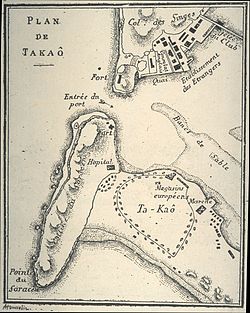
The written history of Kaohsiung can be traced back to the early 17th century, though archeological studies have found signs of human activity in the region from as long as 7000 years ago. Prior to the 17th century, the region was inhabited by the Makatau clan of the Siraya aboriginal tribe, who settled on what they named Ta-kau Isle (translated to 打狗嶼 by Ming Chinese explorers), "Takau" meaning "bamboo forest" in the Siraya language. Dutch settlers colonizing Taiwan in 1624 referred to the region as Tankoya and named the harbor Tancoia.
Contents
- Early history
- Fengbitou ruins
- Taochiyuan ruins
- Pirate records
- Recent settlement and development
- Dutch rule (1624–1661)
- Kingdom of Tungning (1661–1683)
- Qing dynasty rule (1683–1895)
- Japanese rule (1895–1945)
- Postwar period (after 1945)
- Economy
- Cultural and artistic development
- References
- Bibliography
The first Chinese records of the region were written in 1603 by Chen Di, a member of Ming admiral Shen You-rong's expedition to rid the waters around Taiwan and Penghu of wokou pirates. In his report on the "Eastern Barbarian Lands" (Dong Fan Ji), Chen Di referred to Ta-kau Isle as "It is unknown when the barbarians of the Eastern Lands arose on this island in the ocean beyond Penghu".
Various later historical documents of both the Ming and Qing dynasties referred to Kaohsiung as either "Ta-kau" (打狗) or "Ta-ku" (打鼓). The modern name of 高雄 (pronounced "Takao" in Japanese and "Kaohsiung" in Mandarin) was not adopted until the Japanese colonial period in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.



