
Biology – The natural science that studies life. Areas of focus include structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy.

Cnidaria is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic animals found both in fresh water and marine environments, including jellyfish, hydroids, sea anemones, corals and some of the smallest marine parasites. Their distinguishing features are a decentralized nervous system distributed throughout a gelatinous body and the presence of cnidocytes or cnidoblasts, specialized cells with ejectable flagella used mainly for envenomation and capturing prey. Their bodies consist of mesoglea, a non-living, jelly-like substance, sandwiched between two layers of epithelium that are mostly one cell thick. Cnidarians are also some of the only animals that can reproduce both sexually and asexually.
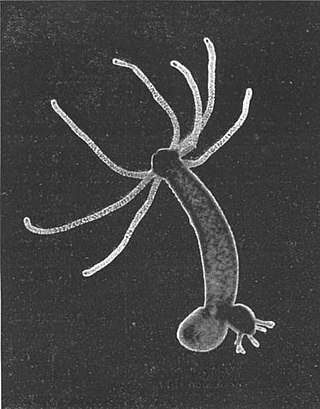
Hydra is a genus of small freshwater hydrozoans of the phylum Cnidaria. They are native to the temperate and tropical regions. The genus was named by Linnaeus in 1758 after the Hydra, which was the many-headed beast of myth defeated by Heracles, as when the animal has a part severed, it will regenerate much like the mythical hydra’s heads. Biologists are especially interested in Hydra because of their regenerative ability; they do not appear to die of old age, or to age at all.

A polyp in zoology is one of two forms found in the phylum Cnidaria, the other being the medusa. Polyps are roughly cylindrical in shape and elongated at the axis of the vase-shaped body. In solitary polyps, the aboral end is attached to the substrate by means of a disc-like holdfast called a pedal disc, while in colonies of polyps it is connected to other polyps, either directly or indirectly. The oral end contains the mouth, and is surrounded by a circlet of tentacles.

Jellyfish, also known as sea jellies, are the medusa-phase of certain gelatinous members of the subphylum Medusozoa, which is a major part of the phylum Cnidaria.
Senescence or biological aging is the gradual deterioration of functional characteristics in living organisms. Whole organism senescence involves an increase in death rates and/or a decrease in fecundity with increasing age, at least in the later part of an organism's life cycle. However, the resulting effects of senescence can be delayed. The 1934 discovery that calorie restriction can extend lifespans by 50% in rats, the existence of species having negligible senescence, and the existence of potentially immortal organisms such as members of the genus Hydra have motivated research into delaying senescence and thus age-related diseases. Rare human mutations can cause accelerated aging diseases.

Hydrozoa is a taxonomic class of individually very small, predatory animals, some solitary and some colonial, most of which inhabit saline water. The colonies of the colonial species can be large, and in some cases the specialized individual animals cannot survive outside the colony. A few genera within this class live in freshwater habitats. Hydrozoans are related to jellyfish and corals and belong to the phylum Cnidaria.

A nerve net consists of interconnected neurons lacking a brain or any form of cephalization. While organisms with bilateral body symmetry are normally associated with a condensation of neurons or, in more advanced forms, a central nervous system, organisms with radial symmetry are associated with nerve nets, and are found in members of the Ctenophora, Cnidaria, and Echinodermata phyla, all of which are found in marine environments. In the Xenacoelomorpha, a phylum of bilaterally symmetrical animals, members of the subphylum Xenoturbellida also possess a nerve net. Nerve nets can provide animals with the ability to sense objects through the use of the sensory neurons within the nerve net.

Budding or blastogenesis is a type of asexual reproduction in which a new organism develops from an outgrowth or bud due to cell division at one particular site. For example, the small bulb-like projection coming out from the yeast cell is known as a bud. Since the reproduction is asexual, the newly created organism is a clone and excepting mutations is genetically identical to the parent organism. Organisms such as hydra use regenerative cells for reproduction in the process of budding.

Siphonophorae is an order within Hydrozoa, which is a class of marine organisms within the phylum Cnidaria. According to the World Register of Marine Species, the order contains 175 species described thus far.
Biological immortality is a state in which the rate of mortality from senescence is stable or decreasing, thus decoupling it from chronological age. Various unicellular and multicellular species, including some vertebrates, achieve this state either throughout their existence or after living long enough. A biologically immortal living being can still die from means other than senescence, such as through injury, poison, disease, predation, lack of available resources, or changes to environment.

Gonionemus is a genus of hydrozoans that uses adhesive discs near the middle of each tentacle to attach to eelgrass, sea lettuce, or various types of algae instead of swimming. They are small and hard to see when hanging onto swaying seaweed. Nevertheless, they are capable of swimming when necessary. The bell is transparent, revealing the four orange to yellowish-tan gonads that lie along most of the length of the four radial canals. The pale yellow manubrium has four short, frilly lips. Up to 80 tentacles line the bell margin, with about an equal number of statocysts. Copepods are a favored prey.

Hydra oligactis, also known as the brown hydra, is a species of hydra found widely dispersed in the northern temperate zone. It is a common organism found in still waters from early Spring to late Autumn.

Negligible senescence is a term coined by biogerontologist Caleb Finch to denote organisms that do not exhibit evidence of biological aging (senescence), such as measurable reductions in their reproductive capability, measurable functional decline, or rising death rates with age. There are many species where scientists have seen no increase in mortality after maturity. This may mean that the lifespan of the organism is so long that researchers' subjects have not yet lived up to the time when a measure of the species' longevity can be made. Turtles, for example, were once thought to lack senescence, but more extensive observations have found evidence of decreasing fitness with age.
Vallentinia gabriellae, the hitch-hiking jellyfish, is a species of small, inconspicuous hydrozoan in the family Olindiidae. It is endemic to a few isolated parts of the western Atlantic Ocean. It is elusive in the wild but sometimes makes its appearance unexpectedly in seawater cultures of other organisms in the laboratory.

The Enthemonae is a suborder of sea anemones in the order Actiniaria. It comprises those sea anemones with typical arrangement of mesenteries for actiniarians.

Turritopsis rubra, commonly referred to as the Crimson Jelly, is a hydrozoan within the family Oceaniidae. The species is native to New Zealand and southern Australia, typically appearing near shorelines in the summer months. The species follows a distribution pattern across the southern Pacific Ocean and can frequently be found in shallow coastal waters.

Hydra viridissima is a species of cnidarian which is commonly found in still or slow-moving freshwater in the Northern temperate zone. Hydra viridissima is commonly called green hydra due to its coloration, which is due to the symbiotic green algae Chlorella vulgaris which live within its body. These creatures are typically 10 mm long and have tentacles that are about half of their length. They are strictly carnivorous and typically feed on small crustaceans, insects and annelids. Hydra are normally sessile and live on aquatic vegetation. They secrete mucous to attach to substrate using their basal disc.

Clava is a monotypic genus of hydrozoans in the family Hydractiniidae. It contains only one accepted species, Clava multicornis. Other names synonymous with Clava multicornis include Clava cornea, Clava diffusa, Clava leptostyla, Clava nodosa, Clava parasitica, Clava squamata, Coryne squamata, Hydra multicornis, and Hydra squamata. The larvae form of the species has a well developed nervous system compared to its small size. The adult form is also advanced due to its ability to stay dormant during unfavorable periods.
Notoplana acticola is a species of flatworms that belongs to Turbellarians. The flatworm is one of the most primitive flatworm that has a brain. This species has the ability to consume prey without a brain present. There is no specific evidence on what the flatworms eat regularly, but some research shows that they may eat limpets. Notoplana acticola are able to ingest food at a rapid rate. Research shows a normal flatworm can ingest one brine shrimp in less than a minute and eat up to 5 shrimp. The amount of shrimp consumed by a decerebrated flatworm is different due to the lack of control.

















