
Enoplea (enopleans) is a class, which with the classes Secernentea and Chromadorea make up the phylum Nematoda in current taxonomy. The Enoplea are considered to be a more ancestral group than the Chromadorea, and researchers have referred to its members as the "ancestrally diverged nematodes", compared to the "more recently diverged nematodes" of Chromadorea.
The Chromadorea are a class of the roundworm phylum, Nematoda. They contain a single subclass (Chromadoria) and several orders. With such a redundant arrangement, the Chromadoria are liable to be divided if the orders are found to form several clades, or abandoned if they are found to constitute a single radiation.
Pratylenchus brachyurus is a plant parasitic nematode.

Tobacco rattle virus (TRV) is a pathogenic plant virus. Over 400 species of plants from 50 families are susceptible to infection.

Anguina is a genus of plant pathogenic nematodes.

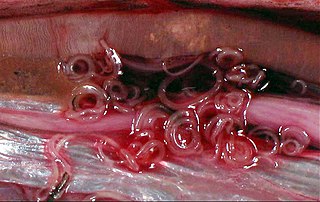
The nematodes, roundworms or eelworms constitute the phylum Nematoda. They are a diverse animal phylum inhabiting a broad range of environments. Most species are free-living, feeding on microorganisms, but many species are parasitic. The parasitic worms (helminths) are the cause of soil-transmitted helminthiases.

Capillariidae is a family of parasitic nematodes. All its members are parasites in vertebrates when they are in their adult stage.
Enoplida is an order of nematodes. It is one of two orders in Enoplia, which is one of two subclasses in Class Enoplea.
Dorylaimia is a subclass of nematodes.
Hoplolaimus galeatus is a plant pathogenic nematode.
The Enoplia are a subclass of nematodes in the class Enoplea.

Diplogastridae, formerly Diplogasteridae, are a family of nematodes (roundworms) known from a wide range of habitats, often in commensal or parasitic associations with insects.

Root-gall nematodes are plant-parasitic nematodes from the genus Subanguina that affect grasses, including cereals, and some other plants, such as mugwort. They are distinct from the Root-knot nematodes which are from the genus Meloidogyne. So far around twenty-five separate species of Subanguina have been identified, although the most well-known and type species is Subanguina radicicola.
Paratrichodorus is a genus of terrestrial root feeding (stubby-root) nematodes in the Trichodoridae family (trichorids), being one of five genera. They are economically important plant parasites and virus vectors. The females are didelphic, and are distributed worldwide.
Triplonchida is an order of terrestrial nematodes, and is one of two orders making up the subclass Enoplia.
Diphtherophorina is a suborder of terrestrial nematodes, being one of three that constitute suborder Triplonchida.
Trichodoridae is a family of terrestrial root feeding nematodes, being one of two that constitute suborder Triplonchida. They are economically important plant parasites and virus vectors.

Trichodorus is a genus of terrestrial root feeding (stubby-root) nematodes in the Trichodoridae family (trichorids), being one of five genera. They are economically important plant parasites and virus vectors.

František Moravec is a Czech parasitologist who specialises on the Nematodes, especially the nematodes parasites of fishes. His research is mainly in the field of taxonomy of the Nematoda.
Tripyloididae is a family of nematodes belonging to the order Araeolaimida.









