Related Research Articles

MIPS Technologies, Inc., formerly MIPS Computer Systems, Inc., was an American fabless semiconductor design company that is most widely known for developing the MIPS architecture and a series of RISC CPU chips based on it. MIPS provides processor architectures and cores for digital home, networking, embedded, Internet of things and mobile applications.

In computer science, a thread of execution is the smallest sequence of programmed instructions that can be managed independently by a scheduler, which is typically a part of the operating system. The implementation of threads and processes differs between operating systems. In Modern Operating Systems, Tanenbaum shows that many distinct models of process organization are possible. In many cases, a thread is a component of a process. The multiple threads of a given process may be executed concurrently, sharing resources such as memory, while different processes do not share these resources. In particular, the threads of a process share its executable code and the values of its dynamically allocated variables and non-thread-local global variables at any given time.
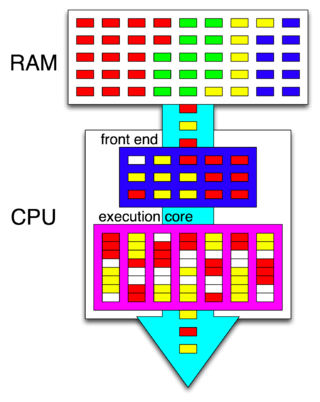
Hyper-threading is Intel's proprietary simultaneous multithreading (SMT) implementation used to improve parallelization of computations performed on x86 microprocessors. It was introduced on Xeon server processors in February 2002 and on Pentium 4 desktop processors in November 2002. Since then, Intel has included this technology in Itanium, Atom, and Core 'i' Series CPUs, among others.
Simultaneous multithreading (SMT) is a technique for improving the overall efficiency of superscalar CPUs with hardware multithreading. SMT permits multiple independent threads of execution to better use the resources provided by modern processor architectures.
OpenRISC is a project to develop a series of open-source hardware based central processing units (CPUs) on established reduced instruction set computer (RISC) principles. It includes an instruction set architecture (ISA) using an open-source license. It is the original flagship project of the OpenCores community.
Enea AB is a global information technology company with its headquarters in Kista, Sweden that provides real-time operating systems and consulting services. Enea, which is an abbreviation of Engmans Elektronik Aktiebolag, also produces the OSE operating system.

μClinux is a variation of the Linux kernel, previously maintained as a fork, that targets microcontrollers without a memory management unit (MMU). It was integrated into the mainline kernel as of 2.5.46; the project continues to develop patches and tools for microcontrollers. The homepage lists Linux kernel releases for 2.0, 2.4 and 2.6.
Wind River Systems, also known as Wind River, is an Alameda, California–based company, subsidiary of Aptiv PLC. The company develops embedded system and cloud software consisting of real-time operating systems software, industry-specific software, simulation technology, development tools and middleware.

The Blackfin is a family of 16-/32-bit microprocessors developed, manufactured and marketed by Analog Devices. The processors have built-in, fixed-point digital signal processor (DSP) functionality supplied by 16-bit multiply–accumulates (MACs), accompanied on-chip by a microcontroller. It was designed for a unified low-power processor architecture that can run operating systems while simultaneously handling complex numeric tasks such as real-time H.264 video encoding.
Sun Microsystems' UltraSPARC T1 microprocessor, known until its 14 November 2005 announcement by its development codename "Niagara", is a multithreading, multicore CPU. Designed to lower the energy consumption of server computers, the CPU typically uses 72 W of power at 1.4 GHz.

A multi-core processor is a microprocessor on a single integrated circuit with two or more separate processing units, called cores, each of which reads and executes program instructions. The instructions are ordinary CPU instructions but the single processor can run instructions on separate cores at the same time, increasing overall speed for programs that support multithreading or other parallel computing techniques. Manufacturers typically integrate the cores onto a single integrated circuit die or onto multiple dies in a single chip package. The microprocessors currently used in almost all personal computers are multi-core.

The Completely Fair Scheduler (CFS) is a process scheduler that was merged into the 2.6.23 release of the Linux kernel and is the default scheduler of the tasks of the SCHED_NORMAL class. It handles CPU resource allocation for executing processes, and aims to maximize overall CPU utilization while also maximizing interactive performance.
Tilera Corporation was a fabless semiconductor company focusing on manycore embedded processor design. The company shipped multiple processors, including the TILE64, TILEPro64, and the TILEPro36, TILE-Gx72, TILE-Gx36, TILE-Gx16 and TILE-Gx9.

The Linux kernel is a free and open-source, monolithic, modular, multitasking, Unix-like operating system kernel. It was originally authored in 1991 by Linus Torvalds for his i386-based PC, and it was soon adopted as the kernel for the GNU operating system, which was written to be a free (libre) replacement for Unix.

Linaro is an engineering organization that works on free and open-source software such as the Linux kernel, the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), QEMU, power management, graphics and multimedia interfaces for the ARM family of instruction sets and implementations thereof as well as for the Heterogeneous System Architecture (HSA). The company provides a collaborative engineering forum for companies to share engineering resources and funding to solve common problems on ARM software.

The Yocto Project is a Linux Foundation collaborative open source project whose goal is to produce tools and processes that enable the creation of Linux distributions for embedded and IoT software that are independent of the underlying architecture of the embedded hardware. The project was announced by the Linux Foundation in 2010 and launched in March, 2011, in collaboration with 22 organizations, including OpenEmbedded.
Hexagon is the brand name for a family of digital signal processor (DSP) products by Qualcomm. Hexagon is also known as QDSP6, standing for “sixth generation digital signal processor.” According to Qualcomm, the Hexagon architecture is designed to deliver performance with low power over a variety of applications.

ARM big.LITTLE is a heterogeneous computing architecture developed by ARM Holdings, coupling relatively battery-saving and slower processor cores (LITTLE) with relatively more powerful and power-hungry ones (big). Typically, only one "side" or the other will be active at once, but all cores have access to the same memory regions, so workloads can be swapped between Big and Little cores on the fly. The intention is to create a multi-core processor that can adjust better to dynamic computing needs and use less power than clock scaling alone. ARM's marketing material promises up to a 75% savings in power usage for some activities. Most commonly, ARM big.LITTLE architectures are used to create a multi-processor system-on-chip (MPSoC).
RPMsg is a protocol enabling inter-processor communication inside multi-core processors.
References
- ↑ Henry Davis (2006-03-20). "Inside the Imagination Technologies Meta processor". EETimes.
- ↑ "Imagination Technologies Announces New Revolutionary DSP Cores and Metagence Technologies Division". Imagination Technologies. 2001-05-08.
- 1 2 "Imagination Technologies META HTP Multi-Threaded Processor IP Core". Design and Reuse. 2007-10-31.
- ↑ Peter Clarke (2007-11-07). "Meta HTP extends support for different operating systems". EE Times Europe.
- ↑ Product Description on Imagination Technologies website
- ↑ Pull new ImgTec Meta architecture from James Hogan
- ↑ "Linux 3.9 has been released". Kernel Newbies.
1.5. New architecture: Meta Imagination processors
- ↑ Richard Chirgwin (2013-05-01). "Linux kernel 3.9 lands. Power management, new processors, SSD caching and more". The Register.
The new kernel is now ported to .. Imagination Meta ATP and HTP processor cores – an embedded Linux play .. the Imagination devices turn in in digital radios.
- ↑ Jonathan Corbet (2018-02-26). "Shedding old architectures and compilers in the kernel". LWN.net. Retrieved 2018-03-11.
- ↑ Linus Torvalds (2018-06-03). "Linux 4.17 Release Notes". lkml.org. Retrieved 2018-06-18.