Related Research Articles

PowerPC is a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architecture (ISA) created by the 1991 Apple–IBM–Motorola alliance, known as AIM. PowerPC, as an evolving instruction set, has been named Power ISA since 2006, while the old name lives on as a trademark for some implementations of Power Architecture–based processors.
The PowerPC 7xx is a family of third generation 32-bit PowerPC microprocessors designed and manufactured by IBM and Motorola. This family is called the PowerPC G3 by Apple Computer, which introduced it on November 10, 1997. The term "PowerPC G3" is often, and incorrectly, imagined to be a microprocessor when in fact a number of microprocessors from different vendors have been used. Such designations were applied to Mac computers such as the PowerBook G3, the multicolored iMacs, iBooks and several desktops, including both the Beige and Blue and White Power Macintosh G3s. The low power requirements and small size made the processors ideal for laptops and the name lived out its last days at Apple in the iBook.
The IBM RS64 is a family of microprocessors used in IBM's RS/6000 and AS/400 servers in the late 1990s.

The PowerPC 970, PowerPC 970FX, and PowerPC 970MP are 64-bit PowerPC processors from IBM introduced in 2002. When used in PowerPC-based Macintosh computers, Apple referred to them as the PowerPC G5.
PowerPC G4 is a designation formerly used by Apple and Eyetech to describe a fourth generation of 32-bit PowerPC microprocessors. Apple has applied this name to various processor models from Freescale, a former part of Motorola. Motorola and Freescale's proper name of this family of processors is PowerPC 74xx.

The POWER4 is a microprocessor developed by International Business Machines (IBM) that implemented the 64-bit PowerPC and PowerPC AS instruction set architectures. Released in 2001, the POWER4 succeeded the POWER3 and RS64 microprocessors, enabling RS/6000 and eServer iSeries models of AS/400 computer servers to run on the same processor, as a step toward converging the two lines. The POWER4 was a multicore microprocessor, with two cores on a single die, the first non-embedded microprocessor to do so. POWER4 Chip was first commercially available multiprocessor chip. The original POWER4 had a clock speed of 1.1 and 1.3 GHz, while an enhanced version, the POWER4+, reached a clock speed of 1.9 GHz. The PowerPC 970 is a derivative of the POWER4.
The PowerPC 400 family is a line of 32-bit embedded RISC processor cores based on the PowerPC or Power ISA instruction set architectures. The cores are designed to fit inside specialized applications ranging from system-on-a-chip (SoC) microcontrollers, network appliances, application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) and field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) to set-top boxes, storage devices and supercomputers.
The megahertz myth, or in more recent cases the gigahertz myth, refers to the misconception of only using clock rate to compare the performance of different microprocessors. While clock rates are a valid way of comparing the performance of different speeds of the same model and type of processor, other factors such as an amount of execution units, pipeline depth, cache hierarchy, branch prediction, and instruction sets can greatly affect the performance when considering different processors. For example, one processor may take two clock cycles to add two numbers and another clock cycle to multiply by a third number, whereas another processor may do the same calculation in two clock cycles. Comparisons between different types of processors are difficult because performance varies depending on the type of task. A benchmark is a more thorough way of measuring and comparing computer performance.

The POWER6 is a microprocessor developed by IBM that implemented the Power ISA v.2.03. When it became available in systems in 2007, it succeeded the POWER5+ as IBM's flagship Power microprocessor. It is claimed to be part of the eCLipz project, said to have a goal of converging IBM's server hardware where practical.
The PowerPC 600 family was the first family of PowerPC processors built. They were designed at the Somerset facility in Austin, Texas, jointly funded and staffed by engineers from IBM and Motorola as a part of the AIM alliance. Somerset was opened in 1992 and its goal was to make the first PowerPC processor and then keep designing general purpose PowerPC processors for personal computers. The first incarnation became the PowerPC 601 in 1993, and the second generation soon followed with the PowerPC 603, PowerPC 604 and the 64-bit PowerPC 620.
Titan was a planned family of 32-bit Power ISA-based microprocessor cores designed by Applied Micro Circuits Corporation (AMCC), but was scrapped in 2010. Applied Micro chose to continue development of the PowerPC 400 core instead, on a 40 nm fabrication process.
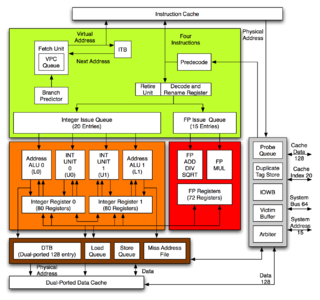
The Alpha 21264 is a Digital Equipment Corporation RISC microprocessor launched on 19 October 1998. The 21264 implemented the Alpha instruction set architecture (ISA).
The SPARC64 V (Zeus) is a SPARC V9 microprocessor designed by Fujitsu. The SPARC64 V was the basis for a series of successive processors designed for servers, and later, supercomputers.

The PA-8000 (PCX-U), code-named Onyx, is a microprocessor developed and fabricated by Hewlett-Packard (HP) that implemented the PA-RISC 2.0 instruction set architecture (ISA). It was a completely new design with no circuitry derived from previous PA-RISC microprocessors. The PA-8000 was introduced on 2 November 1995 when shipments began to members of the Precision RISC Organization (PRO). It was used exclusively by PRO members and was not sold on the merchant market. All follow-on PA-8x00 processors are based on the basic PA-8000 processor core.
The IBM A2 is an open source massively multicore capable and multithreaded 64-bit Power ISA processor core designed by IBM using the Power ISA v.2.06 specification. Versions of processors based on the A2 core range from a 2.3 GHz version with 16 cores consuming 65 W to a less powerful, four core version, consuming 20 W at 1.4 GHz.

Espresso is the codename of the 32-bit central processing unit (CPU) used in Nintendo's Wii U video game console. It was designed by IBM, and was produced using a 45 nm silicon-on-insulator process. The Espresso chip resides together with a GPU from AMD on an MCM manufactured by Renesas. It was revealed at E3 2011 in June 2011 and released in November 2012.
IBM POWER is a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architecture (ISA) developed by IBM. The name is an acronym for Performance Optimization With Enhanced RISC.
IBM Power microprocessors are designed and sold by IBM for servers and supercomputers. The name "POWER" was originally presented as an acronym for "Performance Optimization With Enhanced RISC". The Power line of microprocessors has been used in IBM's RS/6000, AS/400, pSeries, iSeries, System p, System i, and Power Systems lines of servers and supercomputers. They have also been used in data storage devices and workstations by IBM and by other server manufacturers like Bull and Hitachi.
The Power Processing Element (PPE) comprises a Power Processing Unit (PPU) and a 512 KB L2 cache. In most instances the PPU is used in a PPE. The PPU is a 64-bit dual-threaded in-order PowerPC 2.02 microprocessor core designed by IBM for use primarily in the game consoles PlayStation 3 and Xbox 360, but has also found applications in high performance computing in supercomputers such as the record setting IBM Roadrunner.