Microsoft Windows is a product line of proprietary graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and sub-families that cater to particular sectors of the computing industry – Windows (unqualified) for a consumer or corporate workstation, Windows Server for a server and Windows IoT for an embedded system. Defunct families include Windows 9x, Windows Mobile, Windows Phone, and Windows Embedded Compact.
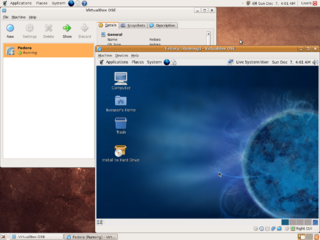
In computing, a virtual machine (VM) is the virtualization or emulation of a computer system. Virtual machines are based on computer architectures and provide the functionality of a physical computer. Their implementations may involve specialized hardware, software, or a combination of the two. Virtual machines differ and are organized by their function, shown here:
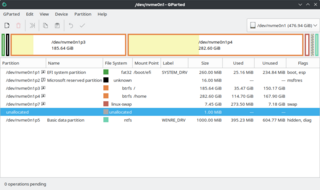
Disk partitioning or disk slicing is the creation of one or more regions on secondary storage, so that each region can be managed separately. These regions are called partitions. It is typically the first step of preparing a newly installed disk after a partitioning scheme is chosen for the new disk before any file system is created. The disk stores the information about the partitions' locations and sizes in an area known as the partition table that the operating system reads before any other part of the disk. Each partition then appears to the operating system as a distinct "logical" disk that uses part of the actual disk. System administrators use a program called a partition editor to create, resize, delete, and manipulate the partitions. Partitioning allows the use of different filesystems to be installed for different kinds of files. Separating user data from system data can prevent the system partition from becoming full and rendering the system unusable. Partitioning can also make backing up easier. A disadvantage is that it can be difficult to properly size partitions, resulting in having one partition with too much free space and another nearly totally allocated.
Virtual PC is a discontinued x86 emulator for PowerPC Mac hosts and Microsoft Windows hosts. It was created by Connectix in 1997 and acquired by Microsoft in 2003. The Mac version was discontinued in 2006 following the Mac transition to Intel, while the Windows version was discontinued in 2011 in favour of Hyper-V.
Installation of a computer program, is the act of making the program ready for execution. Installation refers to the particular configuration of software or hardware with a view to making it usable with the computer. A soft or digital copy of the piece of software (program) is needed to install it. There are different processes of installing a piece of software (program). Because the process varies for each program and each computer, programs often come with an installer, a specialised program responsible for doing whatever is needed for the installation. Installation may be part of a larger software deployment process.
CrossCrypt is an open-source on-the-fly encryption program for the Microsoft Windows XP/2000 operating systems. CrossCrypt allows a user to make virtual drives which encrypt any files stored on them, making the encryption process seamless to the user.
The Windows Registry is a hierarchical database that stores low-level settings for the Microsoft Windows operating system and for applications that opt to use the registry. The kernel, device drivers, services, Security Accounts Manager, and user interfaces can all use the registry. The registry also allows access to counters for profiling system performance.
In computer security, a sandbox is a security mechanism for separating running programs, usually in an effort to mitigate system failures and/or software vulnerabilities from spreading. The sandbox metaphor derives from the concept of a child's sandbox—a play area where kids can build, destroy, and experiment without causing any real-world damage. It is often used to execute untested or untrusted programs or code, possibly from unverified or untrusted third parties, suppliers, users or websites, without risking harm to the host machine or operating system. A sandbox typically provides a tightly controlled set of resources for guest programs to run in, such as storage and memory scratch space. Network access, the ability to inspect the host system, or read from input devices are usually disallowed or heavily restricted.
Virtual DOS machines (VDM) refer to a technology that allows running 16-bit/32-bit DOS and 16-bit Windows programs when there is already another operating system running and controlling the hardware.
OS-level virtualization is an operating system (OS) virtualization paradigm in which the kernel allows the existence of multiple isolated user space instances, including containers, zones, virtual private servers (OpenVZ), partitions, virtual environments (VEs), virtual kernels, and jails. Such instances may look like real computers from the point of view of programs running in them. A computer program running on an ordinary operating system can see all resources of that computer. Programs running inside a container can only see the container's contents and devices assigned to the container.
In computing, SUBST is a command on the DOS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows and ReactOS operating systems used for substituting paths on physical and logical drives as virtual drives.
In Unix-like operating systems, a loop device, vnd, or lofi is a pseudo-device that makes a computer file accessible as a block device.

User Account Control (UAC) is a mandatory access control enforcement feature introduced with Microsoft's Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 operating systems, with a more relaxed version also present in Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows 8, Windows Server 2012, Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows 10, and Windows 11. It aims to improve the security of Microsoft Windows by limiting application software to standard user privileges until an administrator authorises an increase or elevation. In this way, only applications trusted by the user may receive administrative privileges and malware are kept from compromising the operating system. In other words, a user account may have administrator privileges assigned to it, but applications that the user runs do not inherit those privileges unless they are approved beforehand or the user explicitly authorises it.
Application virtualization is a software technology that encapsulates computer programs from the underlying operating system on which they are executed. A fully virtualized application is not installed in the traditional sense, although it is still executed as if it were. The application behaves at runtime like it is directly interfacing with the original operating system and all the resources managed by it, but can be isolated or sandboxed to varying degrees.

Parallels Desktop for Mac is a hypervisor for Macintosh computers; it provides hardware virtualization. Initially developed for Macintosh systems with Intel processors, version 16.5 introduced support for Macs with Apple silicon. Parallels, a subsidiary of Corel since 2018, is the developer of the software.

In computing, the trash, also known by other names such as dustbin, wastebasket, and others, is a graphical user interface desktop metaphor for temporary storage for files set aside by the user for deletion, but not yet permanently erased. The concept and name is part of Mac operating systems, a similar implementation is called the Recycle Bin in Microsoft Windows, and other operating systems use other names.
Turbo is a set of software products and services developed by the Code Systems Corporation for application virtualization, portable application creation, and digital distribution. Code Systems Corporation is an American corporation headquartered in Seattle, Washington, and is best known for its Turbo products that include Browser Sandbox, Turbo Studio, TurboServer, and Turbo.

In computing, virtualization (v12n) is a series of technologies that allows dividing of physical computing resources into a series of virtual machines, operating systems, processes or containers.
Parallels Workstation Extreme is the first workstation virtualization product that lets users virtualize graphics-intensive software programs such as geophysical simulation, financial analysis, and digital content creation programs commonly used by engineers and digital animators in virtual machines on Windows and Linux hosts.






