Jamaican fossil skeleton, described in 2001 by Daryl Domning, a marine mammal paleontologist at Howard University in Washington, DC. It is believed to have had a hippopotamus-like amphibious lifestyle, and is considered a transitional form between land and sea mammals.

Metaspriggina is a genus of chordate initially known from two specimens in the Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale and 44 specimens found in 2012 at the Marble Canyon bed in Kootenay National Park.

Amphistium paradoxum, the only species classified under the genus Amphistium and the family Amphistiidae, is a fossil fish which has been identified as a Paleogene relative of the flatfish, and as a transitional fossil. In a typical modern flatfish, the head is asymmetric with both eyes on one side of the head. In Amphistium, the transition from the typical symmetric head of a vertebrate is incomplete, with one eye placed near the top of the head.

The evolution of fish began about 530 million years ago during the Cambrian explosion. It was during this time that the early chordates developed the skull and the vertebral column, leading to the first craniates and vertebrates. The first fish lineages belong to the Agnatha, or jawless fish. Early examples include Haikouichthys. During the late Cambrian, eel-like jawless fish called the conodonts, and small mostly armoured fish known as ostracoderms, first appeared. Most jawless fish are now extinct; but the extant lampreys may approximate ancient pre-jawed fish. Lampreys belong to the Cyclostomata, which includes the extant hagfish, and this group may have split early on from other agnathans.

Entelognathus primordialis is an early placoderm from the late Silurian of Qujing, Yunnan, 419 million years ago.
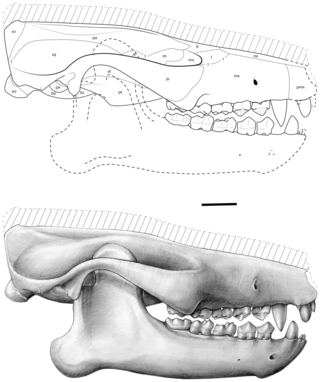
Ocepeia is an extinct genus of afrotherian mammal that lived in present-day Morocco during the middle Paleocene epoch, approximately 60 million years ago. First named and described in 2001, the type species is O. daouiensis from the Selandian stage of Morocco's Ouled Abdoun Basin. A second, larger species, O. grandis, is known from the Thanetian, a slightly younger stage in the same area. In life, the two species are estimated to have weighed about 3.5 kg (7.7 lb) and 10 kg (22 lb), respectively, and are believed to have been specialized leaf-eaters. The fossil skulls of Ocepeia are the oldest known afrotherian skulls, and the best-known of any Paleocene mammal in Africa.

Phocavis is an extinct genus of flightless seabird, belonging to the family Plotopteridae, and distantly related with modern cormorants. Its fossils, found in the Keasey Formation in Oregon, are dated from the Late Eocene.



















