
Coffea is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae. Coffea species are shrubs or small trees native to tropical and southern Africa and tropical Asia. The seeds of some species, called coffee beans, are used to flavor various beverages and products. The fruits, like the seeds, contain a large amount of caffeine, and have a distinct sweet taste.

Venom or zootoxin is a type of toxin produced by an animal that is actively delivered through a wound by means of a bite, sting, or similar action. The toxin is delivered through a specially evolved venom apparatus, such as fangs or a stinger, in a process called envenomation. Venom is often distinguished from poison, which is a toxin that is passively delivered by being ingested, inhaled, or absorbed through the skin, and toxungen, which is actively transferred to the external surface of another animal via a physical delivery mechanism.

Rubiaceae is a family of flowering plants, commonly known as the coffee, madder, or bedstraw family. It consists of terrestrial trees, shrubs, lianas, or herbs that are recognizable by simple, opposite leaves with interpetiolar stipules and sympetalous actinomorphic flowers. The family contains about 14,100 species in about 580 genera, which makes it the fourth-largest angiosperm family. Rubiaceae has a cosmopolitan distribution; however, the largest species diversity is concentrated in the tropics and subtropics. Economically important genera include Coffea, the source of coffee; Cinchona, the source of the antimalarial alkaloid quinine; ornamental cultivars ; and historically some dye plants.

Colubridae is a family of snakes. With 249 genera, it is the largest snake family. The earliest fossil species of the family date back to the Late Eocene epoch, with earlier origins suspected. Colubrid snakes are found on every continent except Antarctica.

Latrodectus is a broadly distributed genus of spiders with several species that are commonly known as the true widows. This group is composed of those often loosely called black widow spiders, brown widow spiders, and similar spiders. However, the diversity of species is much greater. A member of the family Theridiidae, this genus contains 34 species, which include several North American "black widows". Besides these, North America also has the red widow Latrodectus bishopi and the brown widow Latrodectus geometricus, which, in addition to North America, has a much wider geographic distribution. Elsewhere, others include the European black widow, the Australian redback spider and the closely related New Zealand katipō, several different species in Southern Africa that can be called button spiders, and the South American black-widow spiders. Species vary widely in size. In most cases, the females are dark-coloured and can be readily identified by reddish markings on the central underside (ventral) abdomen, which are often hourglass-shaped.

Liolaemus is a genus of iguanian lizards, containing many species, all of which are endemic to South America.

Coffea canephora is a species of coffee plant that has its origins in central and western sub-Saharan Africa. It is a species of flowering plant in the family Rubiaceae. Though widely known as Coffea robusta, the plant is scientifically identified as Coffea canephora, which has two main varieties, robusta and nganda.

Nesohedyotis is a genus of flowering plants endemic to the island of Saint Helena in the South Atlantic Ocean. It in the family Rubiaceae.

Schumanniophyton problematicum is a species of plant in the family Rubiaceae. It is found in Ivory Coast, Ghana, and Sierra Leone. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Tityus is a large genus of thick-tailed scorpions, the namesake of its subfamily Tityinae. As of 2021, Tityus contains more than 220 described species distributed in Central America and South America, from Costa Rica to Argentina. Species in the genus Tityus have been studied for hundreds of years, long before the taxonomic classification was put in place. Tityus tend to be of medium size for scorpions, roughly 50 to 70 millimeters long. They are dark brown or red in color, and can exhibit sexual dimorphism. They can live in a variety of environments, ranging from urban to arid mountains to the Amazon Rainforest. Tityus scorpions are best known for their venom and potent sting. The genus contains several dangerously venomous scorpions, the best known of which is the Brazilian yellow scorpion, T. serrulatus. Its venom can cause severe illness, and in the young, old and infirm even death. Some experts have argued that the genus as a whole may be paraphyletic, which could explain the knowledge gaps related to Tityus.

The People's Democratic Republic of Algeria and the Argentine Republic are members of the Group of 15, Group of 24, Group of 77 and the United Nations.
The Santacrucian age is a period of geologic time within the Early Miocene epoch of the Neogene, used more specifically with SALMA classification in South America. It follows the Colhuehuapian and precedes the Friasian age.
Pao turgidus is a species of freshwater pufferfish native to the Mekong basin. It may also occur in the Chao Phraya basin in Thailand. This species grows to a length of 18.5 centimetres (7.3 in) SL.

Azaspiracids (AZA) are a group of polycyclic ether marine algal toxins produced by the small dinoflagellate Azadinium spinosum that can accumulate in shellfish and thereby cause illness in humans.

Reina de corazones is an American telenovela produced by Joshua Mintz and Aurelio Valcárcel Carroll for Telemundo.
Bendita mentira is a Mexican telenovela produced by Carlos Moreno Laguillo for Televisa in 1996. On August 5, 1996, Canal de las Estrellas started broadcasting Bendita mentira weekdays at 5:00pm, replacing Para toda la vida. The last episode was broadcast on December 6, 1996 with Luz Clarita replacing it the following day.

Brother and Sister is a 2010 Argentine comedy film directed by Daniel Burman.
Omo Forest Reserve is a preserved area of tropical rainforest in Ogun state, in the south-western part of Nigeria. It is located about 135 km (84 mi) northeast of Lagos and 80 km (50 mi) east of Ijebu Ode. This nature reserve covers an area of 130,500 hectares. The average rainfall is around 2,000 mm (80 in). The terrain is largely flat and well-drained, with some low rolling hills, and forms part of the Omo River watershed.
Epipeltephilus is an extinct genus of armadillo, belonging to the family Peltephilidae, the "horned armadillos", whose most famous relative was Peltephilus. Epipeltephilus is the last known member of its family, becoming extinct during the Chasicoan period. It was found in the Rio Mayo Formation and the Arroyo Chasicó Formation of Argentina, and in northern Chile.
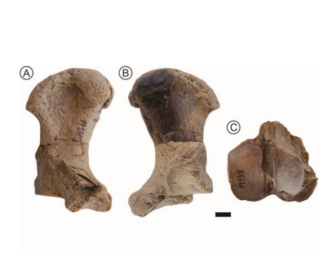
Prepoplanops is an extinct genus of ground sloth of the family Megatheriidae. It lived in the Miocene around 18 to 16 million years ago of what is now Argentina. The only known species is Prepoplanops boleadorensis.















