Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase (glutamine-hydrolysing) is an enzyme that catalyzes the reactions that produce carbamoyl phosphate in the cytosol. Its systemic name is hydrogen-carbonate:L-glutamine amido-ligase .
Purine metabolism refers to the metabolic pathways to synthesize and break down purines that are present in many organisms.

Guanosine monophosphate synthetase, also known as GMPS is an enzyme that converts xanthosine monophosphate to guanosine monophosphate.

Phosphoribosylamine (PRA) is a biochemical intermediate in the formation of purine nucleotides via inosine-5-monophosphate, and hence is a building block for DNA and RNA. The vitamins thiamine and cobalamin also contain fragments derived from PRA.
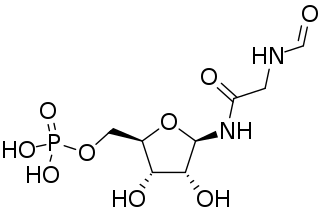
Phosphoribosyl-N-formylglycineamide is a biochemical intermediate in the formation of purine nucleotides via inosine-5-monophosphate, and hence is a building block for DNA and RNA. The vitamins thiamine and cobalamin also contain fragments derived from FGAR.
In enzymology, an adenosylcobyric acid synthase (glutamine-hydrolysing) (EC 6.3.5.10) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an asparaginyl-tRNA synthase (glutamine-hydrolysing) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Cobalt chelatase (EC 6.6.1.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a dihydrofolate synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glutamate—ethylamine ligase (EC 6.3.1.6) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glutaminyl-tRNA synthase (glutamine-hydrolysing) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a NAD+ synthase (glutamine-hydrolysing) (EC 6.3.5.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a phosphoribosylformylglycinamidine synthase (EC 6.3.5.3) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a tetrahydrofolate synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a UDP-N-acetylmuramate—L-alanine ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine—D-glutamate ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

5′-Phosphoribosyl-5-aminoimidazole is a biochemical intermediate in the formation of purine nucleotides via inosine-5-monophosphate, and hence is a building block for DNA and RNA. The vitamins thiamine and cobalamin also contain fragments derived from AIR. It is an intermediate in the adenine pathway and is synthesized from 5′-phosphoribosylformylglycinamidine by AIR synthetase.

Cobalamin biosynthesis is the process by which bacteria and archea make cobalamin, vitamin B12. Many steps are involved in converting aminolevulinic acid via uroporphyrinogen III and adenosylcobyric acid to the final forms in which it is used by enzymes in both the producing organisms and other species, including humans who acquire it through their diet.
Adenosylcobinamide-phosphate synthase is an enzyme with systematic name adenosylcobyric acid:(R)-1-aminopropan-2-yl phosphate ligase (ADP-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Cobyrinate a,c-diamide synthase (EC ), cobyrinic acid a,c-diamide synthetase, CbiA (gene)) is an enzyme which catalyses the chemical reaction









