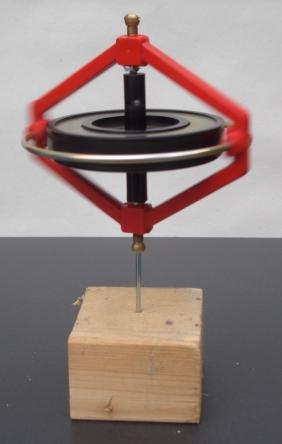
Angular momentum is the rotational analog of linear momentum. It is an important physical quantity because it is a conserved quantity – the total angular momentum of a closed system remains constant. Angular momentum has both a direction and a magnitude, and both are conserved. Bicycles and motorcycles, flying discs, rifled bullets, and gyroscopes owe their useful properties to conservation of angular momentum. Conservation of angular momentum is also why hurricanes form spirals and neutron stars have high rotational rates. In general, conservation limits the possible motion of a system, but it does not uniquely determine it.
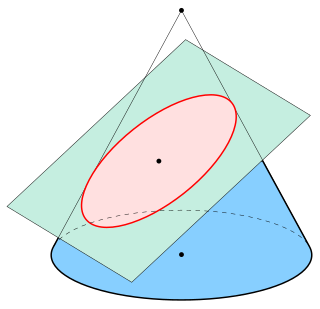
In mathematics, an ellipse is a plane curve surrounding two focal points, such that for all points on the curve, the sum of the two distances to the focal points is a constant. It generalizes a circle, which is the special type of ellipse in which the two focal points are the same. The elongation of an ellipse is measured by its eccentricity , a number ranging from to .

In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the form of energy that it possesses due to its motion.

In Newtonian mechanics, momentum is the product of the mass and velocity of an object. It is a vector quantity, possessing a magnitude and a direction. If m is an object's mass and v is its velocity, then the object's momentum p is: In the International System of Units (SI), the unit of measurement of momentum is the kilogram metre per second (kg⋅m/s), which is dimensionally equivalent to the newton-second.
Power is the amount of energy transferred or converted per unit time. In the International System of Units, the unit of power is the watt, equal to one joule per second. Power is a scalar quantity.

In physics, the special theory of relativity, or special relativity for short, is a scientific theory of the relationship between space and time. In Albert Einstein's 1905 paper, On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies, the theory is presented as being based on just two postulates:
- The laws of physics are invariant (identical) in all inertial frames of reference. This is known as the principle of relativity.
- The speed of light in vacuum is the same for all observers, regardless of the motion of light source or observer. This is known as the principle of light constancy, or the principle of light speed invariance.

In mathematics, a tensor is an algebraic object that describes a multilinear relationship between sets of algebraic objects related to a vector space. Tensors may map between different objects such as vectors, scalars, and even other tensors. There are many types of tensors, including scalars and vectors, dual vectors, multilinear maps between vector spaces, and even some operations such as the dot product. Tensors are defined independent of any basis, although they are often referred to by their components in a basis related to a particular coordinate system; those components form an array, which can be thought of as a high-dimensional matrix.

In electrical engineering, impedance is the opposition to alternating current presented by the combined effect of resistance and reactance in a circuit.

The Boltzmann constant is the proportionality factor that relates the average relative thermal energy of particles in a gas with the thermodynamic temperature of the gas. It occurs in the definitions of the kelvin (K) and the gas constant, in Planck's law of black-body radiation and Boltzmann's entropy formula, and is used in calculating thermal noise in resistors. The Boltzmann constant has dimensions of energy divided by temperature, the same as entropy and heat capacity. It is named after the Austrian scientist Ludwig Boltzmann.
The Schrödinger equation is a partial differential equation that governs the wave function of a non-relativistic quantum-mechanical system. Its discovery was a significant landmark in the development of quantum mechanics. It is named after Erwin Schrödinger, who postulated the equation in 1925 and published it in 1926, forming the basis for the work that resulted in his Nobel Prize in Physics in 1933.
The Black–Scholes or Black–Scholes–Merton model is a mathematical model for the dynamics of a financial market containing derivative investment instruments. From the parabolic partial differential equation in the model, known as the Black–Scholes equation, one can deduce the Black–Scholes formula, which gives a theoretical estimate of the price of European-style options and shows that the option has a unique price given the risk of the security and its expected return. The equation and model are named after economists Fischer Black and Myron Scholes. Robert C. Merton, who first wrote an academic paper on the subject, is sometimes also credited.

In science, work is the energy transferred to or from an object via the application of force along a displacement. In its simplest form, for a constant force aligned with the direction of motion, the work equals the product of the force strength and the distance traveled. A force is said to do positive work if it has a component in the direction of the displacement of the point of application. A force does negative work if it has a component opposite to the direction of the displacement at the point of application of the force.
Some Buddhist terms and concepts lack direct translations into English that cover the breadth of the original term. Below are given a number of important Buddhist terms, short definitions, and the languages in which they appear. In this list, an attempt has been made to organize terms by their original form and give translations and synonyms in other languages along with the definition.

In thermodynamics, the Gibbs free energy is a thermodynamic potential that can be used to calculate the maximum amount of work, other than pressure-volume work, that may be performed by a thermodynamically closed system at constant temperature and pressure. It also provides a necessary condition for processes such as chemical reactions that may occur under these conditions. The Gibbs free energy is expressed asWhere:

In biochemistry, Michaelis–Menten kinetics, named after Leonor Michaelis and Maud Menten, is the simplest case of enzyme kinetics, applied to enzyme-catalysed reactions of one substrate and one product. It takes the form of a differential equation describing the reaction rate to , the concentration of the substrate A. Its formula is given by the Michaelis–Menten equation:
Time dilation is the difference in elapsed time as measured by two clocks, either because of a relative velocity between them, or a difference in gravitational potential between their locations. When unspecified, "time dilation" usually refers to the effect due to velocity.
In fluid dynamics, drag, sometimes referred to as fluid resistance, is a force acting opposite to the relative motion of any object moving with respect to a surrounding fluid. This can exist between two fluid layers, two solid surfaces, or between a fluid and a solid surface. Drag forces tend to decrease fluid velocity relative to the solid object in the fluid's path.
In linear algebra, an eigenvector or characteristic vector is a vector that has its direction unchanged by a given linear transformation. More precisely, an eigenvector, , of a linear transformation, , is scaled by a constant factor, , when the linear transformation is applied to it: . The corresponding eigenvalue, characteristic value, or characteristic root is the multiplying factor .

In electrical engineering, a capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy by accumulating electric charges on two closely spaced surfaces that are insulated from each other. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term still encountered in a few compound names, such as the condenser microphone. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals.
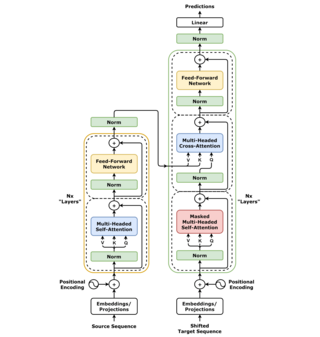
A transformer is a deep learning architecture developed by researchers at Google and based on the multi-head attention mechanism, proposed in the 2017 paper "Attention Is All You Need". Text is converted to numerical representations called tokens, and each token is converted into a vector via lookup from a word embedding table. At each layer, each token is then contextualized within the scope of the context window with other (unmasked) tokens via a parallel multi-head attention mechanism, allowing the signal for key tokens to be amplified and less important tokens to be diminished.













