
The Lacertidae are the family of the wall lizards, true lizards, or sometimes simply lacertas, which are native to Afro-Eurasia. It is a diverse family with at about 360 species in 39 genera. They represent the dominant group of reptiles found in Europe.

Adolfus is a genus of lizards of the family Lacertidae. The genus is endemic to subsaharan Africa.

Gastropholis is a genus of Equatorial African lacertid lizards of the family Lacertidae which is distributed in southern Liberia, Ivory Coast and Ghana, western Cameroon, Equatorial Guinea, Democratic Republic of Congo, eastern Kenya, Tanzania and south to northeastern Mozambique.

Latastia is a genus of lizards of the family Lacertidae. Species of this genus are distributed in Africa but one subspecies lives in Yemen. Collectively, they are known as long-tailed lizards.

Philochortus is a genus of lizards of the family Lacertidae. Species of this genus are distributed in Egypt, Algeria, Libya, Mali, Niger, Ethiopia, Djibouti, Eritrea, Somalia, Kenya, Yemen, and Saudi Arabia.
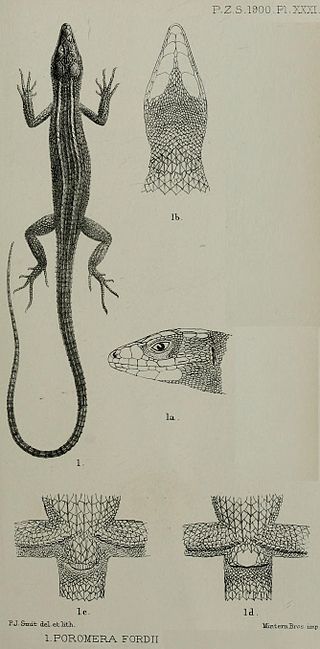
Poromera is a genus of lizard in the family Lacertidae. The genus Poromera is monotypic, containing the single species, Poromera fordii, commonly known as the West African striped lizard. The species is endemic to western Central Africa.

Pseuderemias is a genus of lizards of the family Lacertidae. Common names for the genus are false sand lizards or racerunners.

Calotes calotes, the common green forest lizard, is an agamid lizard found in the forests of the Western Ghats and the Shevaroy Hills in India, and Sri Lanka.

Takydromus sexlineatus, the Asian grass lizard, six-striped long-tailed grass lizard, or long-tailed grass lizard, is an arboreal, diurnal species of lizard. The tail length is usually over three times the body length in this species.

Bosc's fringe-toed lizard or Bosk's [sic] fringe-fingered lizard is a species of lizard in the family Lacertidae. The species is endemic to North Africa and Western Asia. Three subspecies are sometimes recognised; A. boskianus boskianus, from Lower Egypt; A. boskianus euphraticus from Iraq; and A. boskianus asper from the rest of the range; however this division is unsatisfactory because each subspecies has much variation and the differences between them are not consistent.

Dendrelaphis schokari, also known as the common bronze-back or Schokar's bronzeback, is a species of non-venomous arboreal snake in the family Colubridae. The species is endemic to Sri Lanka.

Ichnotropis capensis is a species of African lizard, which is native to the southern Afrotropics. It is the type species for the genus Ichnotropis, and is commonly called the Cape rough-scaled lizard due to them being found in southern Africa's Cape region. They are also called ornate rough-scaled lizard or Smith's rough-scaled sand lizard. The small lizards are terrestrial and occur in grassland, desert and brush areas of southern Africa.

Meroles squamulosa is a species of African lizard originally placed in the genus Ichnotropis, however phylogenetic evidence moves this species to the genus Meroles. The species is commonly called the common rough-scaled lizard or savanna lizard. It is largely found in southern Africa. These lizards are terrestrial and found in the range of mesic savannah. The common rough-scaled lizard is medium in size and well distributed in parts of Namibia, Botswana, Zimbabwe, Angola, Tanzania, and Zambia.
Ichnotropis grandiceps is a species of African lizards in the family Lacertidae. They are commonly called Caprivi rough-scaled lizards as they are largely found in southwestern Africa on the border of the Caprivi Strip. The cape rough-scaled lizards are terrestrial and found in the range of open woodland and mesic savanna. The caprivi rough-scaled lizards are medium in size and distributed in parts of Namibia and Botswana. This species is on the International Union for Conservation of Nature's Red List for endangered species as they are rare and has not been seen or collected since 1998. Data about the population or specimens collected are needed for the IUCN to obtain more information about the unknown threats that may be impacting them.
Ichnotropis microlepidota is a species of African lizard in the family Lacertidae. It is commonly called Marx's rough-scaled lizard and is endemic to Angola. I. microlepidota is a terrestrial lizard and was first discovered at the foot of Mount Moco.

Congolacerta is a genus of equatorial African lacertids of the family Lacertidae. Species of this genus are distributed in western East Africa.

Eremias persica, the Aralo-Caspian racerunner or Persian racerunner, is a species of lizard native to Iranian Azerbaijan, most of Iran, southern Turkmenistan, Afghanistan, and western Pakistan. Eremias intermedia is also known as the Aralo-Caspian racerunner.

Holaspis guentheri, also commonly known as the neon blue-tailed tree lizard, the sawtail lizard, and the western neon blue-tailed tree lizard is a species of lizard in the family Lacertidae. The species is native to portions of West Africa and Central Africa.

Holaspis laevis, commonly known as the eastern serrate-toed tree lizard or eastern neon blue-tailed tree lizard is a species of lizard occurring in Sierra Leone, Ghana, Nigeria, Cameroon, Equatorial Guinea, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Uganda, Tanzania, Malawi, and Mozambique. H. laevis was formerly only a subspecies of H. guentheri.
Atractus guentheri, also known commonly as Günther's ground snake and coral-falsa in Brazilian Portuguese, is a species of snake in the subfamily Dipsadinae of the family Colubridae. The species is endemic to Brazil.























