
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi was an Indian lawyer, anti-colonial nationalist and political ethicist who employed nonviolent resistance to lead the successful campaign for India's independence from British rule. He inspired movements for civil rights and freedom across the world. The honorific Mahātmā, first applied to him in South Africa in 1914, is now used throughout the world.

Fatima Meer was a South African writer, academic, screenwriter, and prominent anti-apartheid activist.

Manilal Mohandas Gandhi was the second son of Mahatma Gandhi and Kasturba Gandhi.
Inanda or eNanda is a township in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa that is situated 21 km north-west of Durban. It forms part of eThekwini, the Greater Durban Metropolitan Municipality. Populated primarily by Zulu-speaking Black Africans, Inanda is the home of John Langalibalele Dube, first President of the African National Congress (ANC), a former residence and base of operations of Mahatma Gandhi, and the birthplace of the syncretic Nazareth Baptist Church

The Story of My Experiments with Truth is the autobiography of Mahatma Gandhi, covering his life from early childhood through to 1921. It was written in weekly installments and published in his journal Navjivan from 1925 to 1929. Its English translation also appeared in installments in his other journal Young India. It was initiated at the insistence of Swami Anand and other close co-workers of Gandhi, who encouraged him to explain the background of his public campaigns. In 1998, the book was designated as one of the "100 Best Spiritual Books of the 20th Century" by a committee of global spiritual and religious authorities.

The Natal Indian Congress (NIC) was a political organisation established in 1894 to fight discrimination against Indians in the Natal Colony, and later the Natal Province, of South Africa. Founded by Mahatma Gandhi, it later served an important role in opposing apartheid. It was the oldest affiliate of the South African Indian Congress.

The Champaran Satyagraha of 1917 was the first satyagraha movement led by Mahatma Gandhi in British India and is considered a historically important rebellion in the Indian independence movement. It was a farmer's uprising that took place in Champaran district of Bihar in the Indian subcontinent, during the [British colonial period]. The farmers were protesting against having to grow indigo with barely any payment for it.

Charles Freer Andrews was an Anglican priest and Christian missionary, educator and social reformer, and an activist for Indian independence. He became a close friend of Rabindranath Tagore and Mahatma Gandhi and identified with the Indian liberation struggle. He was instrumental in convincing Gandhi to return to India from South Africa, where Gandhi had been a leading light in the Indian civil rights struggle.

Govindasamy Krishnasamy Thambi Naidoo was a South African civil rights activist. He was an early collaborator of Mahatma Gandhi leading many protests in then South Africa against racial discrimination targeted at the Indian community.

Manilal Maganlal Doctor was a British Indian barrister and politician, who travelled to numerous countries of the British Empire, including Fiji, Mauritius and Aden, providing legal assistance to the local ethnic Indian population. He met Gandhi, who asked him to go to Mauritius, where he represented Indo-Mauritians in court and edited a newspaper, The Hindustani. Gandhi later informed him of the need for a barrister in Fiji and he arrived in Fiji in 1912. In Fiji he also represented Indo-Fijians in court, started a newspaper, Indian Settler and established an organisation for Fiji Indians, known as the Indian Imperial Association. In 1916 when he was by-passed for nomination to the Legislative Council of Fiji, his relationship with the Government of Fiji deteriorated. The Government accused him of the violence and sabotage of the 1920 strike and deported him. He was barred from practicing law in several British colonies. He later managed to practice law in Aden, Somalia and Bihar State in India but spent his final days in Bombay.

Ela Gandhi, is a South African peace activist and former politician. She served as a Member of Parliament in South Africa from 1994 to 2004, where she aligned with the African National Congress (ANC) party representing the Phoenix area of Inanda in the KwaZulu-Natal province. Her parliamentary committee assignments included the Welfare, and Public Enterprises committees as well as the ad hoc committee on Surrogate Motherhood. She was an alternate member of the Justice Committee and served on Theme Committee 5 on Judiciary and Legal Systems. She is the granddaughter of Mahatma Gandhi.
Babu Ram Singh was a Fiji Indian who had come to Fiji under the indenture system and was one of the few people who, after indenture, prospered and made an attempt to help his less fortunate ex-indentured brethren. Babu Ram Singhs surviving Business, Fiji Rubber Stamp Co Ltd is still under operation in Mark Street, Suva, and is looked after by his children.

Hermann Kallenbach was a Lithuanian-born Jewish South African architect who was one of the foremost friends and associates of Mahatma Gandhi. Kallenbach was introduced to the young Mohandas Gandhi while they were both working in South Africa and, after a series of discussions, they developed a long-lasting association.

Arun Manilal Gandhi was a South African-born Indian-American author, socio-political activist and son of Manilal Gandhi, thus a grandson of nationalist leader Mahatma Gandhi. In 2017, he published The Gift of Anger: And Other Lessons From My Grandfather Mahatma Gandhi.

The online Gandhi Heritage Portal preserves, protects, and disseminates original writings of Mohandas K. Gandhi and makes available to the world the large corpus of “Fundamental Works” which are useful for any comprehensive study of the life and thought of Gandhiji. Gandhiji was 24 years old in South Africa "Natal Indian Congress " made in 1894.
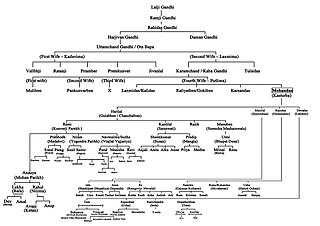
The Gandhi family is the family of Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, commonly known as Mahatma Gandhi; Mahatma meaning "high souled" or "venerable" in Sanskrit; the particular term 'Mahatma' was accorded Mohandas Gandhi for the first time while he was still in South Africa, and not commonly heard as titular for any other civil figure even of similarly rarefied stature or living or posthumous presence.
Rustomjee Jivanji Ghorkhodu, commonly known as Parsee Rustomjee, and by various orthographic variations including Parsi Rustomji and affectionately referred to as Kakaji, was an Indian-South African philanthropist and businessman, well known for his close mentorship, guidance and financial sponsorship of Mahatma Gandhi during his time in South Africa from 1893 to 1914.

Amar Asha is a Gujarati poem by Manilal Dwivedi. It was his last poetic work – published posthumously in the 1898 issue of his own magazine, Sudarshan. Described as Manilal's most important work and cited as one of the most popular poems in Gujarati literature, Amar Asha has been studied and interpreted by several writers since its publication.

Henry Salomon Leon Polak was a British-born lawyer, journalist and activist in South Africa who worked in collaboration with Mohandas Gandhi against racial discrimination. He served as an editor for the journal Indian Opinion and influenced by Theosophy, he believed in humanism and worked for the British Indian Association and several other causes.
















