
Megara Hyblaea – perhaps identical with Hybla Major – is an ancient Greek colony of Magna Graecia in Sicily, situated near Augusta on the east coast, 20 kilometres (12 mi) north-northwest of Syracuse, Italy, on the deep bay formed by the Xiphonian promontory. There were at least three cities named "Hybla" in ancient accounts of Sicily which are often confounded with each other, and among which it is sometimes very difficult to distinguish.

Augusta is a town and comune in the province of Syracuse, located on the eastern coast of Sicily. The city is one of the main harbours in Italy, especially for oil refineries which are in its vicinity.

Hyblaeidae are the "teak moths", a family of insects in the Lepidopteran order. The two genera with about 18 species make up one of the two families of the Hyblaeoidea superfamily, which in the past has been included in the Pyraloidea. Recent phylogenetic studies find varying relationships of Hyblaeoidea among Ditrysian Lepidoptera: Mutanen et al. (2010) find the superfamily to group either with Pyraloidea, or – more often – with Thyridoidea or butterflies. The results of Wahlberg et al. (2013) and Heikilä et al. (2015) indicate a sister-group relationship with Pyraloidea.
Hybla Heraea or Hybla Hera was an ancient city of Sicily; its site is at the modern località of Ibla, in the comune of Ragusa. There were at least three cities named "Hybla" in ancient accounts of Sicily which are often confounded with each other, and which it is sometimes very difficult to distinguish.
Hybla Major or Hybla Magna – the "Greater Hybla" – was a name used to identify the most important of the ancient cities named Hybla in Magna Graecia in Sicily.

Hyblaea puera, the teak defoliator, is a moth and cryptic species complex native to South Asia and South-east Asia. It was first described by Pieter Cramer in 1777. The species has also been recently reported to be present in Central America and Africa. The caterpillar feeds on teak and other trees. It is considered to be one of the major teak pests around the world.

Hyblaea is a genus of moths of the family Hyblaeidae first described by Johan Christian Fabricius in 1793.

Hyblaea constellata is a moth in the family Hyblaeidae first described by Achille Guenée in 1852. It is found in India, Sri Lanka, south-east Asia, including China, Japan, Taiwan, Myanmar and Thailand. It is also found in Queensland, Australia.

Hyblaea ibidias is a moth in the family Hyblaeidae. It is found in New South Wales, Australia.

The Museo Archeologico Regionale Paolo Orsi of Syracuse, Sicily is one of the principal archaeological museums of Europe.
Hyblaea bohemani is a moth in the family Hyblaeidae described by Wallengren in 1856.
Hyblaea erycinoides is a moth in the family Hyblaeidae described by Francis Walker in 1858.
Hyblaea euryzona is a moth in the family Hyblaeidae described by Prout in 1921.
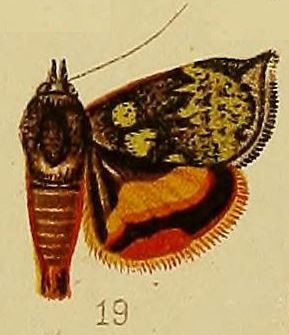
Hyblaea flavipicta is a moth in the family Hyblaeidae described by George Hampson in 1910. A material sample of it was found on the southeast coast of Kenya.
Hyblaea fortissima is a moth in the family Hyblaeidae described by Butler in 1881.
Hyblaea occidentalium is a moth in the family Hyblaeidae described by William Jacob Holland in 1894.
Hyblaea sanguinea is a moth in the family Hyblaeidae described by Max Gaede in 1917.
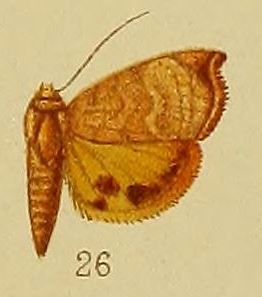
Hyblaea xanthia is a moth in the family Hyblaeidae described by George Hampson in 1910. It is found in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (Katanga), the Seychelles (Aldabra), South Africa and Zambia.






