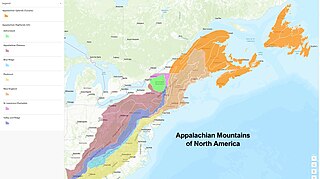
The geology of the Appalachians dates back more than 1.2 billion years to the Mesoproterozoic era when two continental cratons collided to form the supercontinent Rodinia, 500 million years prior to the development of the range during the formation of Pangea. The rocks exposed in today's Appalachian Mountains reveal elongate belts of folded and thrust faulted marine sedimentary rocks, volcanic rocks, and slivers of ancient ocean floor—strong evidences that these rocks were deformed during plate collision. The birth of the Appalachian ranges marks the first of several mountain building plate collisions that culminated in the construction of Pangea with the Appalachians and neighboring Anti-Atlas mountains near the center. These mountain ranges likely once reached elevations similar to those of the Alps and the Rocky Mountains before they were eroded.

Cape Breton Highlands National Park is a Canadian national park on northern Cape Breton Island in Nova Scotia. The park was the first national park in the Atlantic provinces of Canada and covers an area of 948 square kilometres (366 sq mi). It is one of 42 in Canada's system of national parks.
The Llano Uplift is a geologically ancient, low geologic dome that is about 90 miles (140 km) in diameter and located mostly in Llano, Mason, San Saba, Gillespie, and Blanco counties, Texas. It consists of an island-like exposure of Precambrian igneous and metamorphic rocks surrounded by outcrops of Paleozoic and Cretaceous sedimentary strata. At their widest, the exposed Precambrian rocks extend about 65 miles (105 km) westward from the valley of the Colorado River and beneath a broad, gentle topographic basin drained by the Llano River. The subdued topographic basin is underlain by Precambrian rocks and bordered by a discontinuous rim of flat-topped hills. These hills are the dissected edge of the Edwards Plateau, which consist of overlying Cretaceous sedimentary strata. Within this basin and along its margin are down-faulted blocks and erosional remnants of Paleozoic strata which form prominent hills.

Old Red Sandstone, abbreviated ORS, is an assemblage of rocks in the North Atlantic region largely of Devonian age. It extends in the east across Great Britain, Ireland and Norway, and in the west along the eastern seaboard of North America. It also extends northwards into Greenland and Svalbard. These areas were a part of the paleocontinent of Euramerica (Laurussia). In Britain it is a lithostratigraphic unit to which stratigraphers accord supergroup status and which is of considerable importance to early paleontology. The presence of Old in the name is to distinguish the sequence from the younger New Red Sandstone which also occurs widely throughout Britain.
The geology of Shropshire is very diverse with a large number of periods being represented at outcrop. The bedrock consists principally of sedimentary rocks of Palaeozoic and Mesozoic age, surrounding restricted areas of Precambrian metasedimentary and metavolcanic rocks. The county hosts in its Quaternary deposits and landforms, a significant record of recent glaciation. The exploitation of the Coal Measures and other Carboniferous age strata in the Ironbridge area made it one of the birthplaces of the Industrial Revolution. There is also a large amount of mineral wealth in the county, including lead and baryte. Quarrying is still active, with limestone for cement manufacture and concrete aggregate, sandstone, greywacke and dolerite for road aggregate, and sand and gravel for aggregate and drainage filters. Groundwater is an equally important economic resource.
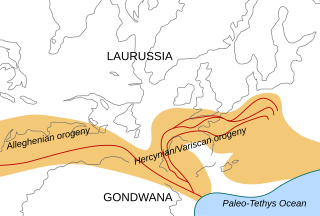
The Variscan orogeny, or Hercynian orogeny, was a geologic mountain-building event caused by Late Paleozoic continental collision between Euramerica (Laurussia) and Gondwana to form the supercontinent of Pangaea.

South Wales is an area with many features of outstanding interest to geologists, who have for long used the area for University field trips.

The geology of Wales is complex and varied; its study has been of considerable historical significance in the development of geology as a science. All geological periods from the Cryogenian to the Jurassic are represented at outcrop, whilst younger sedimentary rocks occur beneath the seas immediately off the Welsh coast. The effects of two mountain-building episodes have left their mark in the faulting and folding of much of the Palaeozoic rock sequence. Superficial deposits and landforms created during the present Quaternary period by water and ice are also plentiful and contribute to a remarkably diverse landscape of mountains, hills and coastal plains.
Gloucestershire is one of the most geologically and scenically diverse counties in England, with rocks from the Precambrian through to the Jurassic represented. These varying rock-types are responsible for the three major areas of the county, each with its own distinctive scenery and land-use - the Forest of Dean in the west, bordering Wales, the Cotswolds in the east, and in between, the Severn Vale.
The geology of Monmouthshire in southeast Wales largely consists of a thick series of sedimentary rocks of different types originating in the Silurian, Devonian, Carboniferous, Triassic and Jurassic periods.
The geology of Northumberland in northeast England includes a mix of sedimentary, intrusive and extrusive igneous rocks from the Palaeozoic and Cenozoic eras. Devonian age volcanic rocks and a granite pluton form the Cheviot massif. The geology of the rest of the county is characterised largely by a thick sequence of sedimentary rocks of Carboniferous age. These are intruded by both Permian and Palaeogene dykes and sills and the whole is overlain by unconsolidated sediments from the last ice age and the post-glacial period. The Whin Sill makes a significant impact on Northumberland's character and the former working of the Northumberland Coalfield significantly influenced the development of the county's economy. The county's geology contributes to a series of significant landscape features around which the Northumberland National Park was designated.

The geology of England's Lake District is dominated by sedimentary and volcanic rocks of mainly Ordovician age underpinned by large granitic intrusions. Younger sedimentary sequences outcrop on the edges of the Lake District area, with Silurian to the south, Carboniferous to the north, east, and west and Permo-Triassic to the west and east. The entire area was covered by a Mesozoic sequence that was eroded off during the Paleogene uplift related to the opening of the North Atlantic. During the Quaternary the area was affected by repeated glaciations, which sculpted the current mountainous landscape.
The geology of Belgium encompasses rocks, minerals and tectonic events stretching back more than 500 million years. Belgium covers an area of about 30,507 square kilometers and was instrumental in the development of geology. The extensive outcrops in Belgium became the standard reference points in stratigraphy as early as the mid-19th century. Some of them are internationally recognized features related to the Carboniferous and the Devonian periods. These rocks were folded by two mountain building events: the Hercynian orogeny and Caledonian Orogeny. Paleozoic basement rocks cover much of the country and are overlain by Mesozoic and Cenozoic sediments.

The geology of Afghanistan includes nearly one billion year old rocks from the Precambrian. The region experienced widespread marine transgressions and deposition during the Paleozoic and Mesozoic, that continued into the Cenozoic with the uplift of the Hindu Kush mountains.

The geology of the Czech Republic is very tectonically complex, split between the Western Carpathian Mountains and the Bohemian Massif.
The geology of Yukon includes sections of ancient Precambrian Proterozoic rock from the western edge of the proto-North American continent Laurentia, with several different island arc terranes added through the Paleozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic, driving volcanism, pluton formation and sedimentation.
The geology of national parks in Britain strongly influences the landscape character of each of the fifteen such areas which have been designated. There are ten national parks in England, three in Wales and two in Scotland. Ten of these were established in England and Wales in the 1950s under the provisions of the National Parks and Access to the Countryside Act 1949. With one exception, all of these first ten, together with the two Scottish parks were centred on upland or coastal areas formed from Palaeozoic rocks. The exception is the North York Moors National Park which is formed from sedimentary rocks of Jurassic age.
This article describes the geology of the Brecon Beacons National Park in mid/south Wales. The area gained national park status in 1957 with the designated area of 1,344 km2 (519 sq mi) including mountain massifs to both the east and west of the Brecon Beacons proper. The geology of the national park consists of a thick succession of sedimentary rocks laid down from the late Ordovician through the Silurian and Devonian to the late Carboniferous period. The rock sequence most closely associated with the park is the Old Red Sandstone from which most of its mountains are formed. The older parts of the succession, in the northwest, were folded and faulted during the Caledonian orogeny. Further faulting and folding, particularly in the south of the park is associated with the Variscan orogeny.

The Black Country UNESCO Global Geopark is a geopark in the Black Country, a part of the West Midlands region of England. Having previously been an ‘aspiring Geopark’, it was awarded UNESCO Global Geopark status on 10 July 2020.
The geology of the Yorkshire Dales National Park in northern England largely consists of a sequence of sedimentary rocks of Ordovician to Permian age. The core area of the Yorkshire Dales is formed from a layer-cake of limestones, sandstones and mudstones laid down during the Carboniferous period. It is noted for its karst landscape which includes extensive areas of limestone pavement and large numbers of caves including Britain's longest cave network.









