
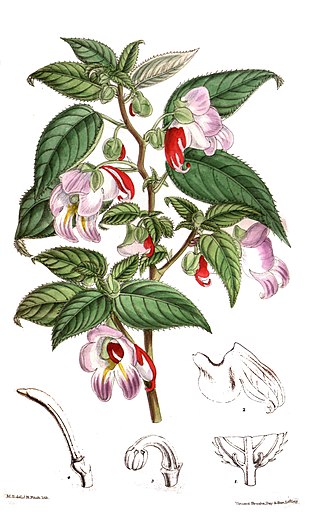
Impatiens is a genus of more than 1,000 species of flowering plants, widely distributed throughout the Northern Hemisphere and the tropics. Together with the genus Hydrocera, Impatiens make up the family Balsaminaceae.

Hesperis matronalis is an herbaceous flowering plant species in the family Brassicaceae. It has numerous common names, including dame's rocket, damask-violet, dame's-violet, dames-wort, dame's gilliflower, night-scented gilliflower, queen's gilliflower, rogue's gilliflower, summer lilac, sweet rocket, mother-of-the-evening, Good & Plenties, and winter gilliflower.

Impatiens walleriana, also known as busy Lizzie, balsam, sultana, or simply impatiens, is a species of the genus Impatiens, native to eastern Africa from Kenya to Mozambique. The Latin specific epithet walleriana honours a British missionary, Horace Waller (1833–1896).

Lotus corniculatus is a flowering plant in the pea family Fabaceae, native to grasslands in temperate Eurasia and North Africa. Common names include common bird's-foot trefoil, eggs and bacon, birdsfoot deervetch, and just bird's-foot trefoil, though the latter name is often also applied to other members of the genus.

Aquilegia canadensis, the Canadian or Canada columbine, eastern red columbine, or wild columbine, is a species of flowering plant in the buttercup family Ranunculaceae. It is an herbaceous perennial native to woodland and rocky slopes in eastern North America, prized for its red and yellow flowers. It readily hybridizes with other species in the genus Aquilegia.

Dendromecon rigida, also called bush poppy or tree poppy, is a shrub or small tree of the Papaveraceae native to California and Baja California.

Impatiens capensis, the orange jewelweed, common jewelweed, spotted jewelweed, jewelweed, spotted touch-me-not, or orange balsam, is an annual plant in the family Balsaminaceae that is native to North America. It is common in bottomland soils, ditches, and along creeks, often growing side by side with its less common relative, yellow jewelweed.

Impatiens noli-tangere is an annual herbaceous plant in the family Balsaminaceae found in damp places in Europe, Asia and North America. The yellow flowers are followed by pods which forcefully explode when ripe, ejecting the seeds for some distance.

Impatiens balsamina, commonly known as balsam, garden balsam, rose balsam, touch-me-not or spotted snapweed, is a species of plant native to India and Myanmar.

Iris lacustris, the dwarf lake iris, is a plant species in the genus Iris, subgenus Limniris and in the section Lophiris. It is a rhizomatous, beardless perennial plant, native to the Great Lakes region of eastern North America. It has lavender blue or violet-blue flowers, a very short stem and long fan-like green leaves. It is cultivated as an ornamental plant in temperate regions. It is closely related to Iris cristata.

Iris cristata is a species in the genus Iris, it is also in the subgenus of Limniris. It is a rhizomatous perennial plant, endemic to the eastern United States. It has pale lavender flowers with a white patch and orange or yellow crest. It is a close relative to Iris lacustris, the only other crested iris native to North America. It is cultivated as an ornamental plant in temperate regions.

Impatiens pallida, with the common names pale jewelweed, pale touch-me-not, or yellow jewelweed, is a flowering annual plant in the family Balsaminaceae native to Canada and the United States. It grows in moist to wet soils, generally alongside the closely related Impatiens capensis, producing flowers from midsummer through fall.
Impatiens psittacina, known variously as the "parrot flower" or "parrot balsam" is a species of balsam from Southeast Asia that was described by the botanist Joseph Dalton Hooker and was noted for its flower that resemble a "flying cockatoo". It is known from Thailand, Burma and parts of India.

Claytonia lanceolata is a species of wildflower in the family Montiaceae, known by the common names lanceleaf springbeauty and western springbeauty.

Hammarbya paludosa is a small orchid commonly known as bog orchid, bog adder's-mouth or bog adder's-mouth orchid. It grows in bogs in temperate and subarctic regions of the Northern Hemisphere.

Impatiens balfourii is a species of the genus Impatiens known by the common names Balfour's touch-me-not, Kashmir balsam, and poor man's orchid. It belongs to the family Balsaminaceae.

Iris japonica, commonly known as fringed iris, shaga and butterfly flower, is a native of China and Japan. It is a species in the genus Iris, in the subgenus Limniris and within the Lophiris section. It is a rhizomatous perennial plant, with pale blue, lavender or white flowers with an orange or yellow crest. It is cultivated as an ornamental plant in temperate regions.

Croton monanthogynus is a species of flowering plant in the spurge family. The undersides are gray. It is a summer annual that produces small, inconspicuous flowers. The plant is monoecious and has both male and female reproductive organs in separate clusters on the same plant. Its leaves are alternate. It is native to the southeastern United States and the southern Great Plains. It is considered adventive in more northern states. AL, AR, AZ, GA, IA, IL, IN, KS, KY, LA, MD, MI, MO, MS, NC, NE, OH, OK, PA, SC, TN, TX, VA, WI, WV.

Ranunculus hispidus is a species of perennial flowering plant in the buttercup family, Ranunculaceae. It is commonly known as bristly buttercup or hispid buttercup. It is a small plant native to central and eastern North America that grows to a height up to 30 cm (1 ft) and has 5-petaled yellow flowers.

Oenothera versicolor, the red evening-primrose, is a species of flowering plant in the family Onagraceae, native to South America, from Peru and Ecuador down to Bolivia and Northern Argentina This species is not as common in cultivation as other members of the genus but popular cultivars including 'Sunset Boulevard' are grown in gardens around the temperate world as the plant is hardy down to at least −10 °C (14 °F).





















