Alpha is a 64-bit reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architecture (ISA) developed by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC). Alpha was designed to replace 32-bit VAX complex instruction set computers (CISC) and to be a highly competitive RISC processor for Unix workstations and similar markets.
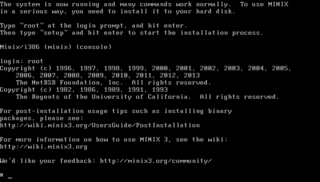
MINIX is a Unix-like operating system based on a microkernel architecture, first released in 1987 and written by American-Dutch computer scientist Andrew S. Tanenbaum. It was designed as a clone of the Unix operating system and one that could run on affordable, Intel 8086 based home computers; MINIX was targeted for use in classrooms by computer science students at universities.

The PDP–11 is a series of 16-bit minicomputers originally sold by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) from 1970 into the late 1990s, one of a set of products in the Programmed Data Processor (PDP) series. In total, around 600,000 PDP-11s of all models were sold, making it one of DEC's most successful product lines. The PDP-11 is considered by some experts to be the most popular minicomputer.

VAX is a series of computers featuring a 32-bit instruction set architecture (ISA) and virtual memory that was developed and sold by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) in the late 20th century. The VAX-11/780, introduced October 25, 1977, was the first of a range of popular and influential computers implementing the VAX ISA. The VAX family was a huge success for DEC, with the last members arriving in the early 1990s. The VAX was succeeded by the DEC Alpha, which included several features from VAX machines to make porting from the VAX easier.

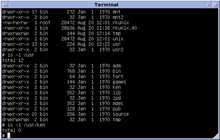
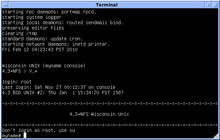
OpenVMS, often referred to as just VMS, is a multi-user, multiprocessing and virtual memory-based operating system. It is designed to support time-sharing, batch processing, transaction processing and workstation applications. Customers using OpenVMS include banks and financial services, hospitals and healthcare, telecommunications operators, network information services, and industrial manufacturers. During the 1990s and 2000s, there were approximately half a million VMS systems in operation worldwide.

Ultrix is the brand name of Digital Equipment Corporation's (DEC) discontinued native Unix operating systems for the PDP-11, VAX, MicroVAX and DECstations.

Coherent is a clone of the Unix operating system for IBM PC compatibles and other microcomputers, developed and sold by the now-defunct Mark Williams Company (MWC). Historically, the operating system was a proprietary product, but it became open source in 2015, released under the BSD-3-Clause license.

Version 7 Unix, also called Seventh Edition Unix, Version 7 or just V7, was an important early release of the Unix operating system. V7, released in 1979, was the last Bell Laboratories release to see widespread distribution before the commercialization of Unix by AT&T Corporation in the early 1980s. V7 was originally developed for Digital Equipment Corporation's PDP-11 minicomputers and was later ported to other platforms.
In software engineering, a compatibility layer is an interface that allows binaries for a legacy or foreign system to run on a host system. This translates system calls for the foreign system into native system calls for the host system. With some libraries for the foreign system, this will often be sufficient to run foreign binaries on the host system. A hardware compatibility layer consists of tools that allow hardware emulation.

The Quick Emulator (QEMU) is a free and open-source emulator that uses dynamic binary translation to emulate a computer's processor; that is, it translates the emulated binary codes to an equivalent binary format which is executed by the machine. It provides a variety of hardware and device models for the virtual machine, enabling it to run different guest operating systems. QEMU can be used with a Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM) to emulate hardware at near-native speeds. Additionally, it supports user-level processes, allowing applications compiled for one processor architecture to run on another.

The Professional 325 (PRO-325), Professional 350 (PRO-350), and Professional 380 (PRO-380) are PDP-11 compatible microcomputers. The Pro-325/350 were introduced in 1982 and the Pro-380 in 1985 by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) as high-end competitors to the IBM PC.

The VAXstation is a discontinued family of workstation computers developed and manufactured by Digital Equipment Corporation using processors implementing the VAX instruction set architecture. VAXstation systems were typically shipped with either the OpenVMS or ULTRIX operating systems. Many members of the VAXstation family had corresponding MicroVAX variants, which primarily differ by the lack of graphics hardware.

Ancient UNIX is any early release of the Unix code base prior to Unix System III, particularly the Research Unix releases prior to and including Version 7.
Portable Batch System is the name of computer software that performs job scheduling. Its primary task is to allocate computational tasks, i.e., batch jobs, among the available computing resources. It is often used in conjunction with UNIX cluster environments.
Research Unix refers to the early versions of the Unix operating system for DEC PDP-7, PDP-11, VAX and Interdata 7/32 and 8/32 computers, developed in the Bell Labs Computing Sciences Research Center (CSRC). The term Research Unix first appeared in the Bell System Technical Journal to distinguish it from other versions internal to Bell Labs whose code-base had diverged from the primary CSRC version. However, that term was little-used until Version 8 Unix (1985), but has been retroactively applied to earlier versions as well. Prior to V8, the operating system was most commonly called simply UNIX or the UNIX Time-Sharing System.

Minix 3 is a small, Unix-like operating system. It is published under a BSD-3-Clause license and is a successor project to the earlier versions, Minix 1 and 2.

The Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD), also known as Berkeley Unix or BSD Unix, is a discontinued Unix operating system developed and distributed by the Computer Systems Research Group (CSRG) at the University of California, Berkeley, beginning in 1978. It began as an improved derivative of AT&T's original Unix that was developed at Bell Labs, based on the source code but over time diverging into its own code. BSD would become a pioneer in the advancement of Unix and computing.
The history of the Berkeley Software Distribution began in the 1970s when University of California, Berkeley received a copy of Unix. Professors and students at the university began adding software to the operating system and released it as BSD to select universities. Since it contained proprietary Unix code, it originally had to be distributed subject to AT&T licenses. The bundled software from AT&T was then rewritten and released as free software under the BSD license. However, this resulted in a lawsuit with Unix System Laboratories, the AT&T subsidiary responsible for Unix. Eventually, in the 1990s, the final versions of BSD were publicly released without any proprietary licenses, which led to many descendants of the operating system that are still maintained today.