
A Petoskey stone is a rock and a fossil, often pebble-shaped, that is composed of a fossilized rugose coral, Hexagonaria percarinata. Such stones were formed as a result of glaciation, in which sheets of ice plucked stones from the bedrock, grinding off their rough edges and depositing them in the northwestern portion of Michigan's lower peninsula. In those same areas of Michigan, complete fossilized coral colony heads can be found in the source rocks for the Petoskey stones.
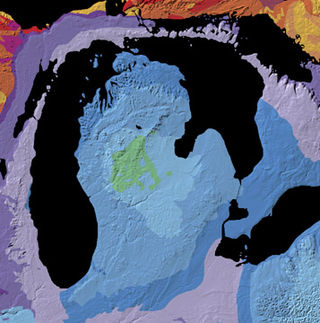
The Michigan Basin is a geologic basin centered on the Lower Peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan. The feature is represented by a nearly circular pattern of geologic sedimentary strata in the area with a nearly uniform structural dip toward the center of the peninsula.

Eldredgeops is a genus of trilobites in the order Phacopida, family Phacopidae, known from the late Middle and earliest Upper Devonian of Morocco and the USA.

The Marcellus Formation or the Marcellus Shale is a Middle Devonian age unit of sedimentary rock found in eastern North America. Named for a distinctive outcrop near the village of Marcellus, New York, in the United States, it extends throughout much of the Appalachian Basin.

Coralville Lake is an artificial lake in Johnson County, Iowa, United States, formed by the Coralville Dam, a dam built from 1949 to 1958 on the Iowa River upstream from the city of Coralville, Iowa.

Holonema is an extinct genus of relatively large, barrel-shaped arthrodire placoderms that were found in oceans throughout the world from the Mid to Late Devonian, when the last species perished in the Frasnian-Fammian extinction event. Most species of the genus are known from fragments of their armor, but the Gogo Reef species, H. westolli, is known from whole, articulated specimens.
Lithographic limestone is hard limestone that is sufficiently fine-grained, homogeneous and defect free to be used for lithography.

The Columbus Limestone is a mapped bedrock unit consisting primarily of fossiliferous limestone, and it occurs in Ohio, Pennsylvania, and Virginia in the United States, and in Ontario, Canada.

Berea Sandstone, also known as Berea Grit, is a sandstone formation in the U.S. states of Michigan, Ohio, Pennsylvania, West Virginia, and Kentucky. It is named after Berea, Ohio. The sandstone has been used as a building stone and is a source of oil and gas.

The Devonian Jeffersonville Limestone is a mapped bedrock unit in Indiana and Kentucky. It is highly fossiliferous.
Paleontology in Michigan refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of Michigan. During the Precambrian, the Upper Peninsula was home to filamentous algae. The remains it left behind are among the oldest known fossils in the world. During the early part of the Paleozoic Michigan was covered by a shallow tropical sea which was home to a rich invertebrate fauna including brachiopods, corals, crinoids, and trilobites. Primitive armored fishes and sharks were also present. Swamps covered the state during the Carboniferous. There are little to no sedimentary deposits in the state for an interval spanning from the Permian to the end of the Neogene. Deposition resumed as glaciers transformed the state's landscape during the Pleistocene. Michigan was home to large mammals like mammoths and mastodons at that time. The Holocene American mastodon, Mammut americanum, is the Michigan state fossil. The Petoskey stone, which is made of fossil coral, is the state stone of Michigan.

Paleontology in Wisconsin refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of Wisconsin. The state has fossils from the Precambrian, much of the Paleozoic, some a parts of the Mesozoic and the later part of the Cenozoic. Most of the Paleozoic rocks are marine in origin. Because of the thick blanket of Pleistocene glacial sediment that covers the rock strata in most of the state, Wisconsin’s fossil record is relatively sparse. In spite of this, certain Wisconsin paleontological occurrences provide exceptional insights concerning the history and diversity of life on Earth.
The Traverse Group is a geologic group in Michigan, Indiana and Ohio comprising middle Devonian limestones with calcareous shale components. Its marine fossils notably include Michigan's state stone, the Petoskey stone, among other corals and records of ancient marine life. A range of trilobites has also been found in the Traverse Group.

The Four Mile Dam Formation, also called the Four Mile Dam Limestone, is a geologic formation in Michigan. It preserves fossils dating back to the middle Devonian period.

The Gravel Point Formation is a geologic formation in western Michigan. It preserves fossils dating back to the middle Devonian period and correlates with the Long Lake Limestone and Alpena Limestone.

The Norway Point Formation is a geologic formation in Michigan. It preserves fossils dating back to the middle Devonian period.

The Thunder Bay Limestone is a geologic formation in Michigan. It preserves fossils dating back to the Devonian period.

The Milwaukee Formation is a fossil-bearing geological formation of Middle Devonian age in Milwaukee County, Wisconsin. It stands out for the exceptional diversity of its fossil biota. Included are many kinds of marine protists, invertebrates, and fishes, as well as early trees and giant fungi.

Ptyctodus is an extinct armour-plated fish of the late Devonian. Ptyctodus belongs to the family Ptyctodontidae and is of the class Placodermi. They share a close resemblance to modern day chimaeras (Holocephali). Fossils of this armour-plated fish have been found in locations such as in Russia, the Michigan Basis, and Arizona, United States.
Tabulophyllum is an extinct genus of horn coral belonging to the order Stariidae and family Kyphophyllidae. Specimens have been found in Devonian beds in Australia North America, and most other major areas of Devonian outcrops. The genus was highly adaptable to a variety of substrates, including muddy, sandy, and firm substrates. The genus had a low-magnesium calcite skeleton and may have flourished in times of "calcite seas". There is evidence from fossil reefs in the Onate Formation of New Mexico, US that the genus favored the receptaculitid Sphaerospongia as a firm substrate for growth.



















