
The K6 microprocessor was launched by AMD in 1997. The main advantage of this particular microprocessor is that it was designed to fit into existing desktop designs for Pentium-branded CPUs. It was marketed as a product that could perform as well as its Intel Pentium II equivalent but at a significantly lower price. The K6 had a considerable impact on the PC market and presented Intel with serious competition.

PowerPC is a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architecture (ISA) created by the 1991 Apple–IBM–Motorola alliance, known as AIM. PowerPC, as an evolving instruction set, has been named Power ISA since 2006, while the old name lives on as a trademark for some implementations of Power Architecture–based processors.

The Pentium is a x86 microprocessor introduced by Intel on March 22, 1993. It is the first CPU using the Pentium brand. Considered the fifth generation in the 8086 compatible line of processors, its implementation and microarchitecture was internally called P5.

In electronics and computer science, a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) is a computer architecture designed to simplify the individual instructions given to the computer to accomplish tasks. Compared to the instructions given to a complex instruction set computer (CISC), a RISC computer might require more instructions in order to accomplish a task because the individual instructions are written in simpler code. The goal is to offset the need to process more instructions by increasing the speed of each instruction, in particular by implementing an instruction pipeline, which may be simpler to achieve given simpler instructions.
The PowerPC 7xx is a family of third generation 32-bit PowerPC microprocessors designed and manufactured by IBM and Motorola. This family is called the PowerPC G3 by Apple Computer, which introduced it on November 10, 1997. A number of microprocessors from different vendors have been used under the "PowerPC G3" name. Such designations were applied to Mac computers such as the PowerBook G3, the multicolored iMacs, iBooks and several desktops, including both the Beige and Blue and White Power Macintosh G3s. The low power requirements and small size made the processors ideal for laptops and the name lived out its last days at Apple in the iBook.
The IBM RS64 is a family of microprocessors introduced in the mid 1990s, and used in IBM's RS/6000 and AS/400 servers.

The PowerPC 970, PowerPC 970FX, and PowerPC 970MP are 64-bit PowerPC CPUs from IBM introduced in 2002. Apple branded the 970 as PowerPC G5 for its Power Mac G5.
PowerPC G4 is a designation formerly used by Apple to describe a fourth generation of 32-bit PowerPC microprocessors. Apple has applied this name to various processor models from Freescale, a former part of Motorola. Motorola and Freescale's proper name of this family of processors is PowerPC 74xx.

The Emotion Engine is a central processing unit developed and manufactured by Sony Computer Entertainment and Toshiba for use in the PlayStation 2 video game console. It was also used in early PlayStation 3 models sold in Japan and North America to provide PlayStation 2 game support. Mass production of the Emotion Engine began in 1999 and ended in late 2012 with the discontinuation of the PlayStation 2.
The POWER1 is a multi-chip CPU developed and fabricated by IBM that implemented the POWER instruction set architecture (ISA). It was originally known as the RISC System/6000 CPU or, when in an abbreviated form, the RS/6000 CPU, before introduction of successors required the original name to be replaced with one that used the same naming scheme (POWERn) as its successors in order to differentiate it from the newer designs.
The PowerPC 400 family is a line of 32-bit embedded RISC processor cores based on the PowerPC or Power ISA instruction set architectures. The cores are designed to fit inside specialized applications ranging from system-on-a-chip (SoC) microcontrollers, network appliances, application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) and field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) to set-top boxes, storage devices and supercomputers.
The PowerPC 600 family was the first family of PowerPC processors built. They were designed at the Somerset facility in Austin, Texas, jointly funded and staffed by engineers from IBM and Motorola as a part of the AIM alliance. Somerset was opened in 1992 and its goal was to make the first PowerPC processor and then keep designing general purpose PowerPC processors for personal computers. The first incarnation became the PowerPC 601 in 1993, and the second generation soon followed with the PowerPC 603, PowerPC 604 and the 64-bit PowerPC 620.
The PowerPC e600 is a family of 32-bit PowerPC microprocessor cores developed by Freescale for primary use in high performance system-on-a-chip (SoC) designs with speed ranging over 2 GHz, thus making them ideal for high performance routing and telecommunications applications. The e600 is the continuation of the PowerPC 74xx design.

Gekko is a superscalar out-of-order 32-bit PowerPC microprocessor custom-made by IBM in 2000 for Nintendo to use as the CPU in their sixth generation game console, the GameCube, and later the Triforce Arcade Board.
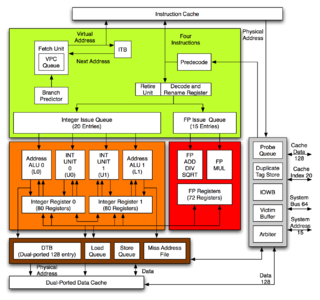
The Alpha 21264 is a RISC microprocessor developed by Digital Equipment Corporation launched on 19 October 1998. The 21264 implemented the Alpha instruction set architecture (ISA).
The R4200 is a microprocessor designed by MIPS Technologies, Inc. (MTI) that implemented the MIPS III instruction set architecture (ISA). It was also known as the VRX during development. The microprocessor was licensed to NEC, and the company fabricated and marketed it as the VR4200. The first VR4200, an 80 MHz part, was introduced in 1993. A faster 100 MHz part became available in 1994.

Espresso is the codename of the 32-bit central processing unit (CPU) used in Nintendo's Wii U video game console. It was designed by IBM, and was produced using a 45 nm silicon-on-insulator process. The Espresso chip resides together with a GPU from AMD on an MCM manufactured by Renesas. It was revealed at E3 2011 in June 2011 and released in November 2012.
IBM POWER is a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architecture (ISA) developed by IBM. The name is an acronym for Performance Optimization With Enhanced RISC.
IBM Power microprocessors are designed and sold by IBM for servers and supercomputers. The name "POWER" was originally presented as an acronym for "Performance Optimization With Enhanced RISC". The Power line of microprocessors has been used in IBM's RS/6000, AS/400, pSeries, iSeries, System p, System i, and Power Systems lines of servers and supercomputers. They have also been used in data storage devices and workstations by IBM and by other server manufacturers like Bull and Hitachi.















